责任链模式(Chain)
Posted dyg0826
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了责任链模式(Chain)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言:责任链模式在很多框架中都有体现,比如Spring,Mybatis等。
概念:使多个对象都有处理请求的机会,从而避免了请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这些对象串成一条链,并沿着这条链一直传递该请求,直到有对象处理它为止。责任链模式的重点在“链上”,由一条链去处理相似的请求,在链中决定谁来处理这个请求,并返回相应的结果。
生活场景:在公司上班,遇到突发事件都需要请假,而请假根据天数不同需要不同的主管来同意我们的请求,比如我们要请1-3天的假期一级主管就可以直接同意,不需要再往上请求,如果是4-6天就需要二级主管同意,如果是7-10天就需要3级主管同意,大于10天需要我们的boss来同意才行。现在我们用责任链模式来模拟这个场景。
//处理者基类 public abstract class LeaveHandler //持有指向后继者的引用 protected LeaveHandler successor; //设置后继者 public void setSuccessor(LeaveHandler successor) this.successor = successor; public abstract void handleRequest(int request); //一级主管 public class FirstLevelSupervisor extends LeaveHandler @Override public void handleRequest(int request) if (request<=3) System.out.println("一级主管已同意"); else if (successor!=null) //请请求传递给责任链的下一个处理对象处理 successor.handleRequest(request); //二级主管 public class SecondLevelSupervisor extends LeaveHandler @Override public void handleRequest(int request) if (4<=request&&request<=6) System.out.println("二级主管已同意"); else if (successor!=null) //请请求传递给责任链的下一个处理对象处理 successor.handleRequest(request); //三级主管 public class ThirdLevelSupervisor extends LeaveHandler @Override public void handleRequest(int request) if (7<=request&&request<=10) System.out.println("三级主管已同意"); else if (successor!=null) //请请求传递给责任链的下一个处理对象处理 successor.handleRequest(request); //Boss public class Boss extends LeaveHandler @Override public void handleRequest(int request) System.out.println("Boss已同意"); //测试 public static void main(String[] args) LeaveHandler firstLevelSupervisor=new FirstLevelSupervisor(); LeaveHandler secondLevelSupervisor=new SecondLevelSupervisor(); LeaveHandler thirdLevelSupervisor=new ThirdLevelSupervisor(); LeaveHandler boss=new Boss(); //形成责任链 firstLevelSupervisor.setSuccessor(secondLevelSupervisor); secondLevelSupervisor.setSuccessor(thirdLevelSupervisor); thirdLevelSupervisor.setSuccessor(boss); //向一级主管提交7天的假期申请 firstLevelSupervisor.handleRequest(7);
总结:
优点
请求的发送者和处理解耦。
可以根据不同的需求进行动态的组合。
增强了给对象指派职责的灵活性,可以很方便的修改、增加、减少责任链中的元素。
缺点
影响性能。当责任链太长,如果只有最后一个可以处理,就会创建许多处理对象并且请求会在它们之间传递。
下面我们来看责任链模式在Spring和Mybatis源码中的体现
Spring源码中的责任链模式: Spring中对象大多都是代理对象,如果实现了接口,都是通过JDK动态代理生成的,代理类JdkDynamicAopProxy(代理模式),而当调用方法时会调用类的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable MethodInvocation invocation; Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null; try //eqauls()方法,目标对象未实现此方法 if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) return equals(args[0]); //hashCode()方法,目标对象未实现此方法 else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) return hashCode(); else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised); //Advised接口或者其父接口中定义的方法,直接反射调用,不应用通知 else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); Object retVal; if (this.advised.exposeProxy) oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; //获得目标对象的类 target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); //获取可以应用到此方法上的Interceptor列表 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); //如果没有可以应用到此方法的通知(Interceptor),此直接反射调用 method.invoke(target, args) if (chain.isEmpty()) Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); else //创建MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); //开始责任链调用 retVal = invocation.proceed(); Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) retVal = proxy; else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); return retVal; finally if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) targetSource.releaseTarget(target); if (setProxyContext) AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
invocation.proceed()方法:责任链调用
