Storm入门Storm常见模式之流聚合
Posted 静候东风
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Storm入门Storm常见模式之流聚合相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
流聚合(stream join)是指将具有共同元组(tuple)字段的数据流(两个或者多个)聚合形成一个新的数据流的过程。
从定义上看,流聚合和SQL中表的聚合(table join)很像,但是二者有明显的区别:table join的输入是有限的,并且join的语义是非常明确的;而流聚合的语义是不明确的并且输入流是无限的。
数据流的聚合类型跟具体的应用有关。一些应用把两个流发出的所有的tuple都聚合起来——不管多长时间;而另外一些应用则只会聚合一些特定的tuple。而另外一些应用的聚合逻辑又可能完全不一样。而这些聚合类型里面最常见的类型是把所有的输入流进行一样的划分,这个在storm里面用fields grouping在相同字段上进行grouping就可以实现。
1、代码剖析
下面是对storm-starter(代码见:https://github.com/nathanmarz/storm-starter)中有关两个流的聚合的示例代码剖析:
先看一下入口类SingleJoinExample。
(1)这里首先创建了两个发射源spout,分别是genderSpout和ageSpout:
FeederSpout genderSpout = new FeederSpout(new Fields("id", "gender")); FeederSpout ageSpout = new FeederSpout(new Fields("id", "age")); TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder(); builder.setSpout("gender", genderSpout); builder.setSpout("age", ageSpout);
其中genderSpout包含两个tuple字段:id和gender,ageSpout包含两个tuple字段:id和age(这里流聚合就是通过将相同id的tuple进行聚合,得到一个新的输出流,包含id、gender和age字段)。
(2)为了不同的数据流中的同一个id的tuple能够落到同一个task中进行处理,这里使用了storm中的fileds grouping在id字段上进行分组划分:
builder.setBolt("join", new SingleJoinBolt(new Fields("gender", "age")))
.fieldsGrouping("gender", new Fields("id"))
.fieldsGrouping("age", new Fields("id"));
从中可以看到,SingleJoinBolt就是真正进行流聚合的地方。下面我们来看看:
(1)SingleJoinBolt构造时接收一个Fileds对象,其中传进的是聚合后将要被输出的字段(这里就是gender和age字段),保存到变量_outFileds中。
(2)接下来看看完成SingleJoinBolt的构造后,SingleJoinBolt在真正开始接收处理tuple之前所做的准备工作(代码见prepare方法):
a)首先,将保存OutputCollector对象,创建TimeCacheMap对象,设置超时回调接口,用于tuple处理失败时fail消息;紧接着记录数据源的个数:
_collector = collector; int timeout = ((Number) conf.get(Config.TOPOLOGY_MESSAGE_TIMEOUT_SECS)).intValue(); _pending = new TimeCacheMap<List<Object>, Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>>(timeout, new ExpireCallback()); _numSources = context.getThisSources().size();
b)遍历TopologyContext中不同数据源,得到所有数据源(这里就是genderSpout和ageSpout)中公共的Filed字段,保存到变量_idFields中(例子中就是id字段),同时将_outFileds中字段所在数据源记录下来,保存到一张HashMap中_fieldLocations,以便聚合后获取对应的字段值。
Set<String> idFields = null; for(GlobalStreamId source: context.getThisSources().keySet()) { Fields fields = context.getComponentOutputFields(source.get_componentId(), source.get_streamId()); Set<String> setFields = new HashSet<String>(fields.toList()); if(idFields==null) idFields = setFields; else idFields.retainAll(setFields); for(String outfield: _outFields) { for(String sourcefield: fields) { if(outfield.equals(sourcefield)) { _fieldLocations.put(outfield, source); } } } } _idFields = new Fields(new ArrayList<String>(idFields)); if(_fieldLocations.size()!=_outFields.size()) { throw new RuntimeException("Cannot find all outfields among sources"); }
(3)好了,下面开始两个spout流的聚合过程了(代码见execute方法):
首先,从tuple中获取_idFields字段,如果不存在于等待被处理的队列_pending中,则加入一行,其中key是获取到的_idFields字段,value是一个空的HashMap<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>对象,记录GlobalStreamId到Tuple的映射。
List<Object> id = tuple.select(_idFields); GlobalStreamId streamId = new GlobalStreamId(tuple.getSourceComponent(), tuple.getSourceStreamId()); if(!_pending.containsKey(id)) { _pending.put(id, new HashMap<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>()); }
从_pending队列中,获取当前GlobalStreamId streamId对应的HashMap对象parts中:
Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple> parts = _pending.get(id);
如果streamId已经包含其中,则抛出异常,接收到同一个spout中的两条一样id的tuple,否则将该streamid加入parts中:
if(parts.containsKey(streamId)) throw new RuntimeException("Received same side of single join twice"); parts.put(streamId, tuple);
如果parts已经包含了聚合数据源的个数_numSources时,从_pending队列中移除这条记录,然后开始构造聚合后的结果字段:依次遍历_outFields中各个字段,从_fieldLocations中取到这些outFiled字段对应的GlobalStreamId,紧接着从parts中取出GlobalStreamId对应的outFiled,放入聚合后的结果中。
