tty初探—uart驱动框架分析uart_add_one_port
Posted Linux学习之路
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了tty初探—uart驱动框架分析uart_add_one_port相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在前面的一篇文章中,我们分析了一个 uart_driver 的向上注册过程,主要是 tty 的一些东西,知道了 tty 注册了一个字符设备驱动,我们在用户空间 open 时将调用到 uart_port.ops.startup ,在用户空间 write 则调用 uart_port.ops.start_tx ,还知道了如何 read 数据等等。但是,这些都是内核帮我们实现好的,在真正的驱动开发过程中几乎不涉及那些代码的修改移植工作,真正需要我们触碰的是 uart_port 这个结构体,它真正的对应于一个物理的串口。
其实,真正需要我们做的工作就是 分配一个 uart_port 结构,然后 uart_add_one_port 。分析过 s3c2440 uart 的驱动代码之后,我发现,这么一个简单的目标简直就是经历了山路十八弯。
先说一下大体的思路,uart_port 的注册过程是基于 platform 平台设备驱动模型,device 侧提供 3 个串口的硬件信息,并注册到 platform_bus_type 中去。然后 driver 也注册到 platform_bus_type 时,就会根据名字进行匹配,从而调用 driver->probe 函数,在 probe 函数里进行 uart_add_one_port 。思路也是很简单的,复杂在 s3c2440 注册 device 之前的工作扯了太多东西。
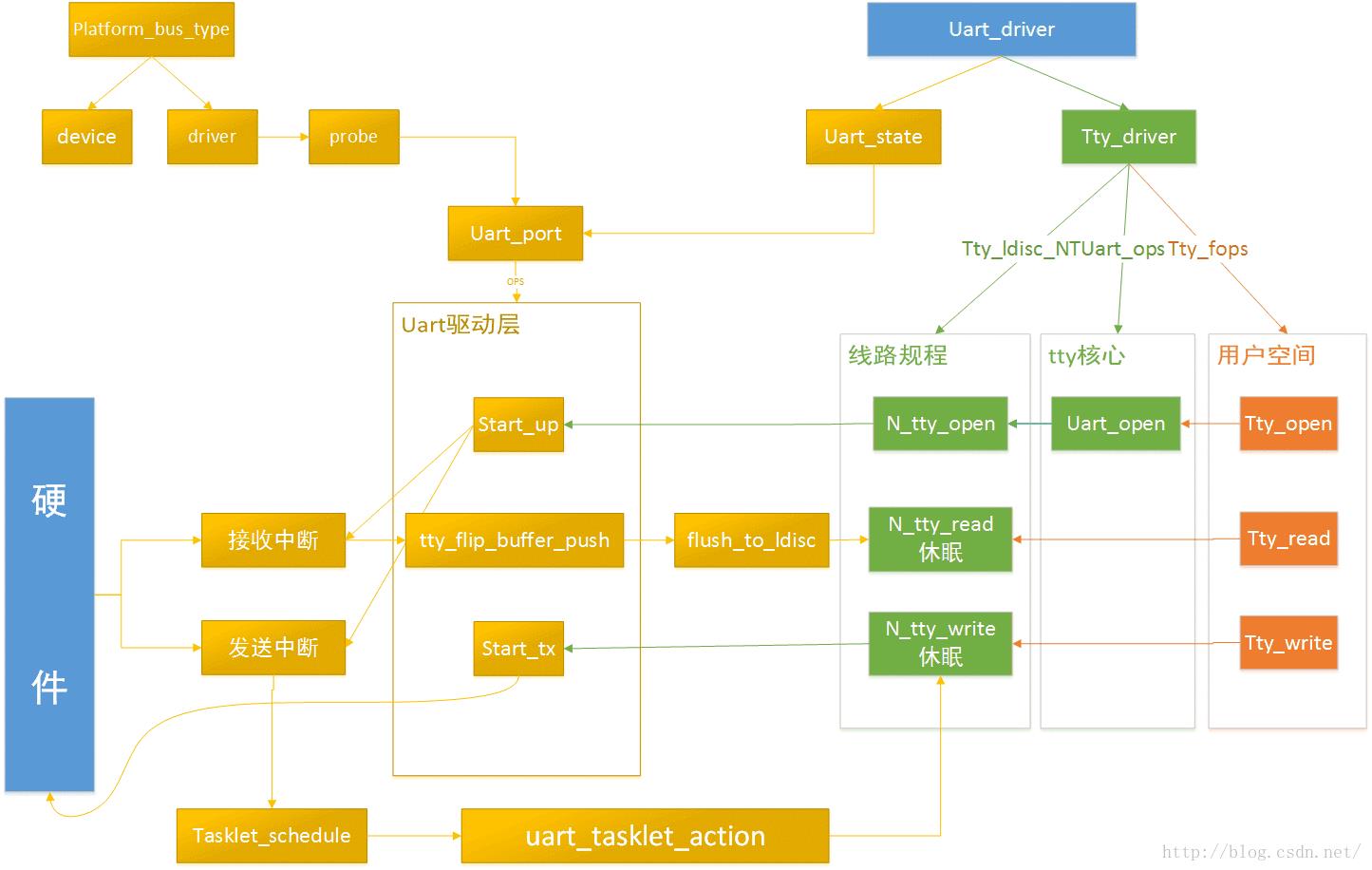
先秀个最终分析的图:
一、Linux 启动过程回忆
在 uboot 启动内核的时候,内核刚刚启动我们就看到串口各种信息就输出来了,也就是说串口驱动的初始化工作是在 Linux 启动过程中一个比较靠前的位置。内核启动的时候首先会去判断 cpu id 是否支持,接着判断是否支持uboot 传递进来的单板 Id ,然后 start_kernel -》setup_arch 进行一系列的初始化工作,其中必然包含串口相关初始化。
内核中所有支持的单板都用 MACHINE_START 和 MACHINE_END 来定义
MACHINE_START(MINI2440, "FriendlyARM Mini2440 development board")
.phys_io = S3C2410_PA_UART,
.io_pg_offst = (((u32)S3C24XX_VA_UART) >> 18) & 0xfffc,
.boot_params = S3C2410_SDRAM_PA + 0x100,
.init_irq = s3c24xx_init_irq,
.map_io = mini2440_map_io,
.init_machine = mini2440_machine_init,
.timer = &s3c24xx_timer,
MACHINE_END请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/lizuobin2/article/details/51779064
如果你自己分析一遍的话,调用先后顺序应该是这样的:
start_kernel -》setup_arch -》 map_io -》 init_irq -》 timer -》 init_machine -》 s3c_arch_init -》 s3c24xx_serial_modinit -》s3c2440_serial_init
后面三个函数是通过类似于 module_init 等被组织进内核里去的放在一个特殊的段里,内核启动到一定时候就去把这个段里的每一个函数取出来去调用,也是与串口相关的,分析过程就不再赘述了。
二、platform device 的注册之路
分析出了整个的串口驱动的初始化、设置、注册流程,问题就简单多了,挨个函数分析便是。
static void __init mini2440_map_io(void)
{
s3c24xx_init_io(mini2440_iodesc, ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_iodesc));
s3c24xx_init_clocks(12000000);
s3c24xx_init_uarts(mini2440_uartcfgs, ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_uartcfgs));
}void __init s3c24xx_init_io(struct map_desc *mach_desc, int size)
{
....
s3c_init_cpu(idcode, cpu_ids, ARRAY_SIZE(cpu_ids));
}static struct cpu_table *cpu;
void __init s3c_init_cpu(unsigned long idcode,
struct cpu_table *cputab, unsigned int cputab_size)
{
cpu = s3c_lookup_cpu(idcode, cputab, cputab_size);
cpu->map_io();
}
static struct cpu_table * __init s3c_lookup_cpu(unsigned long idcode,
struct cpu_table *tab,
unsigned int count)
{
for (; count != 0; count--, tab++) {
