runtime的一些应用
Posted 晚安早安
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了runtime的一些应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、便利类的成员变量、属性、方法
/**遍历类所以成员变量
* @param <#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#> 要遍历的类
* @param <#unsigned int *outCount#> 成员变量数量
*/
// class_copyIvarList(<#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#>, <#unsigned int *outCount#>)
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar * ivars = class_copyIvarList([UIView class], &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char * name = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSString * str = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
NSLog(@"%d:%@",i,str);
}
free(ivars);
/**遍历类所以属性
* @param <#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#> 要遍历的类
* @param <#unsigned int *outCount#> 属性数量
*/
//class_copyPropertyList(<#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#>, <#unsigned int *outCount#>)
unsigned int propertyCount = 0;
objc_property_t * propertys = class_copyPropertyList([UIView class], &propertyCount);
for (int i = 0; i < propertyCount; i++) {
objc_property_t property = propertys[i];
const char * name = property_getName(property);
NSString * str = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
NSLog(@"%d:%@",i,str);
}
free(propertys);
/**遍历类所有方法
* @param <#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#> 要遍历的类
* @param <#unsigned int *outCount#> 属性数量
*/
//class_copyMethodList(<#__unsafe_unretained Class cls#>, <#unsigned int *outCount#>)
unsigned int methodCount = 0;
Method * methods = class_copyMethodList([UIView class], &methodCount);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
SEL sel = method_getName(method);
NSLog(@"%d:%@",i,NSStringFromSelector(sel));
}
free(methods);
二、消息转发
1、重定向
消息转发机制执行前,Runtime 系统允许我们替换消息的接收者为其他对象。通过 - (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector 方法。
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if(aSelector == @selector(mysteriousMethod:)){
return alternateObject;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}如果此方法返回 nil 或者 self,则会计入消息转发机制(forwardInvocation:),否则将向返回的对象重新发送消息。
2、转发
当动态方法解析不做处理返回 NO 时,则会触发消息转发机制。这时 forwardInvocation: 方法会被执行,我们可以重写这个方法来自定义我们的转发逻辑:
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
if ([someOtherObject respondsToSelector:
[anInvocation selector]])
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:someOtherObject];
else
[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}唯一参数是个 NSInvocation 类型的对象,该对象封装了原始的消息和消息的参数。我们可以实现 forwardInvocation: 方法来对不能处理的消息做一些处理。也可以将消息转发给其他对象处理,而不抛出错误。
注意:参数
anInvocation 是从哪来的?
在forwardInvocation:消息发送前,Runtime 系统会向对象发送methodSignatureForSelector:消息,并取到返回的方法签名用于生成 NSInvocation 对象。所以重写forwardInvocation:的同时也要重写methodSignatureForSelector:方法,否则会抛异常。
当一个对象由于没有相应的方法实现而无法相应某消息时,运行时系统将通过 forwardInvocation: 消息通知该对象。每个对象都继承了 forwardInvocation: 方法。但是, NSObject 中的方法实现只是简单的调用了 doesNotRecognizeSelector:。通过实现自己的 forwardInvocation: 方法,我们可以将消息转发给其他对象。
forwardInvocation: 方法就是一个不能识别消息的分发中心,将这些不能识别的消息转发给不同的接收对象,或者转发给同一个对象,再或者将消息翻译成另外的消息,亦或者简单的“吃掉”某些消息,因此没有响应也不会报错。这一切都取决于方法的具体实现。
注意:
forwardInvocation:方法只有在消息接收对象中无法正常响应消息时才会被调用。所以,如果我们向往一个对象将一个消息转发给其他对象时,要确保这个对象不能有该消息的所对应的方法。否则,forwardInvocation:将不可能被调用。
3、转发和多继承
转发和继承相似,可用于为 Objc 编程添加一些多继承的效果。就像下图那样,一个对象把消息转发出去,就好像它把另一个对象中的方法接过来或者“继承”过来一样。
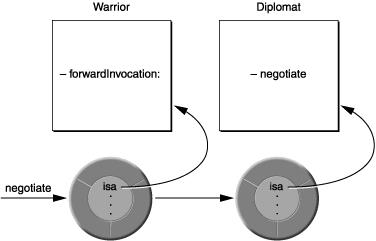
这使得在不同继承体系分支下的两个类可以实现“继承”对方的方法,在上图中 Warrior 和 Diplomat 没有继承关系,但是 Warrior 将 negotiate 消息转发给了 Diplomat 后,就好似 Diplomat 是 Warrior 的超类一样。
消息转发弥补了 Objc 不支持多继承的性质,也避免了因为多继承导致单个类变得臃肿复杂。
4、转发与继承
虽然转发可以实现继承的功能,但是 NSObject 还是必须表面上很严谨,像 respondsToSelector: 和 isKindOfClass: 这类方法只会考虑继承体系,不会考虑转发链。
如果上图中的 Warrior 对象被问到是否能响应 negotiate消息:
if ( [aWarrior respondsToSelector:@selector(negotiate)] )
...回答当然是 NO, 尽管它能接受 negotiate 消息而不报错,因为它靠转发消息给 Diplomat 类响应消息。
如果你就是想要让别人以为 Warrior 继承到了 Diplomat 的 negotiate 方法,你得重新实现 respondsToSelector: 和 isKindOfClass: 来加入你的转发算法:
- (BOOL)respondsToSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if ( [super respondsToSelector:aSelector] )
return YES;
else {
/* Here, test whether the aSelector message can *
* be forwarded to another object and whether that *
* object can respond to it. Return YES if it can. */
}
return NO;