//ReflectiveMethodInvocation类 public Object proceed() throws Throwable //如果Interceptor执行完了,则执行joinPoint if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) return invokeJoinpoint(); Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); //如果要动态匹配joinPoint if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; //动态匹配:运行时参数是否满足匹配条件 if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments))
//interceptor相当于就是一个切面,可能是前置,后置等切面,以前置切面举例
//public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable
//this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() );
//return mi.proceed();重新走proceed方法,开始层层调用
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); else //动态匹配失败时,略过当前Intercetpor,调用下一个Interceptor
//类似递归调用 return proceed(); else //执行当前Intercetpor return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
Mybatis源码中的责任链模式:Mybatis中可以添加插件,比如PageHelper,多个插件对对象的包装采用的动态代理,而且是层层代理。
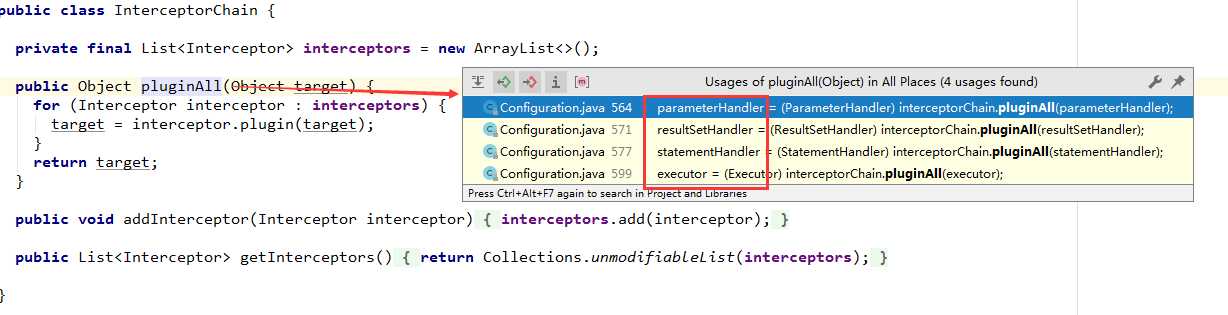
//插件责任链 public class InterceptorChain private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
//生成代理对象 public Object pluginAll(Object target) for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) target = interceptor.plugin(target); return target;
//添加拦截器也就是插件,可以添加很多个,利用层层代理生成的对象,方法调用的时候就是责任链模式,层层处理 public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) interceptors.add(interceptor); public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
什么时候调用pluginAll方法:四种插件类型:ParameterHandler(参数处理器) ResultSetHandler(结果集处理器) StatementHandler(语句集处理器) Executor(执行器)
分页插件PageHelper的PageInterceptor源码
@Intercepts( @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class), @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class), ) public class PageInterceptor implements Interceptor //缓存count查询的ms protected Cache<CacheKey, MappedStatement> msCountMap = null; private Dialect dialect; private String default_dialect_class = "com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"; private Field additionalParametersField; @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable try Object[] args = invocation.getArgs(); MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0]; Object parameter = args[1]; RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2]; ResultHandler resultHandler = (ResultHandler) args[3]; Executor executor = (Executor) invocation.getTarget(); CacheKey cacheKey; BoundSql boundSql; //由于逻辑关系,只会进入一次 if(args.length == 4) //4 个参数时 boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); cacheKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); else //6 个参数时 cacheKey = (CacheKey) args[4]; boundSql = (BoundSql) args[5]; List resultList; //调用方法判断是否需要进行分页,如果不需要,直接返回结果 if (!dialect.skip(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) //反射获取动态参数 Map<String, Object> additionalParameters = (Map<String, Object>) additionalParametersField.get(boundSql); //判断是否需要进行 count 查询 if (dialect.beforeCount(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) //创建 count 查询的缓存 key CacheKey countKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, boundSql); countKey.update("_Count"); MappedStatement countMs = msCountMap.get(countKey); if (countMs == null) //根据当前的 ms 创建一个返回值为 Long 类型的 ms countMs = MSUtils.newCountMappedStatement(ms); msCountMap.put(countKey, countMs); //调用方言获取 count sql String countSql = dialect.getCountSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, countKey); BoundSql countBoundSql = new BoundSql(ms.getConfiguration(), countSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameter); //当使用动态 SQL 时,可能会产生临时的参数,这些参数需要手动设置到新的 BoundSql 中 for (String key : additionalParameters.keySet()) countBoundSql.setAdditionalParameter(key, additionalParameters.get(key)); //执行 count 查询 Object countResultList = executor.query(countMs, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, countKey, countBoundSql); Long count = (Long) ((List) countResultList).get(0); //处理查询总数 //返回 true 时继续分页查询,false 时直接返回 if (!dialect.afterCount(count, parameter, rowBounds)) //当查询总数为 0 时,直接返回空的结果 return dialect.afterPage(new ArrayList(), parameter, rowBounds); //判断是否需要进行分页查询 