if ((idcode & tab->idmask) == tab->idcode)
return tab;
}
return NULL;
}static struct cpu_table cpu_ids[] __initdata = {
{
.idcode = 0x32440000,
.idmask = 0xffffffff,
.map_io = s3c244x_map_io,
.init_clocks = s3c244x_init_clocks,
.init_uarts = s3c244x_init_uarts,
.init = s3c2440_init,
.name = name_s3c2440
},
};void __init s3c244x_map_io(void)
{
/* register our io-tables */
iotable_init(s3c244x_iodesc, ARRAY_SIZE(s3c244x_iodesc));
/* rename any peripherals used differing from the s3c2410 */
s3c_device_sdi.name = "s3c2440-sdi";
s3c_device_i2c0.name = "s3c2440-i2c";
s3c_device_nand.name = "s3c2440-nand";
s3c_device_usbgadget.name = "s3c2440-usbgadget";
}void __init s3c24xx_init_uarts(struct s3c2410_uartcfg *cfg, int no)
{
(cpu->init_uarts)(cfg, no);
}void __init s3c244x_init_uarts(struct s3c2410_uartcfg *cfg, int no)
{
s3c24xx_init_uartdevs("s3c2440-uart", s3c2410_uart_resources, cfg, no);
}s3c24xx_init_uarts(mini2440_uartcfgs, ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_uartcfgs));</span>static struct s3c2410_uartcfg mini2440_uartcfgs[] __initdata = {
[0] = {
.hwport = 0,
.flags = 0,
.ucon = 0x3c5,
.ulcon = 0x03,
.ufcon = 0x51,
},
/* 此处略去了 1、2 两个串口的信息 */
};
struct s3c24xx_uart_resources s3c2410_uart_resources[] __initdata = {
[0] = {
.resources = s3c2410_uart0_resource,
.nr_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(s3c2410_uart0_resource),
},
/* 此处略去了 1、2 串口的信息 */
};static struct resource s3c2410_uart0_resource[] = {
[0] = {
.start = S3C2410_PA_UART0,
.end = S3C2410_PA_UART0 + 0x3fff,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = IRQ_S3CUART_RX0,
.end = IRQ_S3CUART_ERR0,
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
}
};
struct platform_device *s3c24xx_uart_src[4] = {
&s3c24xx_uart_device0,
&s3c24xx_uart_device1,
&s3c24xx_uart_device2,
&s3c24xx_uart_device3,
};
static struct s3c2410_uartcfg uart_cfgs[CONFIG_SERIAL_SAMSUNG_UARTS];
/* 填充平台设备的过程,未注册 */
void __init s3c24xx_init_uartdevs(char *name, struct s3c24xx_uart_resources *res,
struct s3c2410_uartcfg *cfg, int no)
{
struct platform_device *platdev;
struct s3c2410_uartcfg *cfgptr = uart_cfgs;
struct s3c24xx_uart_resources *resp;
int uart;
/* 将 mini2440_uartcfgs 数组里的参数拷贝到 cfgptr */
memcpy(cfgptr, cfg, sizeof(struct s3c2410_uartcfg) * no);
for (uart = 0; uart < no; uart++, cfg++, cfgptr++) {
/* 从 s3c24xx_uart_src 数组里取出平台设备 */
platdev = s3c24xx_uart_src[cfgptr->hwport];
/* 获得对应的 resource ,物理寄存器和中断 */
resp = res + cfgptr->hwport;
/* 将 s3c24xx_uart_src 的平台设备 放到 平台设备数组 s3c24xx_uart_devs */
s3c24xx_uart_devs[uart] = platdev;
/* 设置名字 资源 */
platdev->name = name;
platdev->resource = resp->resources;
