Django之AJAX请求
Posted mofujin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Django之AJAX请求相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
---恢复内容开始---
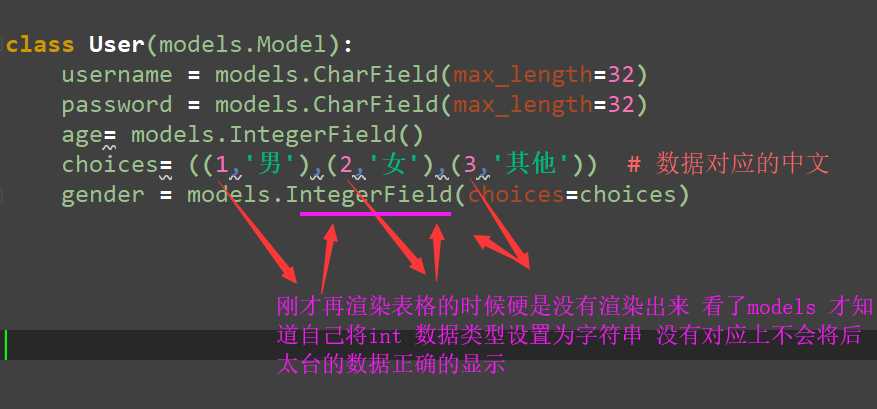
一、choice字段
1.实列
前端代码
<div class=‘container‘> <div class="row"> <h3>用户详情表</h3> <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2"> <table class="table table-striped table-bordered table-hover"> <thead> <tr> <th>序号</th> <th>id</th> <th>用户名</th> <th>密码</th> <th>年龄</th> <th>性别</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> % for user in user_list % <tr> <td> forloop.counter0 </td> <td> user.pk </td> <td> user.username </td> <td> user.password </td> <td> user.age </td> //choice 在前端不需要加括号 <td> user.get_gender_display </td> <td> <a href="" class="btn btn-success">操作</a> <a href="" class="btn btn-danger">删除</a> </td> </tr> % endfor % </tbody> </table> </div> </div> </div>
后端代码
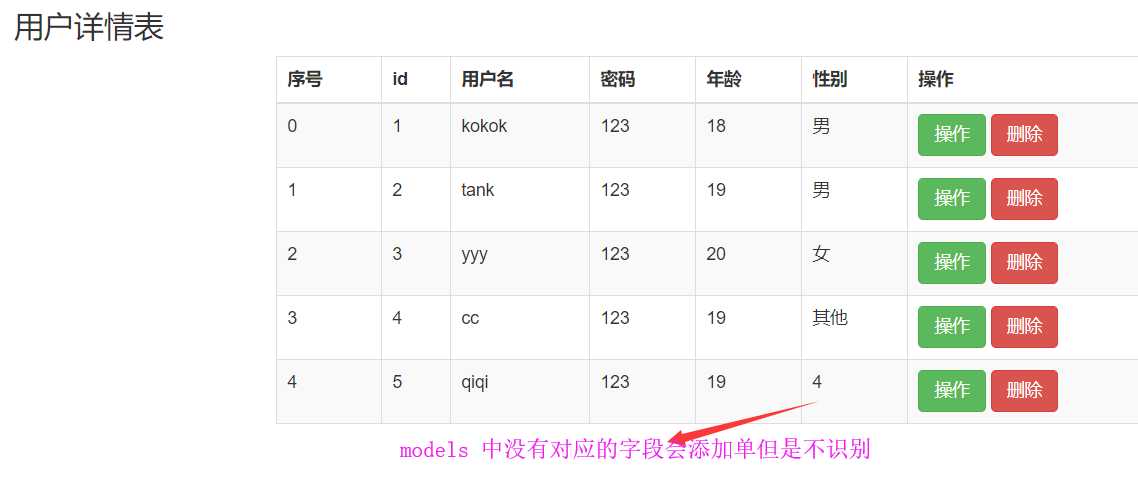
def r(request): # 献给客户一个get请求页面 user_list = models.User.objects.all() return render(request, ‘reg.html‘,locals())
后端展示
二、前端往后端发送数据的几种方法
1.请求方式 GET POST
2.a标签href属性 GET请求
3.浏览器窗口输入url GET请求
4.form表单 GET/POST
5.ajax GET/POST
三、AJAX 发送数据和文件的传输
1.发送普通键值对的格式
前端有点小问题
<input type="text" id="l1">+<input type="text" id="l2">=<input type="text" id="d3"> <button class="btn btn-success" id="b">提交</button> <script> //绑定点击事件 $(‘#b‘).on(‘click‘,function () //用AJAX发送数据 $.ajax( //四大参数。。1 》》》 第一种我们正常提交数据默认发送数据的格式urlencode url:‘‘, // 不写默认往当前的地址提交 type:‘post ‘, //传输据的方式 data:‘l1‘:$(‘#l‘).val(),‘l2‘:$(‘#l2‘), #data:JSON.stringify(‘username‘:‘koko‘,‘password‘:‘123 ‘), //发送字典格式方便我们取值 django 能帮我们识别# #contentType:‘application/json‘, // 告诉你后端我用的json的数据格式# success:function (data) alert(data); $(‘#d3‘).val(data) ) )
后端
def res(request): # 献给客户一个get请求页面 if request.method == ‘POST‘: l1 = request.POST.get(‘l1‘) l2 = request.POST.get(‘l2‘) res = int(l1) + int(l2) return HttpResponse(res) return render(request, ‘reg.html‘)
bug:
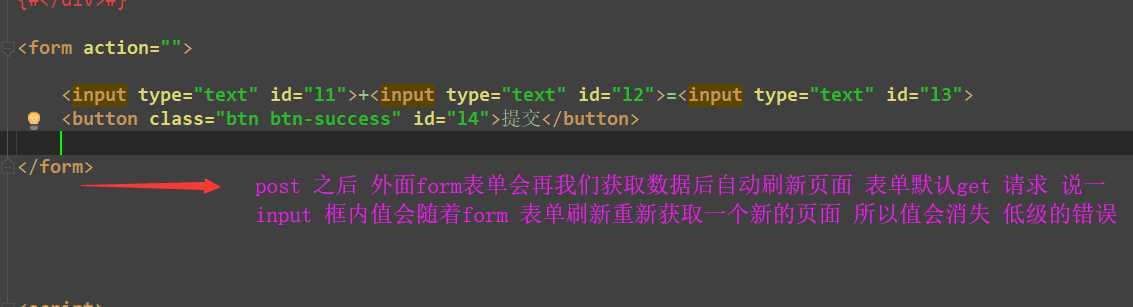
form表单提交后会自动触发页面 所以将数据清除
2.发送json数据格式
后端代码
def test(request): if request.method == ‘POST‘: import json # 将后端ajax 发送的数据格式进行转化 # 转化成字段返回到前端 封装成字典 方便取值 back_data = request.body # 饭序列化成字符串 back_str = back_data.decode(‘utf-8‘) print(back_str) back_dic = json.loads(back_str) print(type(back_dic)) # "username":"koo","password":"123" 这才是真正格式的json格式的字典 # print(request.POST) # <QueryDict: > # print(request.body) # b‘"username":"koo","password":"123"‘ return JsonRsponse(back_dic) return render(request,‘test.html‘)
前端代码
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
% load static %
