C++混合编程之idlcpp教程Python篇
Posted kunana
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++混合编程之idlcpp教程Python篇相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上一篇在这 C++混合编程之idlcpp教程Python篇(7)
第一篇在这 C++混合编程之idlcpp教程(一)
与前面的工程相似,工程PythonTutorial6中,同样加入了四个文件:PythonTutorial6.cpp, Tutorial6.cpp, Tutorial6.i, tutorial6.py。其中PythonTutorial6.cpp的内容基本和PythonTutorial5.cpp雷同,不再赘述。首先看一下Tutorial6.i的内容:
#import "../../paf/src/pafcore/typedef.i" namespace tutorial {
template<N> struct Vector3 { Vector3(); Vector3(const Vector3& v); Vector3(N a, N b, N c); Vector3(const N* p); N getLength(); N length get; N lengthSquare get; static Vector3<N> s_zero; nocode N x; nocode N y; nocode N z; nocode N v[#3]; #{ union { struct { N x,y,z; }; N v[3]; }; #} }; export Vector3<float>; export Vector3<double>; typedef Vector3<float> Vector3f; typedef Vector3<double> Vector3d; #{ template<typename N> Vector3<N> Vector3<N>::s_zero(0, 0, 0); template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3() { } template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3(const Vector3<N>& v) : x(v.x), y(v.y), z(v.z) {} template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3(N a, N b, N c) : x(a), y(b), z(c) {} template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3(const N* p) : x(p[0]), y(p[1]), z(p[2]) {} template<typename N> inline N Vector3<N>::getLength() { return N(sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z)); } template<typename N> inline N Vector3<N>::get_length() { return N(sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z)); } template<typename N> inline N Vector3<N>::get_lengthSquare() { return (x * x + y * y + z * z); } #} }
template<N>
struct Vector3
这是一个模板类,C++的模板功能复杂强大,编译器实在难写。所以大多数C++模板的高级特性在idlcpp中都没有做支持,毕竟idlcpp只负责对脚本语言提供接口,有一些简单的模板功能就够用了。另外由于不准备支持数值做为模板参数,只支持类型做为模板参数。
static Vector3 s_zero;
这一行声明了一个静态成员变量。idlcpp支持静态成员变量,静态成员函数,静态属性(实际上也是静态成员函数)。
nocode N x;
nocode N y;
nocode N z;
nocode N v[#3];
#{
union
{
struct
{
N x,y,z;
};
N v[3];
};
#}
idlcpp 没有提供 union。好在可以通过nocode 和 #{#} 分别在生成的元数据描述代码和C++头文件提供各自的内容。
下面两行代码
export Vector3<float>;
export Vector3<double>;
用于生成元数据代码。idlcpp中通过这样的声明语句才会生成相应类型的元数据信息。
再下面两行代码
typedef Vector3<float> Vector3f;
typedef Vector3<double> Vector3d;
为模板类实例类型声明了类型别名。因为这两个类型名分别是::tutorial::Vector3<float> 和 ::tutorial::Vector3<double>,在脚本中使用不方便,有了类型别名之后就可以通过::tutorial::Vector3f和::tutorial::Vector3d来使用。
后面就是成员函数的实现代码,不在赘述。
编译后生成的Tutorial6.h的内容如下:
//DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE, it is generated by idlcpp //http://www.idlcpp.org #pragma once namespace tutorial { template<typename N> struct Vector3 { public: Vector3(); Vector3(const Vector3& v); Vector3(N a,N b,N c); Vector3(const N* p); N getLength(); N get_length(); N get_lengthSquare(); static Vector3<N> s_zero; union { struct { N x,y,z; }; N v[3]; }; }; typedef Vector3<float> Vector3f; typedef Vector3<double> Vector3d; template<typename N> Vector3<N> Vector3<N>::s_zero(0, 0, 0); template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3() { } template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3(const Vector3<N>& v) : x(v.x), y(v.y), z(v.z) {} template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3(N a, N b, N c) : x(a), y(b), z(c) {} template<typename N> inline Vector3<N>::Vector3(const N* p) : x(p[0]), y(p[1]), z(p[2]) {} template<typename N> inline N Vector3<N>::getLength() { return N(sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z)); } template<typename N> inline N Vector3<N>::get_length() { return N(sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z)); } template<typename N> inline N Vector3<N>::get_lengthSquare() { return (x * x + y * y + z * z); } }
idlcpp会为只读属性length和lengthSquare 生成对应的函数声明get_length和get_lengthSquare。
其他的内容,C++和idl基本上都是一样的。
然后是Tutorial6.cpp
#include "Tutorial6.h" #include "Tutorial6.mh" #include "Tutorial6.ic" #include "Tutorial6.mc"
因为模板类的代码都写在头文件中了,所以Tutorial6.cpp只需要包含对应的四个文件即可。
最后看一下Tutorial6.py的内容
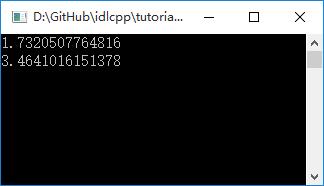
import pafpython; paf = pafpython.paf; v1 = paf.tutorial.Vector3f.New(1,1,2); v1.z = 1; print(v1.length._); v2 = paf.tutorial.Vector3d(2,2,1); v2.v[2] = 2; print(v2.getLength()._);
编译执行,结果如下图:
以上是关于C++混合编程之idlcpp教程Python篇的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章