zmq笔记一: 对象关系
Posted wqchen@
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了zmq笔记一: 对象关系相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
int major, minor, patch;
zmq_version(&major, &minor, &patch); //4.2.0
本文主要是分析代码,方便自己日后查阅.
=========================================
1.上下文对象以及socket对象创建
void *context = zmq_ctx_new(); //创建上下文对象
void *responder = zmq_socket(context, ZMQ_REP); //创建socket类型的对象 zmq::socket_base_t *s = ctx->create_socket (type_);
int rc = zmq_bind(responder, "tcp://*:6666"); //绑定端口
一般一个进程只有一个context对象,它管理着所有socket对象. context是线程安全的,可以在多线程之间传递使用,但是socket对象不是线程安全.
zmq::socket_base_t *zmq::ctx_t::create_socket (int type_)
{
slot_sync.lock ();
if (unlikely (starting)) {
starting = false;
// Initialise the array of mailboxes. Additional three slots are for
// zmq_ctx_term thread and reaper thread.
opt_sync.lock ();
int mazmq = max_sockets;//默认值
int ios = io_thread_count; //最大io线程数量,默认只有1个
opt_sync.unlock ();
slot_count = mazmq + ios + 2; //slot_count决定了邮箱数量, 2这个数字是指下面的 term_tid + reaper_tid 两个mailbox的数组占坑位置
slots = (i_mailbox **) malloc (sizeof (i_mailbox*) * slot_count);
alloc_assert (slots);
// Initialise the infrastructure for zmq_ctx_term thread.
slots [term_tid] = &term_mailbox; //zmq终结处理时的唯一的一个邮箱
// Create the reaper thread.
reaper = new (std::nothrow) reaper_t (this, reaper_tid); //收割线程,回收结束使用的socket
alloc_assert (reaper);
slots [reaper_tid] = reaper->get_mailbox ();//把线程的邮箱放在全局邮箱管理
reaper->start ();
// Create I/O thread objects and launch them.
for (int i = 2; i != ios + 2; i++) {//除终结处理和回收线程邮箱外,还要开启一共ios个io线程
io_thread_t *io_thread = new (std::nothrow) io_thread_t (this, i);
alloc_assert (io_thread);
io_threads.push_back (io_thread); //将所有开启的io线程统一管理
slots [i] = io_thread->get_mailbox (); //线程的邮箱放在全局邮箱管理
io_thread->start ();
}
// In the unused part of the slot array, create a list of empty slots.
for (int32_t i = (int32_t) slot_count - 1;
i >= (int32_t) ios + 2; i--) {
empty_slots.push_back (i); //还没被使用的邮箱占位
slots [i] = NULL;
}
}
// Once zmq_ctx_term() was called, we can\'t create new sockets.
if (terminating) {
slot_sync.unlock ();
errno = ETERM;
return NULL;
}
// If max_sockets limit was reached, return error.
if (empty_slots.empty ()) {
slot_sync.unlock ();
errno = EMFILE;
return NULL;
}
// Choose a slot for the socket.
uint32_t slot = empty_slots.back (); //当前新建的socket类型占一个邮箱位置
empty_slots.pop_back ();
// Generate new unique socket ID.
int sid = ((int) max_socket_id.add (1)) + 1; //原子递增的socket id
// Create the socket and register its mailbox.
socket_base_t *s = socket_base_t::create (type_, this, slot, sid); //创建当前类型socket对象,并初始化它对应的邮箱
if (!s) {
empty_slots.push_back (slot);
slot_sync.unlock ();
return NULL;
}
sockets.push_back (s); //所有创建的socket对象统一管理
slots [slot] = s->get_mailbox (); //对应占坑
slot_sync.unlock ();
return s;
}
每一种socket都有一个与之对应的对象类,创建时需要绑定context,邮箱位置,socket id 等.