}除了 respondsToSelector: 和 isKindOfClass: 之外,instancesRespondToSelector: 中也应该写一份转发算法。如果使用了协议,conformsToProtocol: 同样也要加入到这一行列中。
如果一个对象想要转发它接受的任何远程消息,它得给出一个方法标签来返回准确的方法描述 methodSignatureForSelector:,这个方法会最终响应被转发的消息。从而生成一个确定的 NSInvocation 对象描述消息和消息参数。这个方法最终响应被转发的消息。它需要像下面这样实现:
- (NSMethodSignature*)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)selector
{
NSMethodSignature* signature = [super methodSignatureForSelector:selector];
if (!signature) {
signature = [surrogate methodSignatureForSelector:selector];
}
return signature;
}
三、对象关联
对象关联允许开发者对已经存在的类在 Category 中添加自定义的属性:
|
1
|
OBJC_EXPORT void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy) __OSX_AVAILABLE_STARTING(__MAC_10_6, __IPHONE_3_1); |
·object 是源对象
·value 是被关联的对象
·key 是关联的键,objc_getAssociatedObject 方法通过不同的 key 即可取出对应的被关联对象
·policy 是一个枚举值,表示关联对象的行为,从命名就能看出各个枚举值的含义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
typedef OBJC_ENUM(uintptr_t, objc_AssociationPolicy) { OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN = 0, /**< Specifies a weak reference to the associated object. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC = 1, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object. * The association is not made atomically. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC = 3, /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied. * The association is not made atomically. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN = 01401, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object. * The association is made atomically. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY = 01403 /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied. * The association is made atomically. */}; |
要取出被关联的对象使用 objc_getAssociatedObject 方法即可,要删除一个被关联的对象,使用 objc_setAssociatedObject 方法将对应的 key 设置成 nil 即可:
|
1
|
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, associatedKey, nil, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); |
objc_removeAssociatedObjects 方法将会移除源对象中所有的关联对象.
举个栗子,假如我们要给 UIButton 添加一个监听单击事件的 block 属性,新建 UIButton 的 Category,其.m文件如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#import "UIButton+ClickBlock.h"#import static const void *associatedKey = "associatedKey";@implementation UIButton (ClickBlock)//Category中的属性,只会生成setter和getter方法,不会生成成员变量-(void)setClick:(clickBlock)click{ objc_setAssociatedObject(self, associatedKey, click, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); [self removeTarget:self action:@selector(buttonClick) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; if (click) { [self addTarget:self action:@selector(buttonClick) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; }}-(clickBlock)click{ return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, associatedKey);}-(void)buttonClick{ if (self.click) { self.click(); }}@end |
然后在代码中,就可以使用 UIButton 的属性来监听单击事件了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
UIButton *button = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeCustom];button.frame = self.view.bounds;[self.view addSubview:button];button.click = ^{ NSLog(@"buttonClicked");}; |
完整的对象关联代码点这里。
四、方法交换
Method imp = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(initWithCoder:));
Method myImp = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(myInitWithCoder:));
method_exchangeImplementations(imp, myImp);
举个UILabel字体适配plus屏的例子
#import "UILabel+AdjustSize.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#define isiPhone6P ([[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds].size.height == 736)
#define SizeScale (isiPhone6P?1.18:1)
@interface UILabel()
@property (nonatomic, strong) UIButton *but;
@end
@implementation UILabel (AdjustSize)
+ (void)load{
Method imp = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(initWithCoder:));
Method myImp = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(myInitWithCoder:));
method_exchangeImplementations(imp, myImp);
}
- (id)myInitWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecode{
[self myInitWithCoder:aDecode];
if (self) {
// 部分不想改变字体的 把tag值设置成555跳过
if (self.tag != 555) {
CGFloat fontSize = self.font.pointSize;
self.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:fontSize * SizeScale];
}
}
return self;
}
@end
以上是关于runtime的一些应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章