if(parts.size()==_numSources) { _pending.remove(id); List<Object> joinResult = new ArrayList<Object>(); for(String outField: _outFields) { GlobalStreamId loc = _fieldLocations.get(outField); joinResult.add(parts.get(loc).getValueByField(outField)); }
最后通过_collector将parts中存放的tuple和聚合后的输出结果发射出去,并ack这些tuple已经处理成功。
_collector.emit(new ArrayList<Tuple>(parts.values()), joinResult); for(Tuple part: parts.values()) { _collector.ack(part); } }
否则,继续等待两个spout流中这个streamid都到齐后再进行聚合处理。
(4)最后,声明一下输出字段(代码见declareOutputFields方法):
declarer.declare(_outFields);
2、整体代码展示和测试
SingleJoinExample.java
/** * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one * or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file * distributed with this work for additional information * regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file * to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the * "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance * with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package cn.ljh.storm.streamjoin; import org.apache.storm.Config; import org.apache.storm.LocalCluster; import org.apache.storm.testing.FeederSpout; import org.apache.storm.topology.TopologyBuilder; import org.apache.storm.tuple.Fields; import org.apache.storm.tuple.Values; import org.apache.storm.utils.Utils; /** Example of using a simple custom join bolt * NOTE: Prefer to use the built-in JoinBolt wherever applicable */ public class SingleJoinExample { public static void main(String[] args) { FeederSpout genderSpout = new FeederSpout(new Fields("id","name","address","gender")); FeederSpout ageSpout = new FeederSpout(new Fields("id","name","age")); TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder(); builder.setSpout("gender", genderSpout); builder.setSpout("age", ageSpout); builder.setBolt("join", new SingleJoinBolt(new Fields("address","gender","age"))).fieldsGrouping("gender", new Fields("id","name")) .fieldsGrouping("age", new Fields("id","name")); builder.setBolt("print", new SingleJoinPrintBolt()).shuffleGrouping("join"); Config conf = new Config(); conf.setDebug(true); LocalCluster cluster = new LocalCluster(); cluster.submitTopology("join-example", conf, builder.createTopology()); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { String gender; String name = "Tom" + i; String address = "Beijing " + i; if (i % 2 == 0) { gender = "male"; } else { gender = "female"; } genderSpout.feed(new Values(i,name,address,gender)); } for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) { ageSpout.feed(new Values(i, "Tom" + i , i + 20)); } Utils.sleep(20000); cluster.shutdown(); } }
SingleJoinBolt.java
package cn.ljh.storm.streamjoin; import org.apache.storm.Config; import org.apache.storm.generated.GlobalStreamId; import org.apache.storm.task.OutputCollector; import org.apache.storm.task.TopologyContext; import org.apache.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer; import org.apache.storm.topology.base.BaseRichBolt; import org.apache.storm.tuple.Fields; import org.apache.storm.tuple.Tuple; import org.apache.storm.utils.TimeCacheMap; import java.util.