zmq::socket_base_t *zmq::socket_base_t::create (int type_, class ctx_t *parent_,
uint32_t tid_, int sid_)
{
socket_base_t *s = NULL;
switch (type_) {
case ZMQ_PAIR:
s = new (std::nothrow) pair_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
case ZMQ_PUB:
s = new (std::nothrow) pub_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
case ZMQ_SUB:
s = new (std::nothrow) sub_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
case ZMQ_REQ:
s = new (std::nothrow) req_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
case ZMQ_REP:
s = new (std::nothrow) rep_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
......
case ZMQ_GATHER:
s = new (std::nothrow) gather_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
case ZMQ_SCATTER:
s = new (std::nothrow) scatter_t (parent_, tid_, sid_);
break;
default:
errno = EINVAL;
return NULL;
}
alloc_assert (s);
if (s->mailbox == NULL) {
s->destroyed = true;
LIBZMQ_DELETE(s);
return NULL;
}
return s;
}
object_t 类对象继承关系图:( zmq版本:4.2.0, 生成工具:doxygen,graphviz )

2.线程与通信
I / O线程(io_thread_t)是ZMQ异步处理网络IO的后台线程。io_thread_t实现继承object_t ,并实现 i_poll_events 接口,其内部包含一个邮箱(mailbox_t)和一个poller对象(poller_t)。
class io_thread_t : public object_t, public i_poll_events{
...
}
zmq::io_thread_t::io_thread_t (ctx_t *ctx_, uint32_t tid_) :
object_t (ctx_, tid_)
{
poller = new (std::nothrow) poller_t (*ctx_); //注意,poller_t是根据操作系统来定义的,typedef select_t/poll_t/epoll_t, 本文在windows操作系统分析,用的是select_t,基本逻辑大同小异
alloc_assert (poller);
mailbox_handle = poller->add_fd (mailbox.get_fd (), this);
poller->set_pollin (mailbox_handle);
}
void zmq::io_thread_t::start ()
{
// Start the underlying I/O thread.
poller->start ();
}
void zmq::select_t::start ()
{
ctx.start_thread (worker, worker_routine, this);
}
void zmq::ctx_t::start_thread (thread_t &thread_, thread_fn *tfn_, void *arg_) const
{
thread_.start(tfn_, arg_);
thread_.setSchedulingParameters(thread_priority, thread_sched_policy);
}
void zmq::select_t::worker_routine (void *arg_)
{
((select_t*) arg_)->loop ();
}
void zmq::select_t::loop () //io线程循环是在poller_t(typedef select_t poller_t)的loop函数
{
while (!stopping) {
....
}
}
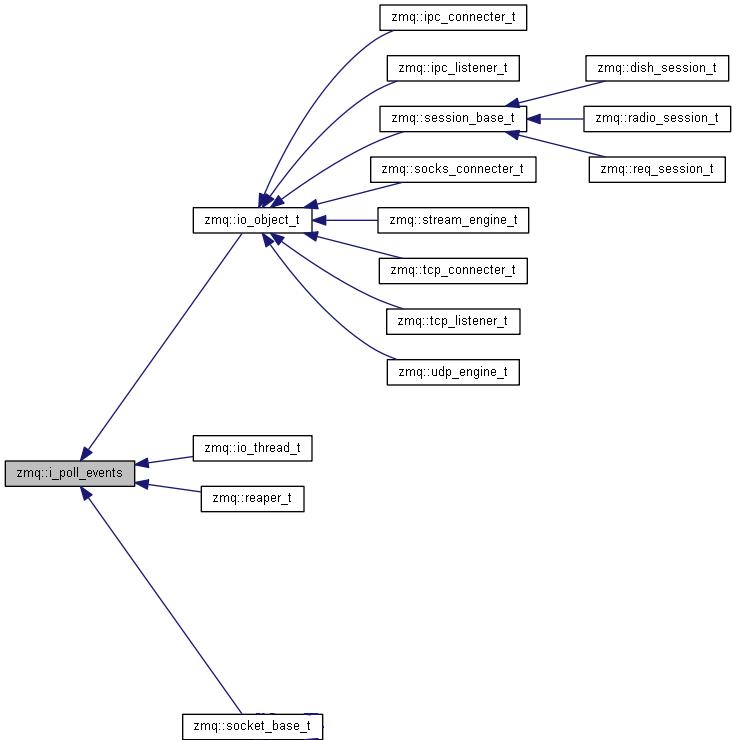