<link rel="stylesheet" href="% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css‘ %">
<script src="% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/js/bootstrap.min.js‘ %"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="d1">+<input type="text" id="d2">=<input type="text" id="d3">
<button class="btn btn-success" id="d4">提交</button>
<script>
$(‘#d4‘).on(‘click‘,function()
$.ajax(
// 四大必要参数
url:‘‘, // 可以不写
type:‘post‘,
data:JSON.stringify(‘username‘:‘koo‘,‘password‘:‘123‘),
contentType:‘application/json‘,
success:function (data)
$(‘#d3‘).val(data).val()
)
)
</script>
</body>
注意:json格式发送的数据要前后端编码格式一致
data:JSON.stringify(‘username‘:‘koo‘,‘password‘:‘123‘),
contentType:‘application/json‘,
# 如何渲染给前端 >>>回调函数的$(‘‘#d3).val() 是连一起的两个key
三.Ajax发送文件
后端代码
def test(request): print(request.is_ajax()) # True if request.method == ‘POST‘: print(request.POST) # <QueryDict: > 为空 print(request.FILES) # 文件是放再我们Files 里面 # <MultiValueDict: ‘myfile‘: [<InMemoryUploadedFile: # 面试总结.md (application/octet-stream)>]> return render(request,‘test.html‘) #
前端代码
<body> <input type="text" id="d3"> <input type="file" name="my_files" id="d5"> <button class="btn btn-success" id="d4">提交</button> <script> $(‘#d4‘).on(‘click‘,function() // ajax 传文件 建议使用内置对象formdata生成一个自定义对象 var formData = new FormData(); // 传文件 // 如何获取文件标签所存储的文件对象? 固定语法 // 1.先用jQery查找到存储文件的input标签 // 2.将jQuery对象转成原生js对象 // 3.利用原生js对象的方法 .files[0]获取到标签内部存储的文件对象 // 4.一定要指定两个参数都为false // 注意里面有两个参数 第一个为key 第二个文value formData.append(‘myfile‘,$(‘#d5‘)[0].files[0]); // 指定两个参数为false $.ajax( // url:‘‘, type:‘post‘, data:formData, // 额外指定俩个参数 processData:false, contentType:false, success:function (data) $(‘#d3‘).val(data) ); ) </script> </body>
四.批量插入数据
后端代码
def index(request): # 批量出入数 # for i in range(1000): # models.Book.objects.create(title=‘第%s本‘%i) # book_list = models.Book.objects.all() # 这种方法相对效率比较慢 l = [] for i in range(10000): l.append(models.Book(title=‘第%s本‘%i)) models.Book.objects.bulk_create(l) # 批量插入数据 book_list = models.Book.objects.all() return render(request,‘index.html‘,locals())
前端代码
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script> % load static % <link rel="stylesheet" href="% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css‘ %"> <script src="% static ‘bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/js/bootstrap.min.js‘ %"></script> </head> <body> % for book in book_list % <p class="text-center"> book </p> 直接放书就可以了 % endfor %
五.分页器
执行函数
