基础知识回顾:迭代器和生成器
Posted Ryana
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基础知识回顾:迭代器和生成器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
迭代器
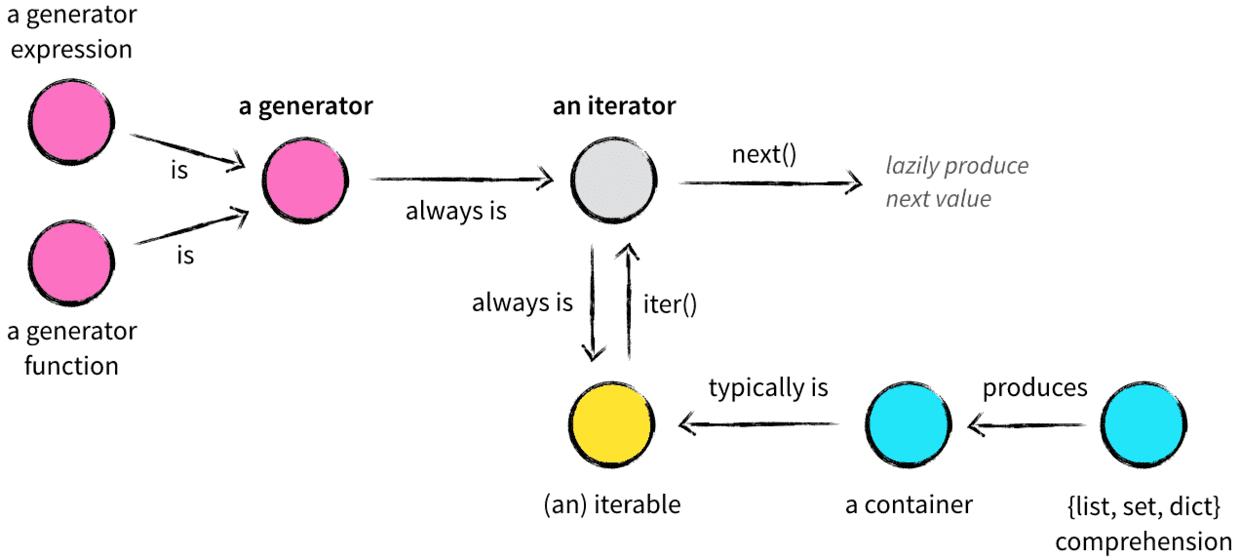
容器是用来储存元素的一种数据结构,将所有数据保存在内存中,在Python中典型的容器有:str,tuple,list,dict。大部分容器都是可迭代的,还有其他一些对象也可以迭代,例如文件对象及管道对象等。能被迭代的对象都称为可迭代对象(Iteratbles),可迭代对象除了被for循环调用,还有sum(),min(),max()等。迭代器对象是支持迭代器协议的对象,在Python中,支持迭代器协议就是能够实现对象的__iter__()和next()方法,其中__iter__()方法返回迭代器对象本身;next()方法返回迭代器对象的下一个元素,在结尾时引发StopIteration异常。
1.认识迭代器
1 >>> x = [1,2,3] 2 >>> y = iter(x) 3 >>> y 4 <listiterator object at 0x02FF39D0> 5 >>> next(y) 6 1 7 >>> next(y) 8 2 9 >>> next(y) 10 3 11 >>> next(y) 12 13 Traceback (most recent call last): 14 File "<pyshell#33>", line 1, in <module> 15 next(y) 16 StopIteration 17 >>> type(x) 18 <type \'list\'> 19 >>> type(y) 20 <type \'listiterator\'> 21 22 >>> list1 = [1,2,3] 23 >>> for i in range(len(list1)): 24 print list1[i] 25 26 27 1 28 2 29 3 30 >>> for i in list1: 31 print i 32 33 34 1 35 2 36 3 37 >>> (i for i in list1) #生成器表达式 38 <generator object <genexpr> at 0x030FEB70> 39 >>> [ i for i in list1] #列表倒推式 40 [1, 2, 3]
2.自定义迭代器
1 class MyRange(object): 2 def __init__(self, n): 3 self.idx = 0 4 self.n = n 5 6 def __iter__(self): 7 return self 8 9 def next(self): 10 if self.idx < self.n: 11 val = self.idx 12 self.idx += 1 13 return val 14 else: 15 raise StopIteration() 16 17 myRange = MyRange(3) 18 19 print myRange is iter(myRange) #说明myRange既是一个可迭代对象,也是一个迭代器对象(迭代器的实例对象),迭代器对象 = iter(可迭代对象) 20 print [i for i in myRange] 21 print [i for i in myRange]
运行结果:
True [0, 1, 2] []
像列表这种序列类型的对象,可迭代对象和迭代器对象是相互独立存在的,在迭代的过程中各个迭代器相互独立;但是,有的可迭代对象本身又是迭代器对象,那么迭代器就没法独立使用,改进后:
1 #可迭代对象 2 class MyRangeIterable: 3 def __init__(self, n): 4 self.n = n 5 6 def __iter__(self): 7 return MyRangeItertor(self.n) 8 9 #迭代器对象 10 class MyRangeItertor(object): 11 def __init__(self, n): 12 self.idx = 0 13 self.n = n 14 15 def __iter__(self): 16 return self 17 18 def next(self): 19 if self.idx < self.n: 20 val = self.idx 21 self.idx += 1 22 return val 23 else: 24 raise StopIteration() 25 26 myRange = MyRangeIterable(3) 27 print myRange is iter(myRange) #说明myRange只是一个可迭代对象 28 print [i for i in myRange] 29 print [i for i in myRange]
运行结果:
False [0, 1, 2] [0, 1, 2]
生成器
生成器其实就是一种特殊的迭代器。
语法上和函数类似:生成器函数和常规函数几乎是一样的。生成器使用yield语句返回一个值,而常规函数使用return语句返回一个值
自动实现迭代器协议:对于生成器可以调用它的iter和next方法,并且,在没有值可以返回的时候,生成器自动产StopIteration异常
状态挂起:生成器用yield语句返回一个值。yield语句挂起该生成器函数的状态,保留足够的信息,以便下次在它离开的地方继续执行。
在Python中有两种类型的生成器:生成器函数以及生成器表达式。生成器函数就是包含yield参数的函数。生成器表达式与列表倒推式类似。
1 #普通函数完成的求平方 2 >>> def gensquares(N): 3 res = [] 4 for i in range(N): 5 res.append(i*i) 6 return res 7 8 >>> for item in gensquares(5): 9 print item 10 11 0 1 4 9 16 12 13 #生成器函数 14 >>> def gensquares(N): 15 for i in range(N): 16 yield i ** 2 17 18 >>> for item in gensquares(5): 19 print item 20 21 0 1 4 9 16 22 23 #列表倒推式 24 >>> squares = [x**2 for x in range(5)] 25 >>> squares 26 [0, 1, 4, 9, 16] 27 28 #生成器表达式 29 >>> squares = (x**2 for x in range(5)) 30 >>> squares 31 <generator object at 0x00B2EC88> 32 >>> next(squares) 33 0 34 >>> next(squares) 35 1 36 >>> next(squares) 37 4 38 >>> list(squares) #生成器只能遍历一次,所以只能输出余下的值 39 [9, 16]
总结:
1.迭代对象自动调用迭代协议,迭代对象除了被for循环调用,还有sum(),min(),max()等
2.生成器是一种特殊迭代器,且只能遍历一次
3.使用生成器的好处除了延迟计算,每次只返回一个值,节省内存外,还代码简洁可读性好。
以上是关于基础知识回顾:迭代器和生成器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章