运维开发入门记录
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了运维开发入门记录相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本人初级运维,
一次偶然事情了 ,有人让我批量捞取灰常多台 机器的配置信息
我想了想 问: shell脚本可以吗
leader: MD好意思给我用shell
=.=:那你要怎么弄
leader :怎么弄你的事
然后 我就谷歌度娘,嗯 所有机器有salt 那就想想怎么搞吧
后来 找了小半下午,python+salt 就可以搞定。
不多废话 直接开搞:
思路如下 ,直接画图:
架构草图
下来这个是基本拓扑:
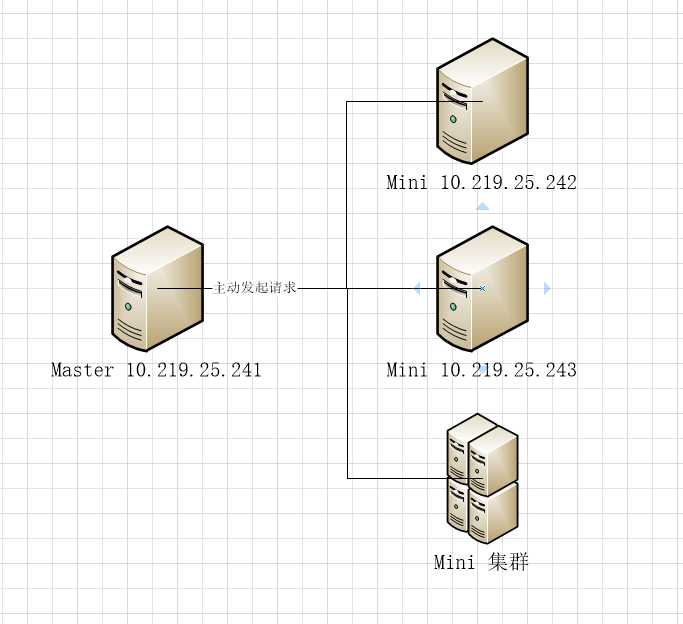
这是一个 用python实现 调用salt的实例,具体思路是这样的
salt 我们介绍一下吧,简单点的,好了我们来看这玩意干嘛的
SALTSTACK
Salt, a new approach to infrastructure management, is easy enough to get running in minutes, scalable enough to manage tens of thousands of servers, and fast enough to communicate with those servers in seconds.
Salt delivers a dynamic communication bus for infrastructures that can be used for orchestration, remote execution, configuration management and much more.
大概意思是
salt一种新的基础设施管理的方法,是很容易得到运行在几分钟内,可扩展到管理成千上万的服务器,并快速足够的沟通与这些服务器在几秒钟。
salt提供了一个动态的通信总线的基础设施,可用于业务流程,远程执行,配置管理和更多......。
那我们先来安装salt
安装很简单 ,楼主是virtualBOX建立两个虚拟机装有linux centos6.5 ,装master 和mini 就是主控制机器 和被控制机器,对没错是被控制哦,SM 嘻嘻嘻嘻~我们想干嘛干嘛的那种 滴蜡 小皮鞭什么的。
虚拟机两台,saltmaster 10.219.25.241
minion 10.219.25.242
下面是安装脚本
master:
#!/usr/bin/bash cd /usr/local/src/; wget http://mirrors.sohu.com/fedora-epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm; rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm; wget http://apt.sw.be/redhat/el6/en/x86_64/rpmforge/RPMS/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm; rpm -ivh rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm; yum install python-jinja2; yum -y install salt-master enablerepr=epel-testing;
minion:
#!/usr/bin/bash cd /usr/local/src/; wget http://mirrors.sohu.com/fedora-epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm; rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm; wget http://apt.sw.be/redhat/el6/en/x86_64/rpmforge/RPMS/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm; rpm -ivh rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm; yum install python-jinja2; yum -y install salt-minion enablerepr=epel-testing;
装完改配置,*注意空格:
Master
vim /etc/salt/master # The address of the interface to bind to: interface: 10.219.25.241
mini
vim /etc/salt/minion # resolved, then the minion will fail to start. master: 10.219.25.241
关闭两台机器防火墙
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
启动两台机器的salt服务
master:
/etc/init.d/salt-master start
mini:
/etc/init.d/salt-minion start
先发证书:
[[email protected] ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: salt-master //这里是娶回家的 slave01 slave02 Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: //这里是小情人 要接进来的 Rejected Keys:
接受证书:
[[email protected] ~]# salt-key -A 点Y 回车
测试下可以调教了不,先来么么哒:
[[email protected] ~]# salt \\* test.ping slave02: True slave01: True
OK没问题
接下来是重头戏
salt 是python写的 提供了api调用
我们装上salt api
比较简单
*这里只需要在master端安装:
