机电传动控制——直流电机调速仿真作业
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机电传动控制——直流电机调速仿真作业相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
机电传动控制——直流电机调速仿真作业
本次调速仿真根据课本中的说明采用转速、电流双闭环调速,原理图如下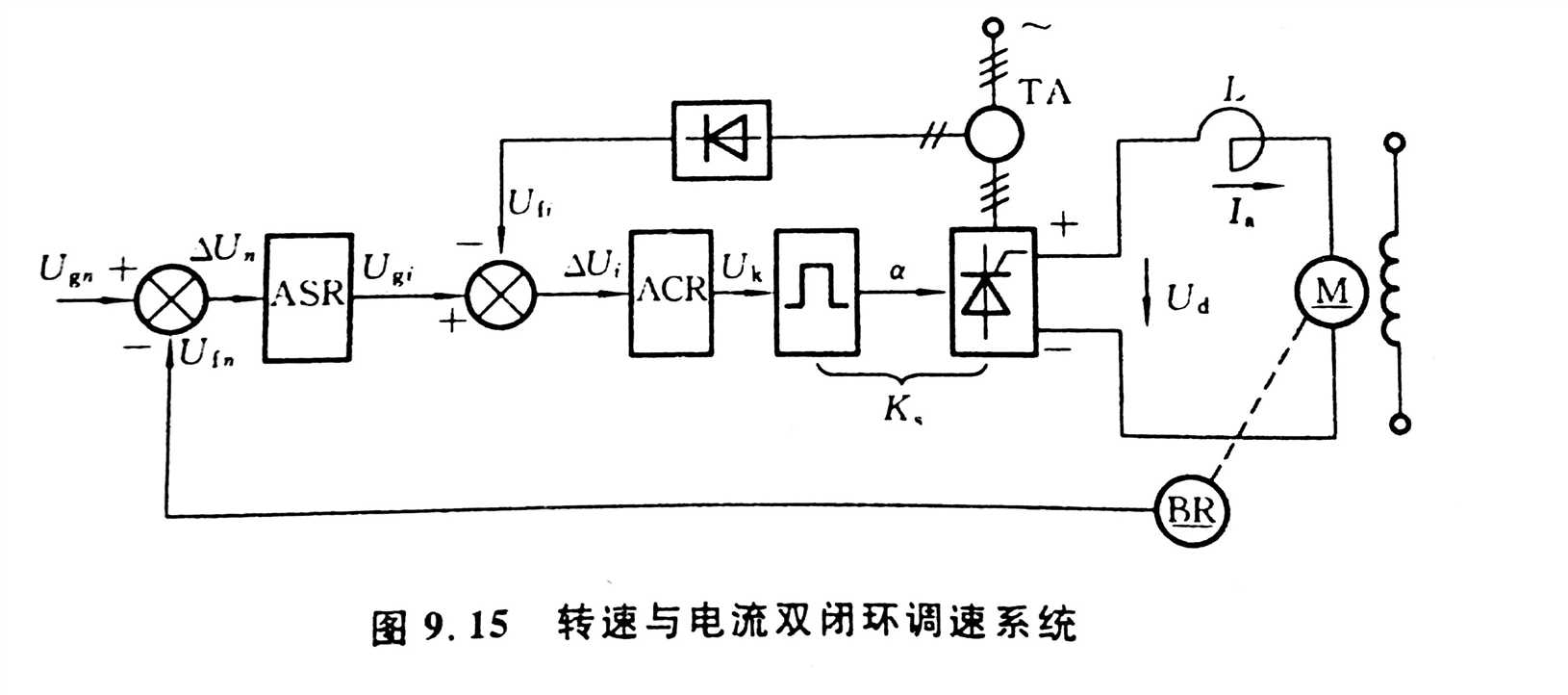
其中,ASR和ACR调节器均使用PI控制器

仿真结果如下
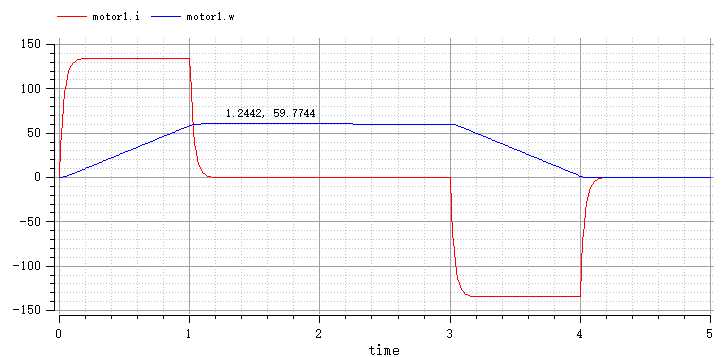
从图中可以看出,电流波形有了明显的改善:电流迅速上升至最大值然后保留在最大值,这时电机开始匀加速。电机速度稳定在59.7744,稳态偏差基本为零。Kp值越大,电流越快上升至最大值,ki值对波形影响不是很大。最终选定Kp=70,ki=20。
全部代码如下
type ElectricPotential = Real; type ElectricCurrent = Real(quantity = "ElectricCurrent", unit = "A"); type Resistance = Real(quantity = "Resistance", unit = "Ohm", min = 0); type Inductance = Real(quantity = "Inductance", unit = "H", min = 0); type Voltage = ElectricPotential; type Current = ElectricCurrent; type Force = Real(quantity = "Force", unit = "N"); type Angle = Real(quantity = "Angle", unit = "rad", displayUnit = "deg"); type Torque = Real(quantity = "Torque", unit = "N.m"); type AngularVelocity = Real(quantity = "AngularVelocity", unit = "rad/s", displayUnit = "rev/min"); type AngularAcceleration = Real(quantity = "AngularAcceleration", unit = "rad/s2"); type MomentOfInertia = Real(quantity = "MomentOfInertia", unit = "kg.m2"); type Time = Real (final quantity="Time", final unit="s"); connector RotFlange_a "1D rotational flange (filled square)" Angle phi "Absolute rotational angle of flange"; flow Torque tau "Torque in the flange"; end RotFlange_a; //From Modelica.Mechanical.Rotational.Interfaces connector RotFlange_b "1D rotational flange (filled square)" Angle phi "Absolute rotational angle of flange"; flow Torque tau "Torque in the flange"; end RotFlange_b; //From Modelica.Mechanical.Rotational.Interfaces connector Pin "Pin of an electrical component" Voltage v "Potential at the pin"; flow Current i "Current flowing into the pin"; end Pin; //From Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Interfaces connector PositivePin "Positive pin of an electrical component" Voltage v "Potential at the pin"; flow Current i "Current flowing into the pin"; end PositivePin; //From Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Interfaces connector NegativePin "Negative pin of an electrical component" Voltage v "Potential at the pin"; flow Current i "Current flowing into the pin"; end NegativePin; //From Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Interfaces connector InPort "Connector with input signals of type Real" parameter Integer n = 1 "Dimension of signal vector"; input Real signal[n] "Real input signals"; end InPort; // From Modelica.Blocks.Interfaces connector OutPort "Connector with output signals of type Real" parameter Integer n = 1 "Dimension of signal vector"; output Real signal[n] "Real output signals"; end OutPort; // From Modelica.Blocks.Interfaces partial model Rigid // Rotational class Rigid "Base class for the rigid connection of two rotational 1D flanges" Angle phi "Absolute rotation angle of component"; RotFlange_a rotFlange_a "(left) driving flange (axis directed into plane)"; RotFlange_b rotFlange_b "(right) driven flange (axis directed out of plane)"; equation rotFlange_a.phi = phi; rotFlange_b.phi = phi; end Rigid; // From Modelica.Mechanics.Rotational.Interfaces model Inertia "1D rotational component with inertia" extends Rigid; parameter MomentOfInertia J = 1 "Moment of inertia"; AngularVelocity w "Absolute angular velocity of component"; AngularAcceleration a "Absolute angular acceleration of component"; equation w = der(phi); a = der(w); J*a = rotFlange_a.tau + rotFlange_b.tau; end Inertia; //From Modelica.Mechanics.Rotational partial model TwoPin // Same as OnePort in Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Interfaces "Component with two electrical pins p and n and current i from p to n" Voltage v "Voltage drop between the two pins (= p.v - n.v)"; Current i "Current flowing from pin p to pin n"; PositivePin p; NegativePin n; equation v = p.v - n.v; 0 = p.i + n.i; i = p.i; end TwoPin; model DCMotor "DC Motor" extends TwoPin; extends Rigid; OutPort SensorVelocity(n=1); OutPort SensorCurrent(n=1); parameter MomentOfInertia J"Total Inertia"; parameter Resistance R"Armature Resistance"; parameter Inductance L"Armature Inductance"; parameter Real Kt"Torque Constant"; parameter Real Ke"EMF Constant"; AngularVelocity w "Angular velocity of motor"; AngularAcceleration a "Absolute angular acceleration of motor"; Torque tau_motor; RotFlange_b rotFlange_b; // Rotational Flange_b equation w = der(rotFlange_b.phi); a = der(w); v = R*i+Ke*w+L*der(i); tau_motor = Kt*i; J*a = tau_motor + rotFlange_b.tau; SensorVelocity.signal[1] = w; SensorCurrent.signal[1] =i; end DCMotor; class Resistor "Ideal linear electrical Resistor" extends TwoPin; // Same as OnePort parameter Real R(unit = "Ohm") "Resistance"; equation R*i = v; end Resistor; // From Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Basic class Inductor "Ideal linear electrical Inductor" extends TwoPin; // Same as OnePort parameter Real L(unit = "H") "Inductance"; equation v = L*der(i); end Inductor; // From Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Basic class Ground "Ground node" Pin p; equation p.v = 0; end Ground; // From Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Basic model PWMVoltageSource extends TwoPin; InPort Command(n=1); parameter Time T = 0.003; parameter Voltage Vin = 200; equation T*der(v)+ v = Vin*Command.signal[1]/10; end PWMVoltageSource; block Controller InPort command(n=1); InPort feedback(n=1); OutPort outPort(n=1); Real error; Real pout; Real intU; parameter Real Kp=70; parameter Real Ki=20; equation error = command.signal[1] - feedback.signal[1]; error =der(intU); pout = Kp * error+Ki*intU; outPort.signal[1] = pout; end Controller; block CommandSignalGenerator OutPort outPort(n=1); Real acc; equation if time <= 1 then acc =60; elseif time <3 then acc = 0; elseif time <4 then acc = -60; else acc = 0; end if; der(outPort.signal[1]) = acc; end CommandSignalGenerator; model DCMotorControlSystem Ground ground1; Inertia inertia1(J = 3, w(fixed = true)); DCMotor motor1(J = 1,R = 0.6,L = 0.01,Kt=1.8, Ke=1.8,rotFlange_b(phi(fixed = true))); CommandSignalGenerator sg1; Controller con1; Controller con2; PWMVoltageSource PowerSource1; equation connect(sg1.outPort, con1.command); connect(con1.feedback, motor1.SensorVelocity); connect(con1.outPort, con2.command); connect(motor1.SensorCurrent,con2.feedback); connect(con2.outPort, PowerSource1.Command); connect(PowerSource1.p, motor1.p); connect(motor1.rotFlange_b, inertia1.rotFlange_a); connect(PowerSource1.n, ground1.p); connect(ground1.p, motor1.n); end DCMotorControlSystem;
以上是关于机电传动控制——直流电机调速仿真作业的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章