机电传动控制第四周仿真作业
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机电传动控制第四周仿真作业相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
机电传动控制第四周仿真作业
题目要求:
结合本周学习的交流电机原理及启动、调速、制动特性,用Modelica设计和仿真一个用三相交流异步电机带动起重机起升机构运行。具体要求如下:
1)实现如下机械运动周期:
- 控制电机带重物上升,从静止加速到800r/min
- 保持800r/min匀速运动0.5s,
- 减速到静止,保持静止状态0.5s,
- 带重物下降,从静止达到600r/min
- 保持600r/min匀速运动0.6s,
- 减速到静止。
(为了便于仿真,匀速和静止持续时间较短)
2) 升降机构和重物折算到到电机转子轴上的等效负载惯量为1Kg.m^2,折算到到电机转子轴上的等效负载转矩是15N.m。
3)使用统一的电机模型,如果控制策略中用到转子串电阻,允许将该电机的转子改为绕线式转子(参数不变)。
4)参照教材中给出的交流电机启动、调速和制动方法,设计控制策略,用Modelica实现控制策略并与电机模型实现联合仿真。
5)可以采用定子串电阻、转子串电阻、定子调压、定子调频等手段,但必须具备工程上的可实施性。
6)评价指标:快速启动、制动,冲击转矩和冲击电流小,能耗小,兼顾实施的经济性。
仿真分析:
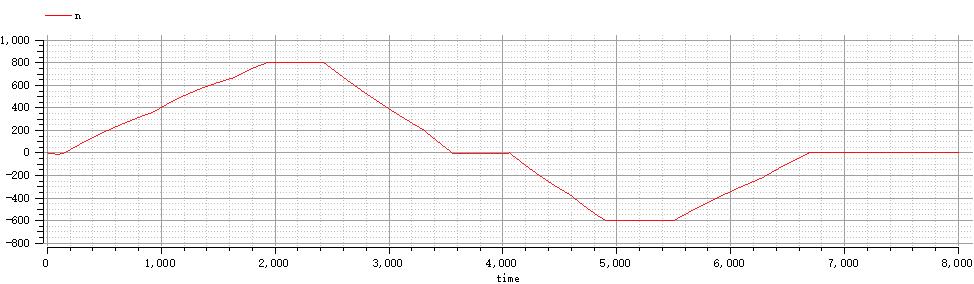
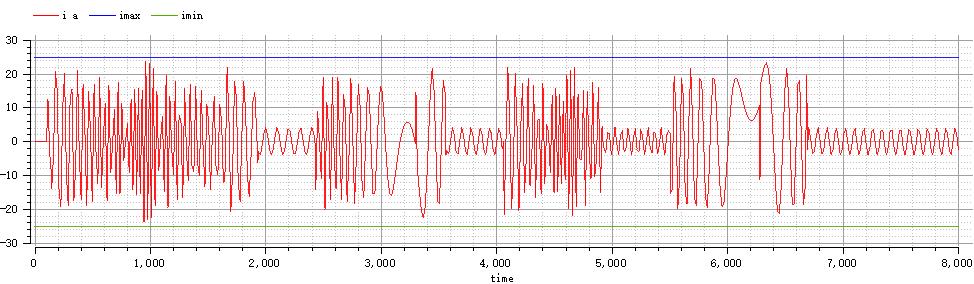
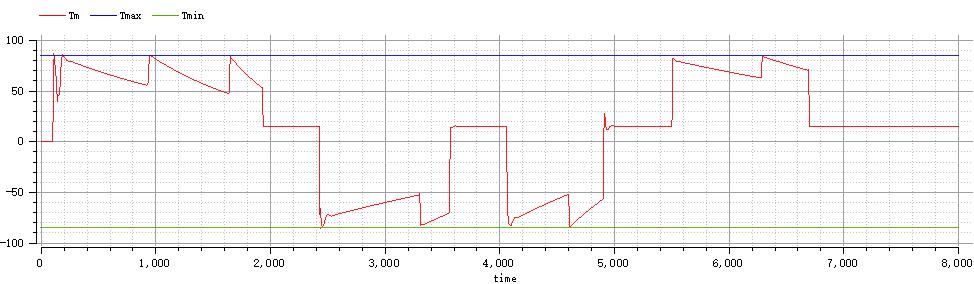
为实现高启动转矩和低启动电流的较好启动特性,仿真选取了绕线异步电动机的逐级切除启动电阻法实现电机的启动,同时选取转子串接电阻法作为调速方法,以反接制动作为制动方式,控制全过程中转矩大小不大于85N·m,全过程电流大小不超过25A,最终仿真全过程用时6690ms,仿真使用电机模型参数为:额定电压(相电压)220 V,额定频率50 Hz,极对数p=3,电机转动惯量0.1 kg.m^2,负载转动惯量1 kg.m^2,定子电阻:0.531 Ohm,转子电阻:0.408 Ohm,定子漏感:2.52 mH,转子漏感:2.52 mH,互感:8.47 mH,仿真过程中使用辅助参数来实现对过程时间点的定位。
仿真代码及结果:
model SACIM "A Simple AC Induction Motor Model"
type Voltage=Real(unit="V");
type Current=Real(unit="A");
type Resistance=Real(unit="Ohm");
type Inductance=Real(unit="H");
type Speed=Real(unit="r/min");
type Torque=Real(unit="N.m");
type Inertia=Real(unit="kg.m^2");
type Frequency=Real(unit="Hz");
type Flux=Real(unit="Wb");
type Angle=Real(unit="rad");
type AngularVelocity=Real(unit="rad/s");
constant Real Pi = 3.1415926;
Real y1;
Real y2;
Real z;
Current i_A"A Phase Current of Stator";
Current i_B"B Phase Current of Stator";
Current i_C"C Phase Current of Stator";
Voltage u_A"A Phase Voltage of Stator";
Voltage u_B"B Phase Voltage of Stator";
Voltage u_C"C Phase Voltage of Stator";
Current i_a"A Phase Current of Rotor";
Current i_b"B Phase Current of Rotor";
Current i_c"C Phase Current of Rotor";
Frequency f_s"Frequency of Stator";
Torque Tm"Torque of the Motor";
Speed n"Speed of the Motor";
Flux Psi_A"A Phase Flux-Linkage of Stator";
Flux Psi_B"B Phase Flux-Linkage of Stator";
Flux Psi_C"C Phase Flux-Linkage of Stator";
Flux Psi_a"a Phase Flux-Linkage of Rotor";
