ZMQ源码分析--对象管理和消息机制
Posted 子曰帅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ZMQ源码分析--对象管理和消息机制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
对象管理
zmq的高效很大一部分原因是因为消息的传递采用无锁的操作,在分析zmq的消息机制之前先来看一下zmq的对象管理机制。
在zmq中所有参与消息机制的对象都继承自object_t对象,该对象只有两个变量,一个ctx和一个tid,tid记录了mailbox在ctx中的索引,send_command方法可以通过tid找到对象对应的mailbox以便发送消息。另外object_t还定义了一套发送命令和处理命令的方法,继承自object_t的类需要重载自身需要处理的消息对应的方法。所有的消息都用command_t结构体来表示。
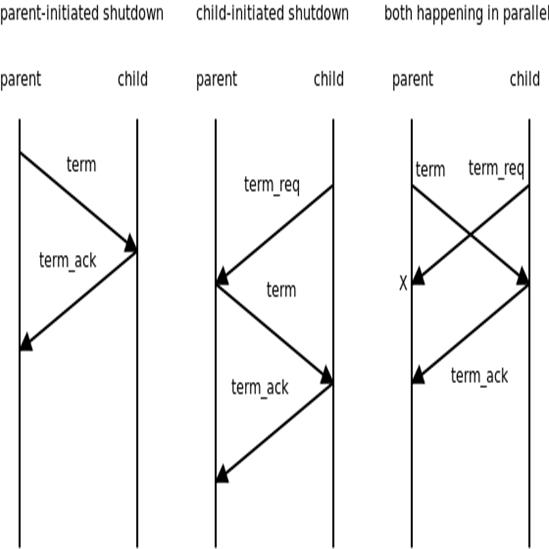
接下来看一下own_t类的实现,own_t继承自object_t,用于管理有从属关系的对象,主要是用于管理和销毁对象,当一个对象的父对象要销毁时,会给每一个子对象发送关闭的命令,如果这个子对象也包含子对象,则需要关闭所有的子对象,当所有子对象关闭之后则通知父对象销毁自身,以此类推。own_t的销毁需要处理不同的情况,比如子对象向父对象发送销毁自身请求,父对象主动销毁子对象以及父子同时发送销毁请求。
消息机制
zmq的消息机制主要通过mail_box类来实现,下面是该类的定义:
class mailbox_t
public:
mailbox_t ();
~mailbox_t ();
fd_t get_fd () const;
void send (const command_t &cmd_);
int recv (command_t *cmd_, int timeout_);
#ifdef HAVE_FORK
// close the file descriptors in the signaller. This is used in a forked
// child process to close the file descriptors so that they do not interfere
// with the context in the parent process.
void forked () signaler.forked ();
#endif
private:
// The pipe to store actual commands.
typedef ypipe_t <command_t, command_pipe_granularity> cpipe_t;
cpipe_t cpipe;
// Signaler to pass signals from writer thread to reader thread.
signaler_t signaler;
// There's only one thread receiving from the mailbox, but there
// is arbitrary number of threads sending. Given that ypipe requires
// synchronised access on both of its endpoints, we have to synchronise
// the sending side.
mutex_t sync;
// True if the underlying pipe is active, ie. when we are allowed to
// read commands from it.
bool active;
// Disable copying of mailbox_t object.
mailbox_t (const mailbox_t&);
const mailbox_t &operator = (const mailbox_t&);
;mail_box类包含一个ypipe_t结构用来存储命令,每个命令也有一个互斥锁,因为向mail_box发送消息的调用可能来自不同的线程,所以需要加锁操作,但是读取命令则不需要加锁,因为读取是在固定线程中进行的。下面是对应的recv和send的实现:
void zmq::mailbox_t::send (const command_t &cmd_)
sync.lock ();
cpipe.write (cmd_, false);
const bool ok = cpipe.flush ();
sync.unlock ();
if (!ok)
signaler.send ();
int zmq::mailbox_t::recv (command_t *cmd_, int timeout_)
// Try to get the command straight away.
if (active)
if (cpipe.read (cmd_))
return 0;
// If there are no more commands available, switch into passive state.
active = false;
// Wait for signal from the command sender.
const int rc = signaler.wait (timeout_);
if (rc == -1)
errno_assert (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EINTR);
return -1;
// Receive the signal.
signaler.recv ();
// Switch into active state.
active = true;
// Get a command.
const bool ok = cpipe.read (cmd_);
zmq_assert (ok);
return 0;
mailbox_t的成员变量中还包含一个signaler_t对象,这个对象类似一个信号量,用来通知命令队列中有新的数据可以读取,signal是通过一读一写两个描述符来实现的,在不同平台上这两个描述符的创建方式不同,比如可以通过eventfd来创建,可以通过socketpari来创建,或者手动创建两个socket描述符然后建立连接。当进行recv操作时,如果当前的是非激活状态,则需要等待signaler有信号,当send中写入命令并且发现当前队列是非激活状态时会发送信号,signaler.wait (timeout_)立刻返回,并且马上读取新的命令,此时队列中一定是有命令的。signaler.wait (timeout_)如果超时,则会返回-1。
zmq 中拥有邮箱的主要是io_thread_t和socket_base以及一个reaper线程和ctx的term_mailbox。io_thread_t会一直监听signaler中的信号,只要有信号,则马上处理所有的命令。socket_base则是在send,recv,bind,connect中调用process_command的。
以上是关于ZMQ源码分析--对象管理和消息机制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章