from app01.utils.mypage import Pagination def book(request): # for i in range(1000): # models.Book.objects.create(title=‘第%s本书‘%i) # l = [] # for i in range(10000): # l.append(models.Book(title=‘第%s本书‘%i)) # models.Book.objects.bulk_create(l) # 批量插入数据 """自己推到的分页器代码""" # current_page = request.GET.get("page",1) # 获取用户想访问的页码 如果没有 默认展示第一页 # # current_page = int(current_page) # # per_page_num = 10 # 规定每页展示10条数据 # # start_page = (current_page - 1) * per_page_num # end_page = current_page * per_page_num # # book_list = models.Book.objects.all()[start_page:end_page] # # all_count = models.Book.objects.all().count() # # page_num,more = divmod(all_count,per_page_num) # if more: # page_num += 1 # # # 在后端生成分页器代码 然后传递给前端 # html = ‘‘ # xxx = current_page # if current_page < 6: # xxx = 6 # for i in range(xxx-5,xxx+6): # if i == current_page: # html += ‘<li class="active"><a href="?page=%s" >%s</a></li>‘%(i,i) # else: # html += ‘<li><a href="?page=%s">%s</a></li>‘ % (i, i) # 使用封装好的自定义分页器 book_list = models.Book.objects.all() current_page = request.GET.get("page",1) all_count = book_list.count() page_obj = Pagination(current_page=current_page,all_count=all_count,per_page_num=10) page_queryset = book_list[page_obj.start:page_obj.end] return render(request,‘booklist.html‘,locals()) """ per_page_num = 10 current_page start_page end_page 1 0 10 2 10 20 3 20 30 4 30 40 per_page_num = 5 current_page start_page end_page 1 0 5 2 5 10 3 10 15 4 15 20 start_page = (current_page - 1) * per_page_num end_page = current_page* per_page_num 10000 10 1000 10001 10 1001
导入模块
class Pagination(object): def __init__(self, current_page, all_count, per_page_num=2, pager_count=11): """ 封装分页相关数据 :param current_page: 当前页 :param all_count: 数据库中的数据总条数 :param per_page_num: 每页显示的数据条数 :param pager_count: 最多显示的页码个数 用法: queryset = model.objects.all() page_obj = Pagination(current_page,all_count) page_data = queryset[page_obj.start:page_obj.end] 获取数据用page_data而不再使用原始的queryset 获取前端分页样式用page_obj.page_html """ try: current_page = int(current_page) except Exception as e: current_page = 1 if current_page < 1: current_page = 1 self.current_page = current_page self.all_count = all_count self.per_page_num = per_page_num # 总页码 all_pager, tmp = divmod(all_count, per_page_num) if tmp: all_pager += 1 self.all_pager = all_pager self.pager_count = pager_count self.pager_count_half = int((pager_count - 1) / 2) @property def start(self): return (self.current_page - 1) * self.per_page_num @property def end(self): return self.current_page * self.per_page_num def page_html(self): # 如果总页码 < 11个: if self.all_pager <= self.pager_count: pager_start = 1 pager_end = self.all_pager + 1 # 总页码 > 11 else: # 当前页如果<=页面上最多显示11/2个页码 if self.current_page <= self.pager_count_half: pager_start = 1 pager_end = self.pager_count + 1 # 当前页大于5 else: # 页码翻到最后 if (self.current_page + self.pager_count_half) > self.all_pager: pager_end = self.all_pager + 1 pager_start = self.all_pager - self.pager_count + 1 else: pager_start = self.current_page - self.pager_count_half pager_end = self.current_page + self.pager_count_half + 1 page_html_list = [] # 添加前面的nav和ul标签 page_html_list.append(‘‘‘ <nav aria-label=‘Page navigation>‘ <ul class=‘pagination‘> ‘‘‘) first_page = ‘<li><a href="?page=%s">首页</a></li>‘ % (1) page_html_list.append(first_page) if self.current_page <= 1: prev_page = ‘<li class="disabled"><a href="#">上一页</a></li>‘ else: prev_page = ‘<li><a href="?page=%s">上一页</a></li>‘ % (self.current_page - 1,) page_html_list.append(prev_page) for i in range(pager_start, pager_end): if i == self.current_page: temp = ‘<li class="active"><a href="?page=%s">%s</a></li>‘ % (i, i,) else: temp = ‘<li><a href="?page=%s">%s</a></li>‘ % (i, i,) page_html_list.append(temp) if self.current_page >= self.all_pager: next_page = ‘<li class="disabled"><a href="#">下一页</a></li>‘ else: next_page = ‘<li><a href="?page=%s">下一页</a></li>‘ % (self.current_page + 1,) page_html_list.append(next_page) last_page = ‘<li><a href="?page=%s">尾页</a></li>‘ % (self.all_pager,) page_html_list.append(last_page) # 尾部添加标签 page_html_list.append(‘‘‘ </nav> </ul> ‘‘‘) return ‘‘.join(page_html_list)
六.利用sweat 弹框 前后端交互 删除 数据
模态框
图书删除验证
前端代码
<script> $(‘.del‘).click(function () // 获取当前标签对象 var $btnEle = $(this); swal( title: "你确定要删吗?", text: "你要是删了,你就准备跑路吧!", type: "warning", showCancelButton: true, confirmButtonClass: "btn-danger", confirmButtonText: "是的,老子就要删!", cancelButtonText: "算了,算了!", closeOnConfirm: false, showLoaderOnConfirm: true , function() // 朝后端发送ajax请求 $.ajax( url:‘‘, type:‘post‘, data:‘delete_id‘:$btnEle.attr(‘user_id‘), success:function (data) // 后端发字典过来 前端不需要你手动转 会自动帮你转换成js自定义对象 if (data.code == 100) #window.location.href = ‘‘; // 不写就是条到当前页面# // 通过DOM操作 实时改变页面 // 将被点击的删除按钮所在的那一行直接从DOM树中删掉 $btnEle.parent().parent().remove(); swal("删掉了!", "赶紧回去收拾行李吧,准备跑路!", "success"); else swal(‘发生了未知的错误‘,‘估计是有bug了‘,‘info‘) ); ); ) </script>
后端
def userlist(request): if request.is_ajax(): time.sleep(3) """ 一般情况下 针对ajax请求 后端通常都是返回一个字典 """ back_dic = ‘code‘:100,‘msg‘:‘‘ # 直接获取用户想删除的数据的id值 delete_id = request.POST.get(‘delete_id‘) # 直接利用queryset方法 批量删除 models.User.objects.filter(pk=delete_id).delete() # 要给前端ajax返回一个消息(字典) back_dic[‘msg‘] = ‘真的删除了!‘ return JsonResponse(back_dic) user_list = models.User.objects.all() return render(request,‘userlist.html‘,locals())
以上是关于Django之AJAX请求的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章