Flux Psi_b"b Phase Flux-Linkage of Rotor";
Flux Psi_c"c Phase Flux-Linkage of Rotor";
Angle phi"Electrical Angle of Rotor";
Angle phi_m"Mechnical Angle of Rotor";
AngularVelocity w"Angular Velocity of Rotor";
Resistance R1;
parameter Torque Tl =15 "Load Torque";
parameter Torque Tmax = 85;
parameter Torque Tmin = -85;
parameter Current imax = 25;
parameter Current imin = -25;
parameter Resistance Rs = 0.531"Stator Resistance";
parameter Resistance Rr = 0.408"Rotor Resistance";
parameter Inductance Ls = 0.00252"Stator Leakage Inductance";
parameter Inductance Lr = 0.00252"Rotor Leakage Inductance";
parameter Inductance Lm = 0.00847"Mutual Inductance";
parameter Frequency f_N = 50"Rated Frequency of Stator";
parameter Voltage u_N = 220"Rated Phase Voltage of Stator";
parameter Real p =3"number of pole pairs";
parameter Inertia Jm = 0.1"Motor Inertia";
parameter Inertia Jl = 1"Load Inertia";
initial equation
Psi_A = 0;
Psi_B = 0;
Psi_C = 0;
Psi_a = 0;
Psi_b = 0;
Psi_c = 0;
phi = 0;
w = 0;
equation
u_A = Rs * i_A + 1000 * der(Psi_A);
u_B = Rs * i_B + 1000 * der(Psi_B);
u_C = Rs * i_C + 1000 * der(Psi_C);
0 = (Rr+R1) * i_a + 1000 * der(Psi_a);
0 = (Rr+R1) * i_b + 1000 * der(Psi_b);
0 = (Rr+R1) * i_c + 1000 * der(Psi_c);
Psi_A = (Lm+Ls)*i_A + (-0.5*Lm)*i_B + (-0.5*Lm)*i_C + (Lm*cos(phi))*i_a + (Lm*cos(phi+2*Pi/3))*i_b + (Lm*cos(phi-2*Pi/3))*i_c;
Psi_B = (-0.5*Lm)*i_A + (Lm+Ls)*i_B + (-0.5*Lm)*i_C + (Lm*cos(phi-2*Pi/3))*i_a + (Lm*cos(phi))*i_b + (Lm*cos(phi+2*Pi/3))*i_c;
Psi_C = (-0.5*Lm)*i_A + (-0.5*Lm)*i_B + (Lm+Ls)*i_C + (Lm*cos(phi+2*Pi/3))*i_a + (Lm*cos(phi-2*Pi/3))*i_b + (Lm*cos(phi))*i_c;
Psi_a = (Lm*cos(phi))*i_A + (Lm*cos(phi-2*Pi/3))*i_B + (Lm*cos(phi+2*Pi/3))*i_C + (Lm+Lr)*i_a + (-0.5*Lm)*i_b + (-0.5*Lm)*i_c;
Psi_b = (Lm*cos(phi+2*Pi/3))*i_A + (Lm*cos(phi))*i_B + (Lm*cos(phi-2*Pi/3))*i_C + (-0.5*Lm)*i_a + (Lm+Lr)*i_b + (-0.5*Lm)*i_c;
Psi_c = (Lm*cos(phi-2*Pi/3))*i_A + (Lm*cos(phi+2*Pi/3))*i_B + (Lm*cos(phi))*i_C + (-0.5*Lm)*i_a + (-0.5*Lm)*i_b + (Lm+Lr)*i_c;
Tm =-p*Lm*((i_A*i_a+i_B*i_b+i_C*i_c)*sin(phi)+(i_A*i_b+i_B*i_c+i_C*i_a)*sin(phi+2*Pi/3)+(i_A*i_c+i_B*i_a+i_C*i_b)*sin(phi-2*Pi/3));
w = 1000 * der(phi_m);
phi_m = phi/p;
n= w*60/(2*Pi);
