Tomcat卷二---请求流程源码分析
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tomcat卷二---请求流程源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Tomcat卷二
- Tomcat 请求处理流程
Tomcat 请求处理流程
请求流程
设计了这么多层次的容器,Tomcat是怎么确定每一个请求应该由哪个Wrapper容器里的 Servlet来处理的呢?
答案是,Tomcat是用Mapper组件来完成这个任务的。
Mapper组件的功能就是将用户请求的URL定位到一个Servlet,它的工作原理是:
Mapper组件里保存了Web应用的配置信息,其实就是容器组件与访问路径的映射关系, 比如Host容器里配置的域名、Context容器里的Web应用路径,以及Wrapper容器里 Servlet映射的路径,你可以想象这些配置信息就是一个多层次的Map。
当一个请求到来时,Mapper组件通过解析请求URL里的域名和路径,再到自己保存的 Map里去查找,就能定位到一个Servlet。请你注意,一个请求URL最后只会定位到一个 Wrapper容器,也就是一个Servlet。
下面的示意图中 , 就描述了 当用户请求链接 http://www.itcast.cn/bbs/findAll 之 后, 是如何找到最终处理业务逻辑的servlet 。
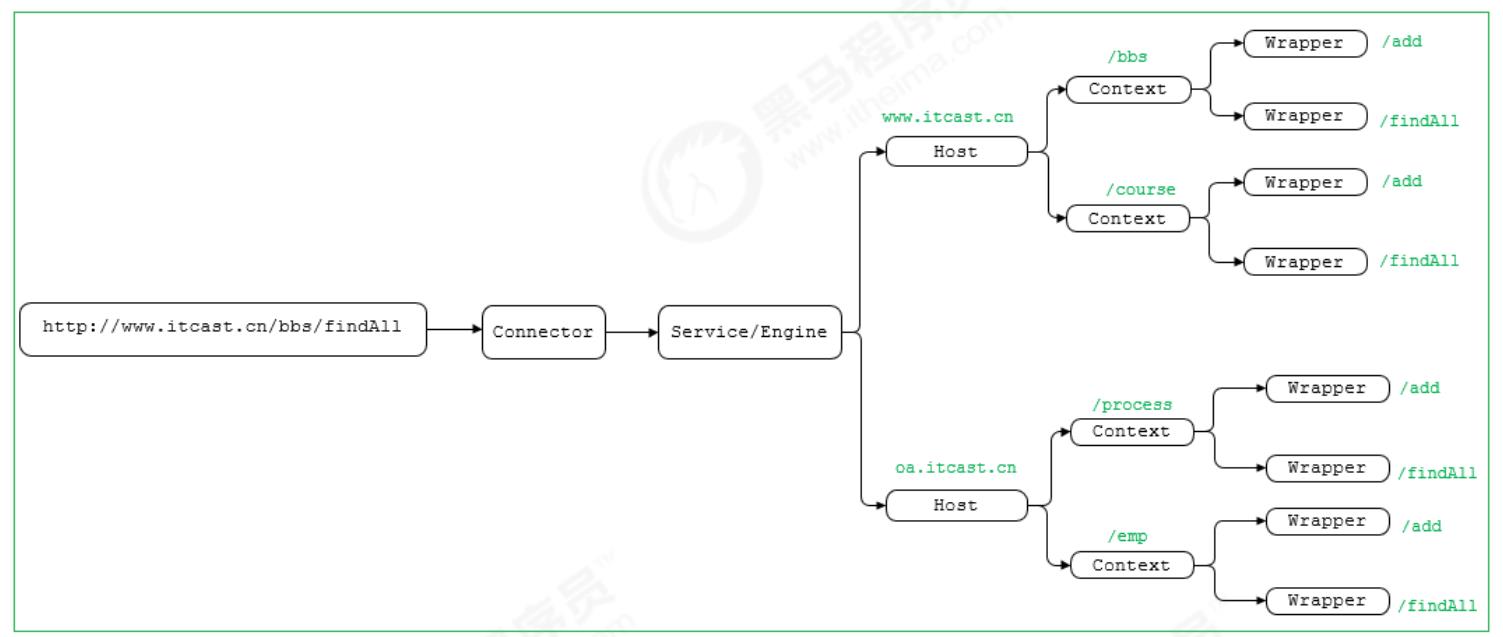
那上面这幅图只是描述了根据请求的URL如何查找到需要执行的Servlet , 那么下面我们 再来解析一下 , 从Tomcat的设计架构层面来分析Tomcat的请求处理
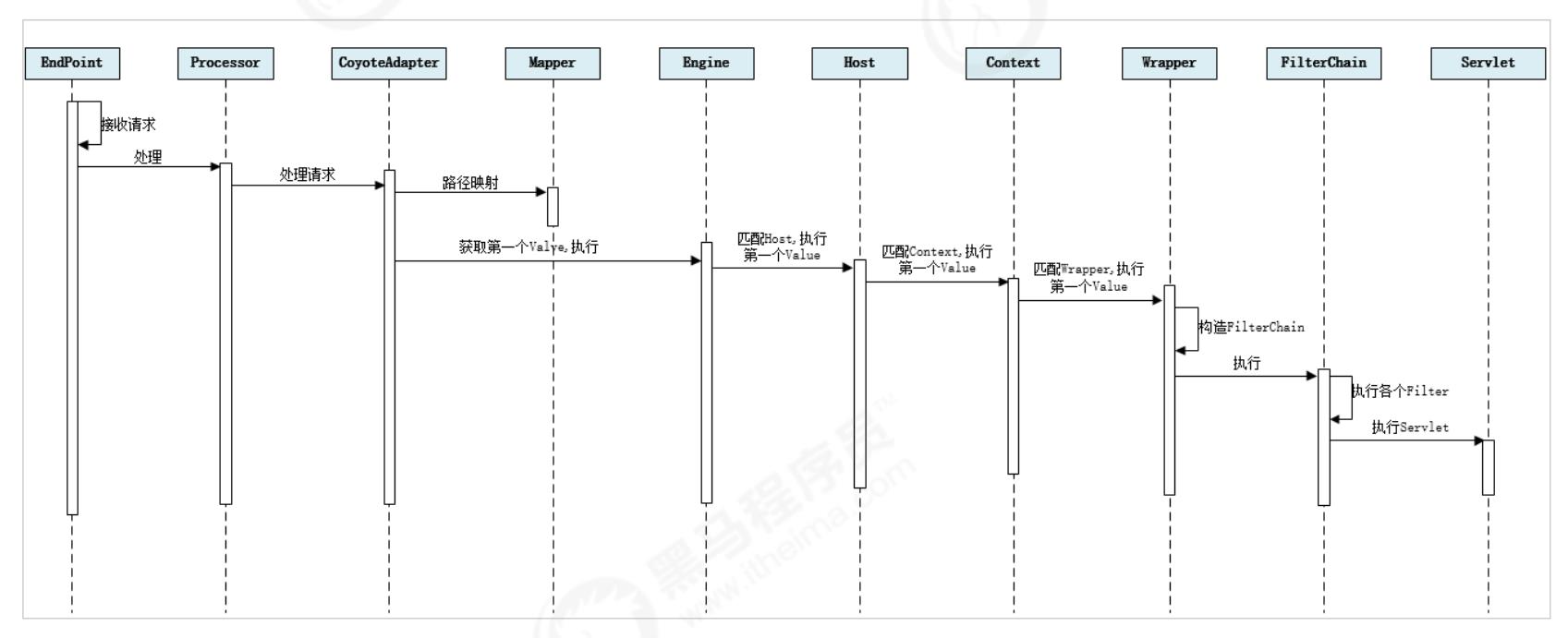
步骤如下:
-
Connector组件Endpoint中的Acceptor监听客户端套接字连接并接收Socket。
-
将连接交给线程池Executor处理,开始执行请求响应任务。
-
Processor组件读取消息报文,解析请求行、请求体、请求头,封装成Request对象。
-
Mapper组件根据请求行的URL值和请求头的Host值匹配由哪个Host容器、Context容器、Wrapper容器处理请求。
-