*; /** Example of a simple custom bolt for joining two streams * NOTE: Prefer to use the built-in JoinBolt wherever applicable */ public class SingleJoinBolt extends BaseRichBolt { OutputCollector _collector; Fields _idFields; Fields _outFields; int _numSources; TimeCacheMap<List<Object>, Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>> _pending; Map<String, GlobalStreamId> _fieldLocations; public SingleJoinBolt(Fields outFields) { _outFields = outFields; } public void prepare(Map conf, TopologyContext context, OutputCollector collector) { _fieldLocations = new HashMap<String, GlobalStreamId>(); _collector = collector; int timeout = ((Number) conf.get(Config.TOPOLOGY_MESSAGE_TIMEOUT_SECS)).intValue(); _pending = new TimeCacheMap<List<Object>, Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>>(timeout, new ExpireCallback()); _numSources = context.getThisSources().size(); Set<String> idFields = null; for (GlobalStreamId source : context.getThisSources().keySet()) { Fields fields = context.getComponentOutputFields(source.get_componentId(), source.get_streamId()); Set<String> setFields = new HashSet<String>(fields.toList()); if (idFields == null) idFields = setFields; else idFields.retainAll(setFields); for (String outfield : _outFields) { for (String sourcefield : fields) { if (outfield.equals(sourcefield)) { _fieldLocations.put(outfield, source); } } } } _idFields = new Fields(new ArrayList<String>(idFields)); if (_fieldLocations.size() != _outFields.size()) { throw new RuntimeException("Cannot find all outfields among sources"); } } public void execute(Tuple tuple) { List<Object> id = tuple.select(_idFields); GlobalStreamId streamId = new GlobalStreamId(tuple.getSourceComponent(), tuple.getSourceStreamId()); if (!_pending.containsKey(id)) { _pending.put(id, new HashMap<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>()); } Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple> parts = _pending.get(id); if (parts.containsKey(streamId)) throw new RuntimeException("Received same side of single join twice"); parts.put(streamId, tuple); if (parts.size() == _numSources) { _pending.remove(id); List<Object> joinResult = new ArrayList<Object>(); for (String outField : _outFields) { GlobalStreamId loc = _fieldLocations.get(outField); joinResult.add(parts.get(loc).getValueByField(outField)); } _collector.emit(new ArrayList<Tuple>(parts.values()), joinResult); for (Tuple part : parts.values()) { _collector.ack(part); } } } public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) { declarer.declare(_outFields); } private class ExpireCallback implements TimeCacheMap.ExpiredCallback<List<Object>, Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple>> { public void expire(List<Object> id, Map<GlobalStreamId, Tuple> tuples) { for (Tuple tuple : tuples.values()) { _collector.fail(tuple); } } } }
SingleJoinPrintBolt.java
package cn.ljh.storm.streamjoin; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.storm.task.OutputCollector; import org.apache.storm.task.TopologyContext; import org.apache.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer; import org.apache.storm.topology.base.BaseRichBolt; import org.apache.storm.tuple.Tuple; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class SingleJoinPrintBolt extends BaseRichBolt { private static Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SingleJoinPrintBolt.class); OutputCollector _collector; private FileWriter fileWriter; public void prepare(Map conf, TopologyContext context, OutputCollector collector) { _collector = collector; } public void execute(Tuple tuple) { try { if(fileWriter == null){ fileWriter = new FileWriter("D:\\\\test\\\\"+this); } fileWriter.write("address: " + tuple.getString(0) + " gender: " + tuple.getString(1) + " age: " + tuple.getInteger(2)); fileWriter.write("\\r\\n"); fileWriter.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } _collector.ack(tuple); } public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) { } }
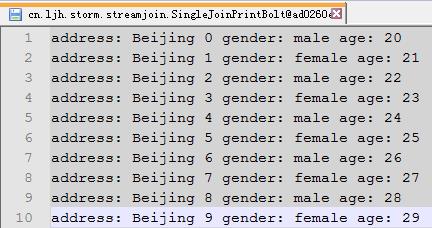
测试结果
以上是关于Storm入门Storm常见模式之流聚合的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Storm入门经典文章:本地模式运行storm的demo 单机模式跑直一个Word Count & kafka to Storm