递归算法应用——实体树过滤解析
Posted coshaho
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了递归算法应用——实体树过滤解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
监控一个地区网络设备的性能指标,会通过报表或告警展现,报表或告警往往只关心部分设备,此时在数据查询中我们就会进行设备实体过滤。实体树过滤是一种常见的过滤方式,但是网络设备数量巨大,我们不可能在页面上加载所有实体,前台也就无法把用户选择的所有实体(叶子节点)传递到后台,这时候就不能简单的采用in条件来过滤选择实体,我们必须综合使用in,not in,=,!=来过滤实体。
树显然是一种递归的数据结构,那么解析它必然就要使用递归算法。
一、从例子开始
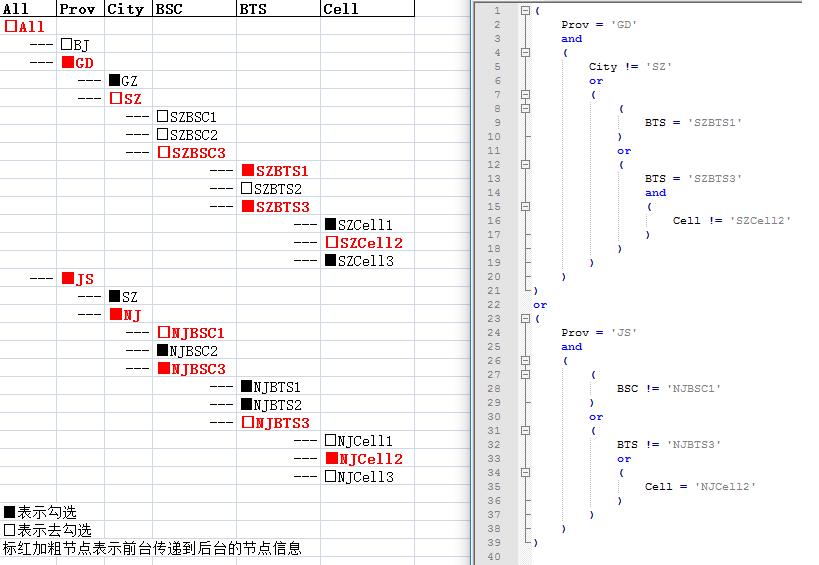
下图是一棵勾选了的网元实体树,从图上我们可以看出以下几点
1、 网元层级关系为 Prov <- City <- BSC <- BTS <- Cell;
2、 实心方框为勾选节点,空心方框为去勾选节点;
3、 红色加粗节点为前台传递到后台的节点信息(json格式);
4、 右侧sql是根据前台传递的节点信息解析出来的实体过滤条件。
二、算法归纳
1、 同层节点条件之间的关系为or;
2、 被勾选的节点与子节点条件之间的关系是and;
3、 去勾选的节点与子节点条件之间的关系是or;
4、 节点与父节点勾选状态相同,则不必解析该节点条件,直接解析子节点条件;
5、 节点与父节点勾选状态不同,先解析该节点条件,再解析子节点条件;
6、 节点没有子节点,则直接返回该节点条件。
三、递归算法原理
1、 算法重复被自身调用;
2、 存在出口条件。
显然,例子中每个节点的解析算法一致,并且节点递归嵌套,满足条件1;
出口条件为节点不存在叶子节点。
四、代码实现
1、 节点代码TreeNode
package com.coshaho.learn.recursion;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* Node.java Create on 2017年5月19日 下午10:34:13
*
* 类功能说明: 树节点定义
*
* Copyright: Copyright(c) 2013
* Company: COSHAHO
* @Version 1.0
* @Author coshaho
*/
public class TreeNode
{
private String name;
private String type;
private boolean isCheck;
private List<TreeNode> children;
public TreeNode(String name, String type, boolean isCheck)
{
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.isCheck = isCheck;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public List<TreeNode> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List<TreeNode> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public boolean isCheck() {
return isCheck;
}
public void setCheck(boolean isCheck) {
this.isCheck = isCheck;
}
}
2、 递归解析算法TreeSqlTranslator
package com.coshaho.learn.recursion;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
/**
*
* TreeSqlTranslator.java Create on 2017年5月19日 下午11:38:07
*
* 类功能说明: 实体书过滤条件翻译
*
* Copyright: Copyright(c) 2013
* Company: COSHAHO
* @Version 1.0
* @Author coshaho
*/
public class TreeSqlTranslator
{
public String parseTree2Sql(TreeNode root)
{
if(root.isCheck())
{
return "1=1 and (" + parseChildrenNode2Sql(root) + \')\';
}
return parseChildrenNode2Sql(root);
}
/**
* 解析子节点为sql
*
* @author coshaho
* @param node
* @return
*/
private String parseChildrenNode2Sql(TreeNode node)
{
StringBuffer childCondition = new StringBuffer();
for(TreeNode child : node.getChildren())
{
// 1、同层节点之间采用or拼接条件
childCondition.append(\'(\').append(parseNode2Sql(child, node.isCheck())).append(") or ");
}
// 此处代码可以减少非必须的括号
if(1 == node.getChildren().size())
{
return childCondition.substring(1, childCondition.length() - 5);
}
else
{
return childCondition.substring(0, childCondition.length() - 4);
}
}
/**
* 解析单个节点为sql
*
* @author coshaho
* @param node
* @param isCheck
* @return
*/
private String parseNode2Sql(TreeNode node, boolean isCheck)
{
boolean nodeCheck = node.isCheck();
// 2、没有子节点,则直接返回该节点条件
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(node.getChildren()))
{
return generateNodeSql(node);
}
StringBuffer condition = new StringBuffer();
// 3、父节点与当前节点勾选状态不一致,拼接当前节点条件
if(isCheck ^ nodeCheck)