platdev->num_resources = resp->nr_resources;
/* 设置平台数据 mini2440_uartcfgs 数组里的东西 */
platdev->dev.platform_data = cfgptr;
}
nr_uarts = no;
}1、3 个串口的 device 存放在 s3c24xx_uart_devs 数组里,后边肯定会从数组里取出来注册。
2、3 个串口的 device 的名字都是 “s3c2440-uart”。
3、3 个串口的 device 资源文件里存放好了 io 物理地址,Irq 等信息。
4、3 个串口的 device 资源数据。
移植过程中可能需要修改的文件:mini2440_uartcfgs 、s3c2410_uart0_resource 、s3c24xx_uart_src 还有那个晶振频率。
s3c_arch_init 函数中,将 device 注册到 platform_bus_type
static int __init s3c_arch_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = platform_add_devices(s3c24xx_uart_devs, nr_uarts);
return ret;
}三、uart_driver 的注册
注意,是 uart_driver 的注册,是上一篇文章讲的过程,并不是对应于平台设备的平台驱动。为什么在这个时候注册 uart_driver,因为如果先注册平台设备的 driver 的话,那么在probe函数里 uart_add_one_port ,uart_prot 没地方注册!!因此,要先注册 uart_driver ,简单贴下代码,不在分析。
static struct uart_driver s3c24xx_uart_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.dev_name = "s3c2410_serial",
.nr = CONFIG_SERIAL_SAMSUNG_UARTS,
.cons = S3C24XX_SERIAL_CONSOLE,
.driver_name = S3C24XX_SERIAL_NAME,
.major = S3C24XX_SERIAL_MAJOR,
.minor = S3C24XX_SERIAL_MINOR,
};
static int __init s3c24xx_serial_modinit(void)
{
int ret;
ret = uart_register_driver(&s3c24xx_uart_drv);
if (ret < 0) {
printk(KERN_ERR "failed to register UART driver\\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}四、platform driver 的注册以及 probe 函数
static int s3c2440_serial_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
dbg("s3c2440_serial_probe: dev=%p\\n", dev);
return s3c24xx_serial_probe(dev, &s3c2440_uart_inf);
}
static struct platform_driver s3c2440_serial_driver = {
.probe = s3c2440_serial_probe,
.remove = __devexit_p(s3c24xx_serial_remove),
.driver = {
.name = "s3c2440-uart",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
s3c24xx_console_init(&s3c2440_serial_driver, &s3c2440_uart_inf);
static int __init s3c2440_serial_init(void)
{
return s3c24xx_serial_init(&s3c2440_serial_driver, &s3c2440_uart_inf);
}
static struct s3c24xx_uart_port s3c24xx_serial_ports[CONFIG_SERIAL_SAMSUNG_UARTS] = {
[0] = {
.port = {
.lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(s3c24xx_serial_ports[0].port.lock),
.iotype = UPIO_MEM,
.irq = IRQ_S3CUART_RX0,
.uartclk = 0,
.fifosize = 16,
.ops = &s3c24xx_serial_ops,/* 底层的操作函数 */
.flags = UPF_BOOT_AUTOCONF,
.line = 0,
}
},
/* 此处略去了两个串口的信息 */
};int s3c24xx_serial_probe(struct platform_device *dev,
struct s3c24xx_uart_info *info)
{
struct s3c24xx_uart_port *ourport;
int ret;
/* 取出 uart_port */
ourport = &s3c24xx_serial_ports[probe_index];
probe_index++;
/* 对 uart_port 进一步设置 */
ret = s3c24xx_serial_init_port(ourport, info, dev);