yum -y install salt-api
进入python 注意 这里python是2.6.6的:[centos6.5 redhat6.5 默认安装2.6.6python ubuntu 为python2.7]
做个简单的测试,执行cmd.run没有问题,返回结果是dict字典
>>> import salt.client
>>> local = salt.client.LocalClient()
>>> local.cmd(‘*‘,‘cmd.run‘,[‘whoami‘])
{‘slave01‘: ‘root‘}
我们获取静态信息试试:
>>> local.cmd(‘*‘,‘grains.items‘,) {‘slave01‘: {‘biosversion‘: ‘VirtualBox‘, ‘kernel‘: ‘Linux‘, ‘domain‘: ‘‘, ‘zmqversion‘: ‘3.2.5‘, ‘kernelrelease‘: ‘2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64‘, ‘selinux‘: {‘enforced‘: ‘Enforcing‘, ‘enabled‘: True}, ‘serialnumber‘: ‘0‘, ‘ip_interfaces‘: {‘lo‘: [‘127.0.0.1‘, ‘::1‘], ‘eth1‘: [‘10.219.25.242‘, ‘fe80::a00:27ff:fe8b:263e‘]}, ‘shell‘: ‘/bin/bash‘, ‘mem_total‘: 996, ‘saltversioninfo‘: [2015, 5, 8, 0], ‘host‘: ‘slave01‘, ‘SSDs‘: [], ‘mdadm‘: [], ‘id‘: ‘slave01‘, ‘osrelease‘: ‘6.5‘, ‘ps‘: ‘ps -efH‘, ‘server_id‘: 1039472111, ‘ip6_interfaces‘: {‘lo‘: [‘::1‘], ‘eth1‘: [‘fe80::a00:27ff:fe8b:263e‘]}, ‘num_cpus‘: 1, ‘hwaddr_interfaces‘: {‘lo‘: ‘00:00:00:00:00:00‘, ‘eth1‘: ‘08:00:27:8b:26:3e‘}, ‘init‘: ‘upstart‘, ‘ip4_interfaces‘: {‘lo‘: [‘127.0.0.1‘], ‘eth1‘: [‘10.219.25.242‘]}, ‘osfullname‘: ‘CentOS‘, ‘master‘: ‘10.219.25.241‘, ‘ipv4‘: [‘10.219.25.242‘, ‘127.0.0.1‘], ‘ipv6‘: [‘::1‘, ‘fe80::a00:27ff:fe8b:263e‘], ‘cpu_flags‘: [‘fpu‘, ‘vme‘, ‘de‘, ‘pse‘, ‘tsc‘, ‘msr‘, ‘pae‘, ‘mce‘, ‘cx8‘, ‘apic‘, ‘sep‘, ‘mtrr‘, ‘pge‘, ‘mca‘, ‘cmov‘, ‘pat‘, ‘pse36‘, ‘clflush‘, ‘mmx‘, ‘fxsr‘, ‘sse‘, ‘sse2‘, ‘syscall‘, ‘nx‘, ‘rdtscp‘, ‘lm‘, ‘constant_tsc‘, ‘up‘, ‘rep_good‘, ‘xtopology‘, ‘nonstop_tsc‘, ‘unfair_spinlock‘, ‘pni‘, ‘pclmulqdq‘, ‘monitor‘, ‘ssse3‘, ‘cx16‘, ‘sse4_1‘, ‘sse4_2‘, ‘movbe‘, ‘popcnt‘, ‘aes‘, ‘xsave‘, ‘avx‘, ‘rdrand‘, ‘hypervisor‘, ‘lahf_lm‘, ‘abm‘], ‘localhost‘: ‘slave01‘, ‘lsb_distrib_id‘: ‘CentOS‘, ‘fqdn_ip4‘: [], ‘fqdn_ip6‘: [], ‘nodename‘: ‘slave01‘, ‘saltversion‘: ‘2015.5.8‘, ‘lsb_distrib_release‘: ‘6.5‘, ‘pythonpath‘: [‘/usr/bin‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python26.zip‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python2.6‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python2.6/plat-linux2‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python2.6/lib-tk‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python2.6/lib-old‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python2.6/lib-dynload‘, ‘/usr/lib64/python2.6/site-packages‘, ‘/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages‘, ‘/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/setuptools-0.6c11-py2.6.egg-info‘], ‘saltpath‘: ‘/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/salt‘, ‘pythonversion‘: [2, 6, 6, ‘final‘, 0], ‘osmajorrelease‘: ‘6‘, ‘os_family‘: ‘RedHat‘, ‘oscodename‘: ‘Final‘, ‘osfinger‘: ‘CentOS-6‘, ‘biosreleasedate‘: ‘12/01/2006‘, ‘manufacturer‘: ‘innotek GmbH‘, ‘num_gpus‘: 1, ‘virtual‘: ‘VirtualBox‘, ‘cpu_model‘: ‘Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4200H CPU @ 2.80GHz‘, ‘fqdn‘: ‘slave01‘, ‘pythonexecutable‘: ‘/usr/bin/python2.6‘, ‘productname‘: ‘VirtualBox‘, ‘osarch‘: ‘x86_64‘, ‘cpuarch‘: ‘x86_64‘, ‘lsb_distrib_codename‘: ‘Final‘, ‘osrelease_info‘: [6, 5], ‘locale_info‘: {‘detectedencoding‘: ‘UTF-8‘, ‘defaultlanguage‘: ‘en_US‘, ‘defaultencoding‘: ‘UTF8‘}, ‘gpus‘: [{‘model‘: ‘VirtualBox Graphics Adapter‘, ‘vendor‘: ‘unknown‘}], ‘path‘: ‘/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin‘, ‘machine_id‘: ‘c208c39c323edb1ac57c14a50000000b‘, ‘os‘: ‘CentOS‘}}
返回字典python操作方法
radiansdict.values() 以列表返回字典中的所有值 radiansdict.keys() 以列表返回一个字典所有的键
这是百度到别人处理这类字符串 整合为表格的代码对我启发很大:
#coding=utf-8 import salt.client as sc import json ###salt调用 local = sc.LocalClient() ###目标主机指定 tgt = "*" ###获取grains,disk信息 grains = local.cmd(tgt,"grains.items") diskusage = local.cmd(tgt,"disk.usage") ###主要应用列表即文件开头 app_name = ["tomcat","zookeeper","redis","mysql","nginx"] cols = "主机名,IP地址,内存(GB),CPU核数,操作系统,数据盘/data(GB),所属项目,主要应用" ###打开一个.csv文件,以便写入 ret_file = open("ret.csv","w") ###首先写入开头,有点字段名的意思 ret_file.write(cols + "\\n") try: for i in grains.keys(): ###打印信息可注释掉 print grains[i]["nodename"] print "ipv4" + ":" ,grains[i]["ipv4"] print "mem_total" + ":" , grains[i]["mem_total"] / 1024 + 1 print "num_cpus" + ":" , grains[i]["num_cpus"] print "osfullname" + ":" , grains[i]["osfullname"] print "release" + ":" , grains[i]["lsb_distrib_release"] ###可能一些主机没有/data数据盘1048576是1024x1024 if "/data" not in diskusage[i]: print "diskusage" + ":" + "have no /data disk" else: data_vol = int(diskusage[i]["/data"]["1K-blocks"]) print "diskusage" + ":" , data_vol / 1048576 ###去掉127.0.0.1这个地址 ipv4 = str(grains[i]["ipv4"]).replace(", ‘127.0.0.1‘","") ###因为一些历史遗留问题,这里取得不是主机名,而是salt-minion的id名,用以判断主要应用 hostname = grains[i]["id"] ipv4 = str(grains[i]["ipv4"]).replace(", ‘127.0.0.1‘","") ipv4 = ipv4.replace(",","and") mem = grains[i]["mem_total"] / 1024 + 1 num_cpu = grains[i]["num_cpus"] OS = grains[i]["osfullname"] + grains[i]["lsb_distrib_release"] if "/data" not in diskusage[i]: disk_data = "None" else: disk_data = data_vol / 1048576 ###项目名为空 project = "" ###通过minion ID名来判断主要运行服务,比如xx-mysql-1,则运行mysql for j in app_name: if j in hostname.lower(): app = j break else: app = "undefined" c = "," ###连接并写入 line = hostname + c + ipv4 + c + str(mem) + c + str(num_cpu) + c + str(OS) + c + str(disk_data) + c + project + c + app ret_file.write(line + "\\n") except Exception,e: print "Exception:\\n",e finally: ret_file.close()
不过若要根据自己需求来做cmdb我们的路还要往前走
以上是关于运维开发入门记录的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
基础入门_Python-模块和包.运维开发中日志模块logging的最佳实践?
基础入门_Python-模块和包.运维开发中watchdog事件监视的最佳实践?
错误记录Flutter 混合开发获取 BinaryMessenger 报错 ( FlutterActivityAndFragmentDelegate.getFlutterEngine() )(代码片段