{
condition.append(generateNodeSql(node));
// 4、当前节点被勾选,则与子节点关系为and
if(node.isCheck())
{
// 拼接子节点条件
return condition.append(" and (")
.append(parseChildrenNode2Sql(node)).append(\')\').toString();
}
// 5、当前节点去勾选,则与子节点关系为or
else
{
// 拼接子节点条件
return condition.append(" or (")
.append(parseChildrenNode2Sql(node)).append(\')\').toString();
}
}
// 6、父节点与当前节点勾选状态一致,直接处理子节点
else
{
return parseChildrenNode2Sql(node);
}
}
private String generateNodeSql(TreeNode node)
{
if(node.isCheck())
{
return node.getType() + " = \'" + node.getName() + \'\\\'\';
}
else
{
return node.getType() + " != \'" + node.getName() + \'\\\'\';
}
}
}
3、 测试代码TreeSqlTranslatorTest
package com.coshaho.learn.recursion;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* TreeSqlTranslatorTest.java Create on 2017年5月19日 下午11:39:25
*
* 类功能说明: 递归算法测试
*
* Copyright: Copyright(c) 2013
* Company: COSHAHO
* @Version 1.0
* @Author coshaho
*/
public class TreeSqlTranslatorTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeNode All = new TreeNode("All", "All", false);
TreeNode GD = new TreeNode("GD", "Prov", true);
TreeNode JS = new TreeNode("JS", "Prov", true);
TreeNode SZ = new TreeNode("SZ", "City", false);
TreeNode NJ = new TreeNode("NJ", "City", true);
TreeNode SZBSC3 = new TreeNode("SZBSC3", "BSC", false);
TreeNode NJBSC1 = new TreeNode("NJBSC1", "BSC", false);
TreeNode NJBSC3 = new TreeNode("NJBSC3", "BSC", true);
TreeNode SZBTS1 = new TreeNode("SZBTS1", "BTS", true);
TreeNode SZBTS3 = new TreeNode("SZBTS3", "BTS", true);
TreeNode NJBTS3 = new TreeNode("NJBTS3", "BTS", false);
TreeNode SZCell2 = new TreeNode("SZCell2", "Cell", false);
TreeNode NJCell2 = new TreeNode("NJCell2", "Cell", true);
List<TreeNode> AllGroup = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
AllGroup.add(GD);
AllGroup.add(JS);
All.setChildren(AllGroup);
List<TreeNode> GDGroup = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
GDGroup.add(SZ);
GD.setChildren(GDGroup);
List<TreeNode> JSGroup = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
JSGroup.add(NJ);
JS.setChildren(JSGroup);
List<TreeNode> SZGroup = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
SZGroup.add(SZBSC3);
SZ.setChildren(SZGroup);
List<TreeNode> NJGroup = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
NJGroup.add(NJBSC1);
NJGroup.add(NJBSC3);
NJ.setChildren(NJGroup);
List<TreeNode> SZBSC3Group = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
SZBSC3Group.add(SZBTS1);
SZBSC3Group.add(SZBTS3);
SZBSC3.setChildren(SZBSC3Group);
List<TreeNode> NJBSC3Group = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
NJBSC3Group.add(NJBTS3);
NJBSC3.setChildren(NJBSC3Group);
List<TreeNode> SZBTS3Group = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
SZBTS3Group.add(SZCell2);
SZBTS3.setChildren(SZBTS3Group);
List<TreeNode> NJBTS3Group = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
NJBTS3Group.add(NJCell2);
NJBTS3.setChildren(NJBTS3Group);
System.out.println(new TreeSqlTranslator().parseTree2Sql(All));
}
}
以上是关于递归算法应用——实体树过滤解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章