ConcurrentHashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析
Posted jing99
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ConcurrentHashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ConcurrentHashMap数据结构
ConcurrentHashMap相比HashMap而言,是多线程安全的,其底层数据与HashMap的数据结构相同,数据结构如下:
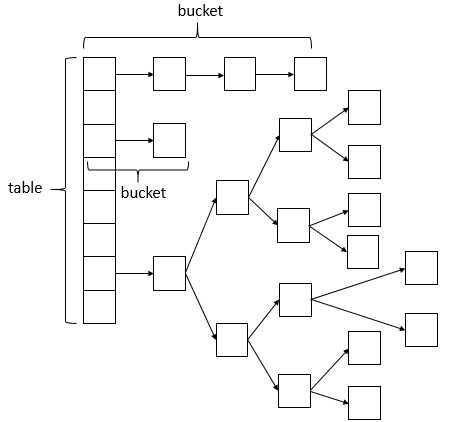
说明:ConcurrentHashMap的数据结构(数组+链表+红黑树),桶中的结构可能是链表,也可能是红黑树,红黑树是为了提高查找效率。
ConcurrentHashMap源码分析
1、类的继承关系
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable
说明:ConcurrentHashMap继承了AbstractMap抽象类,该抽象类定义了一些基本操作,同时,也实现了ConcurrentMap接口,ConcurrentMap接口也定义了一系列操作,实现了Serializable接口表示ConcurrentHashMap可以被序列化。
2、类的内部类
ConcurrentHashMap包含了很多内部类,其中主要的内部类框架图如下图所示:
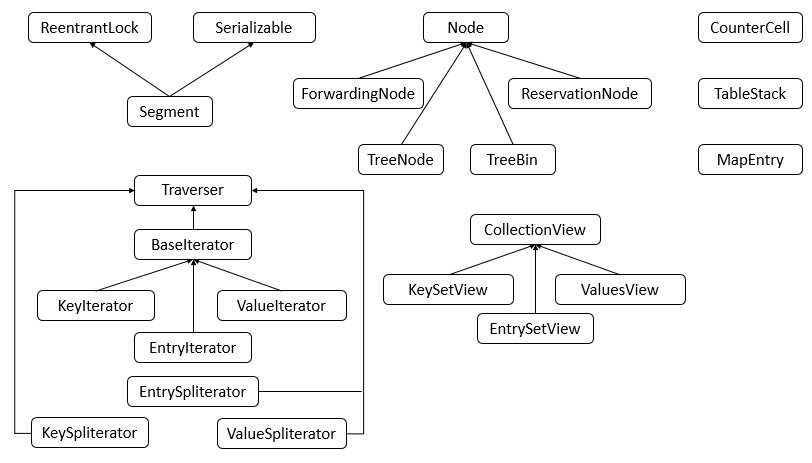
说明:可以看到,ConcurrentHashMap的内部类非常的庞大,第二个图是在JDK1.8下增加的类,下面对其中主要的内部类进行分析和讲解。
1. Node类
Node类主要用于存储具体键值对,其子类有ForwardingNode、ReservationNode、TreeNode和TreeBin四个子类。四个子类具体的代码在之后的具体例子中进行分析讲解。
2. Traverser类
Traverser类主要用于遍历操作,其子类有BaseIterator、KeySpliterator、ValueSpliterator、EntrySpliterator四个类,BaseIterator用于遍历操作。KeySplitertor、ValueSpliterator、EntrySpliterator则用于键、值、键值对的划分。
3. CollectionView类
CollectionView抽象类主要定义了视图操作,其子类KeySetView、ValueSetView、EntrySetView分别表示键视图、值视图、键值对视图。对视图均可以进行操作。
4. Segment类
Segment类在JDK1.8中与之前的版本的JDK作用存在很大的差别,JDK1.8下,其在普通的ConcurrentHashMap操作中已经没有失效,其在序列化与反序列化的时候会发挥作用。
5. CounterCell
CounterCell类主要用于对baseCount的计数。
3 、类的属性
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246763182397L; // 表的最大容量 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 默认表的大小 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16; // 最大数组大小 static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; // 默认并发数 private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16; // 装载因子 private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 转化为红黑树的阈值 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // 由红黑树转化为链表的阈值 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; // 转化为红黑树的表的最小容量 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // 每次进行转移的最小值 private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16; // 生成sizeCtl所使用的bit位数 private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16; // 进行扩容所允许的最大线程数 private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1; // 记录sizeCtl中的大小所需要进行的偏移位数 private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS; // 一系列的标识 static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash // /** Number of CPUS, to place bounds on some sizings */ // 获取可用的CPU个数 static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); // /** For serialization compatibility. */ // 进行序列化的属性 private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields = new ObjectStreamField("segments", Segment[].class), new ObjectStreamField("segmentMask", Integer.TYPE), new ObjectStreamField("segmentShift", Integer.TYPE) ; // 表 transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table; // 下一个表 private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable; // /** * Base counter value, used mainly when there is no contention, * but also as a fallback during table initialization * races. Updated via CAS. */ // 基本计数 private transient volatile long baseCount; // /** * Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the * table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization, * else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise, * when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon * creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the * next element count value upon which to resize the table. */ // 对表初始化和扩容控制 private transient volatile int sizeCtl; /** * The next table index (plus one) to split while resizing. */ // 扩容下另一个表的索引 private transient volatile int transferIndex; /** * Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells. */ // 旋转锁 private transient volatile int cellsBusy; /** * Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2. */ // counterCell表 private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells; // views // 视图 private transient KeySetView<K,V> keySet; private transient ValuesView<K,V> values; private transient EntrySetView<K,V> entrySet; // Unsafe mechanics private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U; private static final long SIZECTL; private static final long TRANSFERINDEX; private static final long BASECOUNT; private static final long CELLSBUSY; private static final long CELLVALUE; private static final long ABASE; private static final int ASHIFT; static try U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> k = ConcurrentHashMap.class; SIZECTL = U.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("sizeCtl")); TRANSFERINDEX = U.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("transferIndex")); BASECOUNT = U.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("baseCount")); CELLSBUSY = U.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("cellsBusy")); Class<?> ck = CounterCell.class; CELLVALUE = U.objectFieldOffset (ck.getDeclaredField("value")); Class<?> ak = Node[].class; ABASE = U.arrayBaseOffset(ak); int scale = U.arrayIndexScale(ak); if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0) throw new Error("data type scale not a power of two"); ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale); catch (Exception e) throw new Error(e);
说明:ConcurrentHashMap的属性很多,其中不少属性在HashMap中就已经介绍过,而对于ConcurrentHashMap而言,添加了Unsafe实例,主要用于反射获取对象相应的字段。
4 、类的构造函数
1. ConcurrentHashMap()型构造函数
public ConcurrentHashMap()
说明:该构造函数用于创建一个带有默认初始容量 (16)、加载因子 (0.75) 和 concurrencyLevel (16) 的新的空映射。
2. ConcurrentHashMap(int)型构造函数
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) if (initialCapacity < 0) // 初始容量小于0,抛出异常 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1)); // 找到最接近该容量的2的幂次方数 // 初始化 this.sizeCtl = cap;
以上是关于ConcurrentHashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
深入浅出 ~ ConCurrentHashMap底层原理透析
java中HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap实现原理