poller_t 是从不同操作系统提供的事件通知机制中抽象出来的概念,用来通知描述符和计时器事件,poller_t 通过 typedef定义为操作系统首选的通知机制(select_t/poll_t/epoll_t 等)。所有运行在 io_thread_t上的对象都继承自辅助类 io_object_t,该类实现了向io_thread_t注册/删除文件描述符 (add_fd/rm_fd)和计时器(add_timer/cancel_timer)事件的功能,同时io_object_t 还继承了 i_poll_events 接口来实现事件回调功能。i_poll_events 接口定义了文件描述符和计时器事件就绪时的回调处理函数(in_event/out_event/timer_event)。io_thread_t 实现此接口(in_event)来处理来自mailbox的事件。
继承object_t使得io_thread_t能够发送和接收command,mailbox_t 用来存储发送给任何居住在io_thread_t 上的object_t 的命令,每个io_thread_t 上有多个对象,这些对象公用同一个邮箱,邮箱的收件人就是对象。mailbox_t本质是一个具有就绪通知功能的存储命令的队列。就绪通知机制由signaler_t提供的文件描述符实现。队列是由ypipe_t实现的无锁无溢出队列。当mailbox_t事件触发时,io线程从mailbox中获取命令,并让命令的接收者进行处理。
io线程之间的通信是通过发命令消息(command_t)到对方的mailbox,而socket_base_t实例与session的消息通信则通过发送消息对象msg_t.
ZMQ内部使用两种不同类型的线程(拥有邮箱的对象):I/O线程(io_thread_t)和socket(socket_base_t). 其中io线程,像reaper_t、io_thread_t都属于这一类,这类线程的特点就是内含一个轮询器poller及mailbox_t,通过poller可以监听激活mailbox_t的信号 ;另一类是zmq的socket,所有socket_base_t实例化的对象都可以看做一个单独的线程,这类线程不含poller,但同样含有一个mailbox_t,可以用于收发命令; 由于不含poller,只能在每次使用socket_base_t实例的时候先处理一下mailbox_t,看是否有命令需要处理(process_commands函数), 例如:
int zmq::socket_base_t::send (msg_t *msg_, int flags_)
{
ENTER_MUTEX ();
......
// Process pending commands, if any.
int rc = process_commands (0, true); //处理一次邮箱里的命令
if (unlikely (rc != 0)) {
EXIT_MUTEX ();
return -1;
}
// Clear any user-visible flags that are set on the message.
msg_->reset_flags (msg_t::more);
// At this point we impose the flags on the message.
if (flags_ & ZMQ_SNDMORE)
msg_->set_flags (msg_t::more);
msg_->reset_metadata ();
// Try to send the message using method in each socket class
rc = xsend (msg_);
......
while (true) {
if (unlikely (process_commands (timeout, false) != 0)) {//再次处理邮箱里的命令
EXIT_MUTEX ();
return -1;
}
rc = xsend (msg_);
......
return 0;
}
i_poll_events 类对象继承关系图:( zmq版本:4.2.0, 生成工具:doxygen,graphviz )
参考文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/zengzy/p/5132437.html
http://watter1985.iteye.com/blog/1736023
以上是关于zmq笔记一: 对象关系的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
spring练习,在Eclipse搭建的Spring开发环境中,使用set注入方式,实现对象的依赖关系,通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext实体类获取Bean对象(代码片段