if (dialect.beforePage(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) //生成分页的缓存 key CacheKey pageKey = cacheKey; //处理参数对象 parameter = dialect.processParameterObject(ms, parameter, boundSql, pageKey); //调用方言获取分页 sql String pageSql = dialect.getPageSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, pageKey); BoundSql pageBoundSql = new BoundSql(ms.getConfiguration(), pageSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameter); //设置动态参数 for (String key : additionalParameters.keySet()) pageBoundSql.setAdditionalParameter(key, additionalParameters.get(key)); //执行分页查询 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, pageKey, pageBoundSql); else //不执行分页的情况下,也不执行内存分页 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql); else //rowBounds用参数值,不使用分页插件处理时,仍然支持默认的内存分页 resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql); return dialect.afterPage(resultList, parameter, rowBounds); finally dialect.afterAll();
//为了生成代理对象 @Override public Object plugin(Object target) return Plugin.wrap(target, this); @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) //缓存 count ms msCountMap = CacheFactory.createCache(properties.getProperty("msCountCache"), "ms", properties); String dialectClass = properties.getProperty("dialect"); if (StringUtil.isEmpty(dialectClass)) dialectClass = default_dialect_class; try Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(dialectClass); dialect = (Dialect) aClass.newInstance(); catch (Exception e) throw new PageException(e); dialect.setProperties(properties); try //反射获取 BoundSql 中的 additionalParameters 属性 additionalParametersField = BoundSql.class.getDeclaredField("additionalParameters"); additionalParametersField.setAccessible(true); catch (NoSuchFieldException e) throw new PageException(e);
Plugin类源码
//Plugin类源码 public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler private final Object target; private final Interceptor interceptor; private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap; private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) this.target = target; this.interceptor = interceptor; this.signatureMap = signatureMap; //生成代理对象,这里有点特别是层层代理,代理对象又生成代理对象 public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor); Class<?> type = target.getClass(); Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); if (interfaces.length > 0) return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); return target; //代理对象真实调用方法 @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable try Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (methods != null && methods.contains(method))
//插件调用 return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args)); return method.invoke(target, args); catch (Exception e) throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e); private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class); if (interceptsAnnotation == null) throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName()); Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value(); Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>(); for (Signature sig : sigs) Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.computeIfAbsent(sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>()); try Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args()); methods.add(method); catch (NoSuchMethodException e) throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e); return signatureMap; private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<>(); while (type != null) for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) interfaces.add(c); type = type.getSuperclass(); return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
以上是关于责任链模式(Chain)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
责任链模式 职责链模式 Chain of Responsibility Pattern 行为型 设计模式(十七)
行为型设计模式—— 责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)