Tm-Tl = (Jm+Jl) * 1000 * der(w);
if time <= 100 then
u_A = 0;
u_B = 0;
u_C = 0;
f_s = 0;
elseif time <= 2430 then
f_s = f_N;
u_A = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000);
u_B = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-2*Pi/3);
u_C = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-4*Pi/3);
elseif time <= 3560 then
f_s = f_N;
u_A = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000);
u_B = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-4*Pi/3);
u_C = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-2*Pi/3);
elseif time <= 4060 then
f_s = f_N;
u_A = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000);
u_B = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-2*Pi/3);
u_C = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-4*Pi/3);
elseif time <= 4901 then
f_s = f_N;
u_A = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000);
u_B = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-4*Pi/3);
u_C = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-2*Pi/3);
else
f_s = f_N;
u_A = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000);
u_B = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-2*Pi/3);
u_C = u_N * 1.414 * sin(2*Pi*f_s*time/1000-4*Pi/3);
end if;
if time<=160 then
R1=17;
elseif time<=930 then
R1=10;
elseif time<=1640 then
R1=6;
elseif time<=1930 then
R1=3;
elseif time<=2430 then
R1=12.2;
elseif time<=3300 then
R1=20.5;
elseif time<=3560 then
R1=12.2;
elseif time<=4060 then
R1=62.4;
elseif time<=4600 then
R1=10.5;
elseif time<=4901 then
R1=6;
elseif time<=5501 then
R1=100;
elseif time<=6280 then
R1=17;
elseif time<=6690 then
R1=12.2;
else
R1=62.4;
end if;
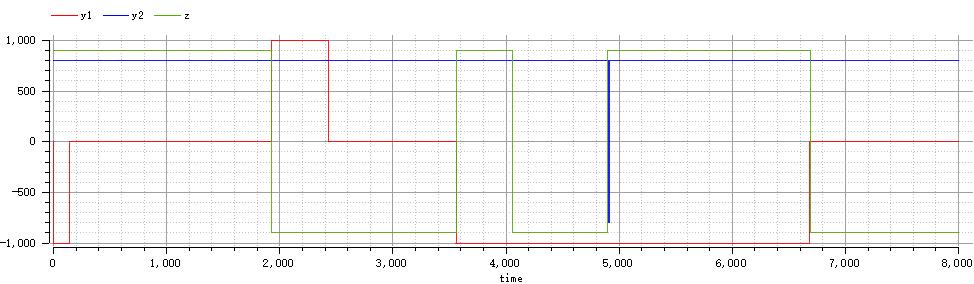
if n>=800 then
y1=1000;
elseif n>=0 then
y1=0;
else y1=-1000;
end if;
if n>=-600 then
y2=800;
else y2=-800;
end if;
if time<=1930 then
z=900;
elseif time<=3560 then
z=-900;
elseif time<=4060 then
z=900;
elseif time<=4901 then
z=-900;
elseif time<=6690 then
z=900;
else
z=-900;
end if;
end SACIM;
simulate(SACIM,startTime=0,stopTime=8000)
plot(n)
plot({y1,y2,z})
plot({i_a,imax,imin})
plot({Tm,Tmax,Tmin})
以上是关于机电传动控制第四周仿真作业的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章