/* 将 uart_port 注册到 uart_driver */
uart_add_one_port(&s3c24xx_uart_drv, &ourport->port);
platform_set_drvdata(dev, &ourport->port);
ret = device_create_file(&dev->dev, &dev_attr_clock_source);
ret = s3c24xx_serial_cpufreq_register(ourport);
return 0;
}static int s3c24xx_serial_init_port(struct s3c24xx_uart_port *ourport,
struct s3c24xx_uart_info *info,
struct platform_device *platdev)
{
struct uart_port *port = &ourport->port;
struct s3c2410_uartcfg *cfg;
struct resource *res;
int ret;
cfg = s3c24xx_dev_to_cfg(&platdev->dev);
/* setup info for port */
port->dev = &platdev->dev;
ourport->info = info;
/* copy the info in from provided structure */
ourport->port.fifosize = info->fifosize;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/* 设置时钟 */
port->uartclk = 1;
/* sort our the physical and virtual addresses for each UART */
res = platform_get_resource(platdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/* 设置物理地址,虚拟地址 */
port->mapbase = res->start;
port->membase = S3C_VA_UART + res->start - (S3C_PA_UART & 0xfff00000);
ret = platform_get_irq(platdev, 0);
if (ret < 0)
port->irq = 0;
else {
port->irq = ret;/* 设置中断号 */
ourport->rx_irq = ret;
ourport->tx_irq = ret + 1;
}
ret = platform_get_irq(platdev, 1);
ourport->clk = clk_get(&platdev->dev, "uart");
/* reset the fifos (and setup the uart) */
s3c24xx_serial_resetport(port, cfg);
return 0;
}int uart_add_one_port(struct uart_driver *drv, struct uart_port *uport)
{
struct uart_state *state;
struct tty_port *port;
int ret = 0;
struct device *tty_dev;
BUG_ON(in_interrupt());
if (uport->line >= drv->nr)
return -EINVAL;
state = drv->state + uport->line;
port = &state->port;
mutex_lock(&port_mutex);
mutex_lock(&port->mutex);
if (state->uart_port) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/* 将 uart_prot 绑定到 uart_driver 对应的 state */
state->uart_port = uport;
state->pm_state = -1;
uport->cons = drv->cons;
uport->state = state;
/*
* If this port is a console, then the spinlock is already
* initialised.
*/
if (!(uart_console(uport) && (uport->cons->flags & CON_ENABLED))) {
spin_lock_init(&uport->lock);
lockdep_set_class(&uport->lock, &port_lock_key);
}
/* 实际调用 port->ops->config_port(port, flags) 稍后再看 */
uart_configure_port(drv, state, uport);
/*
* 上一篇文章中,我们提到tty注册了一个字符设备 “ttySAC ”
* 那么,我们平时看到的 “ttySAC0”“ttySAC1”等就是在这里注册的
*/
tty_dev = tty_register_device(drv->tty_driver, uport->line, uport->dev);
if (likely(!IS_ERR(tty_dev))) {
device_init_wakeup(tty_dev, 1);
device_set_wakeup_enable(tty_dev, 0);
} else
printk(KERN_ERR "Cannot register tty device on line %d\\n",
uport->line);
/*
* Ensure UPF_DEAD is not set.
