Express框架
Posted zcy9838
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Express框架相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Node.js的Web开发相关的内容:
- Node.js不需要依赖第三方应用软件(Apache),可以基于API自己实现
- 实现静态资源服务器
- 路由处理
- 动态网站
- 模板引擎
- get和post参数传参和处理
Web开发框架:express是基于上面的底层的API进行包装,然后提供一套新的API,使用更加方便。
下载并安装express:
npm install express --save
创建服务器:
//引入express模块 const app = require(‘express‘)(); //‘/‘表示对根路径的请求 app.get(‘/‘,(req,res)=> res.end(‘ok‘); ).listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); ); //========================================= let server = app.get(‘/‘,(req,res)=> res.end(‘abc‘); ); server.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
创建静态资源:
/** * 托管静态文件: * 可以指定虚拟目录 * 可以指定多个目录作为静态资源目录 */ const express = require(‘express‘); const app = express(); //实现静态资源服务 //可以访问www目录下的所有文件,例如http://localhost:3000/js/app.js //use方法的第一个参数可以指定一个虚拟路径 //必须加上这个虚拟目录才能访问,如:http://localhost:3000/abc/index.html app.use(‘/abc‘,express.static(‘../www‘)); //如果要使用多个静态资源目录,请多次调用 express.static 中间件函数 //let server = app.use(express.static(‘../www‘)); app.use(express.static(‘../buffer‘)); app.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
基本路由操作:
/** * 路由:根据请求路径和请求方式进行路径分发处理 * http的常用请求方式: * post 添加 * get 查询 * put 更新 * delete 删除 * restful api(一种url的格式) */ const express = require(‘express‘); const app = express(); //基本的路由处理 //表单只有两种提交方式:get和post //‘/‘表示对根路径的请求 app.get(‘/‘,(req,res) => res.end(‘get data‘); ); app.post(‘/‘,(req,res) => res.end(‘post data‘); ); app.put(‘/‘,(req,res) => res.end(‘put data‘); ); app.delete(‘/‘,(req,res) => res.end(‘delete data‘); ); //================================================= //直接使用use方法可以处理所有的路由请求 app.use((req,res)=> res.send(‘ok‘); //send的功能和end一样 ); app.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
使用postman工具测试结果:

使用中间件:
1.应用级中间件
/** * 中间件,就是处理过程中的一个环节(本质上就是一个函数) */ //应用级别的中间件 const express = require(‘express‘); const app = express(); let total = 0; //next可以将中间件彼此之间串联起来 app.use(‘/user‘,(req,res,next) => //记录访问时间 console.log(‘Time:‘, Date.now()) //next方法的作用就是把请求传递到下一个中间件,否则后续的中间件是没有办法调用的 next() ); app.use(‘/user‘,(req,res,next) => //记录访问日志 console.log(‘访问了/user‘); next() ); //最后一个中间件不需要往下传递 app.use(‘/user‘,(req,res) => //记录访问次数 total++; console.log(total); res.send(‘result‘); ); app.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
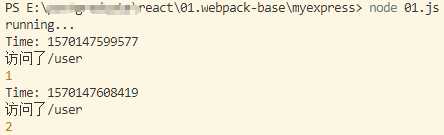
2.路由级中间件
/** * 中间件的挂载方式和执行流程: * 1.use * 2.路由方式:get post put delete */ //路由级的中间件 const express = require(‘express‘); const app = express(); app.get(‘/abc‘,(req,res,next) => console.log(1); //如果不使用next,则后面的函数都无法调用,处于阻塞状态 //next() //如果有next(),打印结果为:1 2 如果没有next(),打印结果只有1,并且浏览器处于阻塞状态,超时报错 //next()带参数表示跳转到下一个路由,只打印:1 3 next(‘route‘) ,(req,res) => console.log(2); res.send(‘abc‘); ); app.get(‘/abc‘,(req,res) => console.log(3); res.send(‘hello‘); ); app.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
/** * 应用中间件 */ const express = require(‘express‘); const app = express(); //下载并安装第三方包body-parser:npm install body-parser const bodyParser = require(‘body-parser‘); //挂载内置中间件 app.use(express.static(__dirname)); //处理get提交参数,get参数不需要中间件,express自己提供了处理get请求的方式 app.get(‘/login‘,(req,res) => let data = req.query; console.log(data); res.send(‘get data‘); ); //挂载参数处理中间件(post) app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded(extended:false)); //处理post提交参数 app.post(‘/login‘,(req,res) => let data = req.body; //注意输入访问链接时输入的login一定要带后缀.html,否则访问不了 /* console.log(data); res.send(‘ok‘); */ if(data.username == ‘admin‘ && data.password == ‘123‘) res.send(‘success‘); else res.send(‘failure‘); ); app.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
对应的login.html文件:
<body> <form action="http://localhost:3000/login" method="get"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 密 码:<input type="password" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body>
3.错误处理中间件
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) console.error(err.stack) res.status(500).send(‘Something broke!‘) )
4.内置中间件:就是静态资源服务的使用
app.use(express.static(‘path‘));
5.第三方中间件
使用模板引擎:
/** * 模板引擎整合:art-template */ //安装模板引擎art-template //npm install art-template 和 npm install express-art-template const express = require(‘express‘); const path = require(‘path‘); const template = require(‘art-template‘); const app = express(); //设置模板引擎 //1.设置模板的路径 app.set(‘views‘,path.join(__dirname,‘views‘)); //2.设置模板引擎的后缀 app.set(‘view engine‘,‘art‘); //3.使用express兼容art-template模板引擎 app.engine(‘art‘,require(‘express-art-template‘)); app.get(‘/list‘,(req,res)=> let data = title : ‘水果‘, list : [‘apple‘,‘orange‘,‘banana‘] res.render(‘list‘,data); ); app.listen(3000,()=> console.log(‘running...‘); );
对应的list.art文件:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>模板</title> </head> <body> <div>title</div> <div> <ul> each list <li>$value</li> /each </ul> </div> </body> </html>

/**
* 托管静态文件:
* 可以指定虚拟目录
* 可以指定多个目录作为静态资源目录
*/
const express = require(‘express‘);
const app = express();
//实现静态资源服务
//可以访问www目录下的所有文件,例如http://localhost:3000/js/app.js
//use方法的第一个参数可以指定一个虚拟路径
//必须加上这个虚拟目录才能访问,如:http://localhost:3000/abc/index.html
app.use(‘/abc‘,express.static(‘../www‘));
//如果要使用多个静态资源目录,请多次调用 express.static 中间件函数
//let server = app.use(express.static(‘../www‘));
app.use(express.static(‘../buffer‘));
app.listen(3000,()=>
console.log(‘running...‘);
);
以上是关于Express框架的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章