图像处理------ 一阶微分应用 (转载)
Posted 川师15级软工研=雁=
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图像处理------ 一阶微分应用 (转载)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/jia20003/article/details/7562092
图像处理之一阶微分应用
一:数学背景
首先看一下一维的微分公式Δf = f(x+1) – f(x), 对于一幅二维的数字图像f(x,y)而言,需要完
成XY两个方向上的微分,所以有如下的公式:
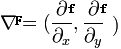
分别对X,Y两个方向上求出它们的偏微分,最终得到梯度Delta F.
对于离散的图像来说,一阶微分的数学表达相当于两个相邻像素的差值,根据选择的梯度算
子不同,效果可能有所不同,但是基本原理不会变化。最常见的算子为Roberts算子,其它
常见还有Sobel,Prewitt等算子。以Roberts算子为例的X,Y的梯度计算演示如下图:

二:图像微分应用
图像微分(梯度计算)是图像边缘提取的重要的中间步骤,根据X,Y方向的梯度向量值,可以
得到如下两个重要参数振幅magnitude, 角度theta,计算公式如下:
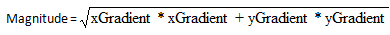
Theta = tan-1(yGradient/xGradient)
magnitude表示边缘强度信息
theta预言边缘的方向走势。
假如对一幅数字图像,求出magnitude之后与原来每个像素点对应值相加,则图像边缘将被
大大加强,轮廓更加明显,是一个很典型的sharp filter的效果。
三:程序效果
X, Y梯度效果,及magnitude效果
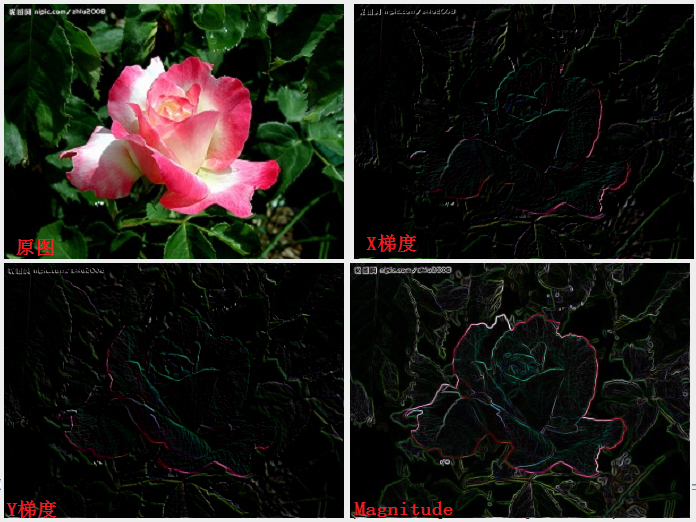

图像微分的Sharp效果:

四:程序源代码
- package com.process.blur.study;
- import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
- // roberts operator
- // X direction 1, 0
- // 0,-1
- // Y direction 0, 1
- // -1, 0
- public class ImageGradientFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
- public final static int X_DIRECTION = 0;
- public final static int Y_DIRECTION = 2;
- public final static int XY_DIRECTION = 4;
- private boolean sharp;
- private int direction;
- public ImageGradientFilter() {
- direction = XY_DIRECTION; // default;
- sharp = false;
- }
- public boolean isSharp() {
- return sharp;
- }
- public void setSharp(boolean sharp) {
- this.sharp = sharp;
- }
- public int getDirection() {
- return direction;
- }
- public void setDirection(int direction) {
- this.direction = direction;
- }
- @Override
- public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
- int width = src.getWidth();
- int height = src.getHeight();
- if (dest == null )
- dest = createCompatibleDestImage( src, null );
- int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];
- int[] outPixels = new int[width*height];
- getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );
- int index = 0;
- double mred, mgreen, mblue;
- int newX, newY;
- int index1, index2, index3;
- for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {
- int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
- for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {
- index = row * width + col;
- // base on roberts operator
- newX = col + 1;
- newY = row + 1;
- if(newX > 0 && newX < width) {
- newX = col + 1;
- } else {
- newX = 0;
- }
- if(newY > 0 && newY < height) {
- newY = row + 1;
- } else {
- newY = 0;
- }
- index1 = newY * width + newX;
- index2 = row * width + newX;
- index3 = newY * width + col;
- ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;
- tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
- tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
- tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
- int ta1 = (inPixels[index1] >> 24) & 0xff;
- int tr1 = (inPixels[index1] >> 16) & 0xff;
- int tg1 = (inPixels[index1] >> 8) & 0xff;
- int tb1 = inPixels[index1] & 0xff;
- int xgred = tr -tr1;
- int xggreen = tg - tg1;
- int xgblue = tb - tb1;
- int ta2 = (inPixels[index2] >> 24) & 0xff;
- int tr2 = (inPixels[index2] >> 16) & 0xff;
- int tg2 = (inPixels[index2] >> 8) & 0xff;
- int tb2 = inPixels[index2] & 0xff;
- int ta3 = (inPixels[index3] >> 24) & 0xff;
- int tr3 = (inPixels[index3] >> 16) & 0xff;
- int tg3 = (inPixels[index3] >> 8) & 0xff;
- int tb3 = inPixels[index3] & 0xff;
- int ygred = tr2 - tr3;
- int yggreen = tg2 - tg3;
- int ygblue = tb2 - tb3;
- mred = Math.sqrt(xgred * xgred + ygred * ygred);
- mgreen = Math.sqrt(xggreen * xggreen + yggreen * yggreen);
- mblue = Math.sqrt(xgblue * xgblue + ygblue * ygblue);
- if(sharp) {
- tr = (int)(tr + mred);
- tg = (int)(tg + mgreen);
- tb = (int)(tb + mblue);
- outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp(tr) << 16) | (clamp(tg) << 8) | clamp(tb);
- } else {
- outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp((int)mred) << 16) | (clamp((int)mgreen) << 8) | clamp((int)mblue);
- // outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp((int)ygred) << 16) | (clamp((int)yggreen) << 8) | clamp((int)ygblue);
- // outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (clamp((int)xgred) << 16) | (clamp((int)xggreen) << 8) | clamp((int)xgblue);
- }
- }
- }
- setRGB(dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels );
- return dest;
- }
- public static int clamp(int c) {
- if (c < 0)
- return 0;
- if (c > 255)
- return 255;
- return c;
- }
- }
以上是关于图像处理------ 一阶微分应用 (转载)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章