tomcat NIOEndpoint中的Acceptor实现
Posted guanghuiqq
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了tomcat NIOEndpoint中的Acceptor实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
EndPoint的组件就是属于连接器Connector里面的。它是一个通信的端点,就是负责对外实现TCP/IP协议。EndPoint是个接口,它的具体实现类就是AbstractEndpoint,而AbstractEndpoint具体的实现类就有AprEndpoint、Nio2Endpoint、NioEndpoint。
AprEndpoint:对应的是APR模式,简单理解就是从操作系统级别解决异步IO的问题,大幅度提高服务器的处理和响应性能。但是启用这种模式需要安装一些其他的依赖库。
Nio2Endpoint:利用代码来实现异步IO
NioEndpoint:利用了JAVA的NIO实现了非阻塞IO,Tomcat默认启动是以这个来启动的,而这个也是我们的讲述重点。
在代码NioEndpoint.class中定义的这五个组件。具体这五个组件是干嘛的呢?
LimitLatch:连接控制器,负责控制最大的连接数
Acceptor:负责接收新的连接,然后返回一个Channel对象给Poller
Poller:可以将其看成是NIO中Selector,负责监控Channel的状态
SocketProcessor:可以看成是一个被封装的任务类
Executor:Tomcat自己扩展的线程池,用来执行任务类
组件间的关联关系:
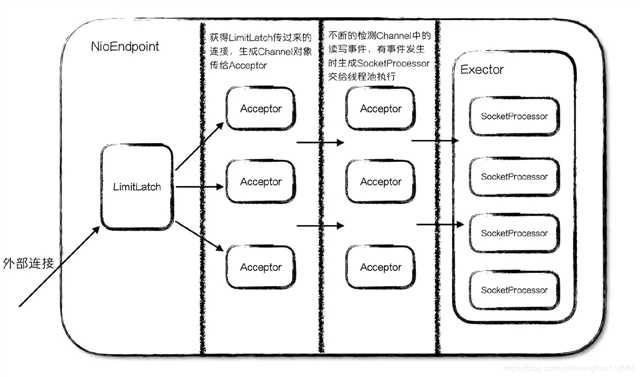
-----------------------------------------------------------
启动NioEndpoint的Acceptor多线程,默认初始化一个Acceptor:
package org.apache.tomcat.util.net;
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S>
/**
* Acceptor是接收连接的,我们可以看到Acceptor实现了Runnable接口,
* 那么在哪会新开启线程来执行Acceptor的run方法呢?
* 在AbstractEndpoint的startAcceptorThreads方法中。
*/
protected final void startAcceptorThreads()
int count = getAcceptorThreadCount();
acceptors = new Acceptor[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
acceptors[i] = createAcceptor();
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i;
acceptors[i].setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptors[i], threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
@Override
protected AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor createAcceptor()
return new Acceptor();
具体类的实现内容:
1、执行run方法,启动socket服务;
2、关闭socket服务。
/**
* The background thread that listens for incoming TCP/IP connections and
* hands them off to an appropriate processor.
* 重要方法
*/
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor
@Override
public void run()
int errorDelay = 0;
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running)
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && running)
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try
Thread.sleep(50);
catch (InterruptedException e)
// Ignore
if (!running)
break;
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try
//if we have reached max connections, wait
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
SocketChannel socket = null;
try
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
socket = serverSock.accept();
catch (IOException ioe)
// We didn‘t get a socket
countDownConnection();
if (running)
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
else
break;
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// Configure the socket
if (running && !paused)
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// an appropriate processor if successful
if (!setSocketOptions(socket))
closeSocket(socket);
else
closeSocket(socket);
catch (Throwable t)
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
private void closeSocket(SocketChannel socket)
countDownConnection();
try
socket.socket().close();
catch (IOException ioe)
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.close"), ioe);
try
socket.close();
catch (IOException ioe)
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.close"), ioe);
以上是关于tomcat NIOEndpoint中的Acceptor实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章