*/
uport->flags &= ~UPF_DEAD;
out:
mutex_unlock(&port->mutex);
mutex_unlock(&port_mutex);
return ret;
}
struct device *tty_register_device(struct tty_driver *driver, unsigned index,
struct device *device)
{
char name[64];
dev_t dev = MKDEV(driver->major, driver->minor_start) + index;
if (index >= driver->num) {
printk(KERN_ERR "Attempt to register invalid tty line number "
" (%d).\\n", index);
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
if (driver->type == TTY_DRIVER_TYPE_PTY)
pty_line_name(driver, index, name);
else
tty_line_name(driver, index, name);
return device_create(tty_class, device, dev, NULL, name);
}<span style="font-family:SimSun;font-size:18px;">static void tty_line_name(struct tty_driver *driver, int index, char *p)
{
sprintf(p, "%s%d", driver->name, index + driver->name_base);
}分析到这里,完了么?没有,还有一个非常重要的东西没有分析呢,那就是底层的操作函数。
static struct uart_ops s3c24xx_serial_ops = {
.pm = s3c24xx_serial_pm,
.tx_empty = s3c24xx_serial_tx_empty,
.get_mctrl = s3c24xx_serial_get_mctrl,
.set_mctrl = s3c24xx_serial_set_mctrl,
.stop_tx = s3c24xx_serial_stop_tx,
.start_tx = s3c24xx_serial_start_tx,
.stop_rx = s3c24xx_serial_stop_rx,
.enable_ms = s3c24xx_serial_enable_ms,
.break_ctl = s3c24xx_serial_break_ctl,
.startup = s3c24xx_serial_startup,
.shutdown = s3c24xx_serial_shutdown,
.set_termios = s3c24xx_serial_set_termios,
.type = s3c24xx_serial_type,
.release_port = s3c24xx_serial_release_port,
.request_port = s3c24xx_serial_request_port,
.config_port = s3c24xx_serial_config_port,
.verify_port = s3c24xx_serial_verify_port,
};
static int s3c24xx_serial_startup(struct uart_port *port)
{
struct s3c24xx_uart_port *ourport = to_ourport(port);
int ret;
dbg("s3c24xx_serial_startup: port=%p (%08lx,%p)\\n",
port->mapbase, port->membase);
rx_enabled(port) = 1;
ret = request_irq(ourport->rx_irq, s3c24xx_serial_rx_chars, 0,
s3c24xx_serial_portname(port), ourport);
if (ret != 0) {
printk(KERN_ERR "cannot get irq %d\\n", ourport->rx_irq);
return ret;
}
ourport->rx_claimed = 1;
dbg("requesting tx irq...\\n");
tx_enabled(port) = 1;
ret = request_irq(ourport->tx_irq, s3c24xx_serial_tx_chars, 0,
s3c24xx_serial_portname(port), ourport);
if (ret) {
printk(KERN_ERR "cannot get irq %d\\n", ourport->tx_irq);
goto err;
}
ourport->tx_claimed = 1;
dbg("s3c24xx_serial_startup ok\\n");
/* the port reset code should have done the correct
* register setup for the port controls */
if (port->line == 2) {
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(S3C2410_GPH(6), S3C2410_GPH6_TXD2);
s3c2410_gpio_pullup(S3C2410_GPH(6), 1);
s3c2410_gpio_cfgpin(S3C2410_GPH(7), S3C2410_GPH7_RXD2);
s3c2410_gpio_pullup(S3C2410_GPH(7), 1);
}
return ret;
err:
s3c24xx_serial_shutdown(port);
return ret;
}
static irqreturn_t
s3c24xx_serial_rx_chars(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
..../* 调用线路规程的...和上篇文章一致 */
tty_flip_buffer_push(tty);
out:
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}static irqreturn_t s3c24xx_serial_tx_chars(int irq, void *id)
{
....
if (uart_circ_chars_pending(xmit) < WAKEUP_CHARS)
uart_write_wakeup(port);
if (uart_circ_empty(xmit))
s3c24xx_serial_stop_tx(port);
out:
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}void uart_write_wakeup(struct uart_port *port)
{
struct uart_state *state = port->state;
/*
* This means you called this function _after_ the port was
* closed. No cookie for you.
*/
BUG_ON(!state);
tasklet_schedule(&state->tlet);/* 也是一致的 */
}以上是关于tty初探—uart驱动框架分析uart_add_one_port的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章