CoyoteAdaptor组件负责将Connector组件和Engine容器关联起来,把生成的 Request对象和响应对象Response传递到Engine容器中,调用 Pipeline。
-
Engine容器的管道开始处理,管道中包含若干个Valve、每个Valve负责部分处理逻 辑。执行完Valve后会执行基础的 Valve–StandardEngineValve,负责调用Host容器的 Pipeline。
-
Host容器的管道开始处理,流程类似,最后执行 Context容器的Pipeline。
-
Context容器的管道开始处理,流程类似,最后执行 Wrapper容器的Pipeline。
-
Wrapper容器的管道开始处理,流程类似,最后执行 Wrapper容器对应的Servlet对象 的 处理方法。
请求流程源码解析
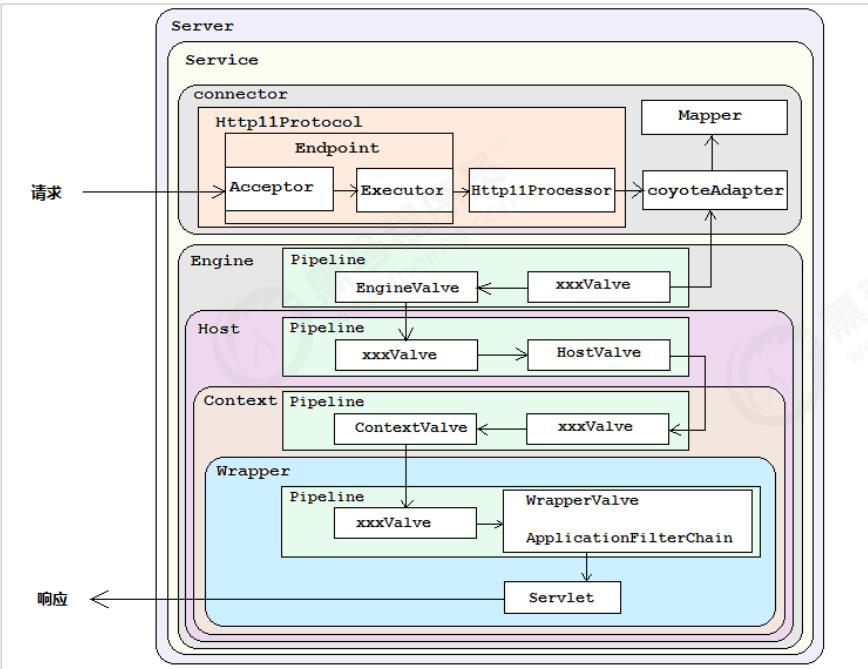
在前面所讲解的Tomcat的整体架构中,我们发现Tomcat中的各个组件各司其职,组件 之间松耦合,确保了整体架构的可伸缩性和可拓展性,那么在组件内部,如何增强组件 的灵活性和拓展性呢? 在Tomcat中,每个Container组件采用责任链模式来完成具体的 请求处理。
在Tomcat中定义了Pipeline 和 Valve 两个接口,Pipeline 用于构建责任链, 后者代表责 任链上的每个处理器。Pipeline 中维护了一个基础的Valve,它始终位于Pipeline的末端 (最后执行),封装了具体的请求处理和输出响应的过程。当然,我们也可以调用 addValve()方法, 为Pipeline 添加其他的Valve, 后添加的Valve 位于基础的Valve之 前,并按照添加顺序执行。Pipiline通过获得首个Valve来启动整合链条的执行 。
源码研究
建议看源码流程前先去回顾一下责任链模式,因为tomcat的请求流程中主要使用了责任链模式
我们把请求过程的源码分为两部分来进行分析:
第一部分: 请求由Endpoint捕获,并转交给Processor处理.
1.Acceptor.run()
请求的流程由NioEndpoint中的Accepter类的run方法开始.
首先一个浏览器的请求会由tomcat中的Endpoint中的Accepter所捕获并开启会话.
protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor
@Override
public void run()
int errorDelay = 0;
while (running)
while (paused && running)
state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
try
Thread.sleep(50);
catch (InterruptedException e)
// Ignore
if (!running)
break;
state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
try
//if we have reached max connections, wait
countUpOrAwaitConnection();
SocketChannel socket = null;
try
//接受客户端请求
socket = serverSock.accept();
catch (IOException ioe)
// We didn't get a socket
countDownConnection();
if (running)
// Introduce delay if necessary
errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
// re-throw
throw ioe;
else
break;
// Successful accept, reset the error delay
errorDelay = 0;
// Configure the socket
if (running && !paused)
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// an appropriate processor if successful
if (!setSocketOptions(socket))
closeSocket(socket);
else
closeSocket(socket);
catch (Throwable t)
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
2.Poller.run()
当接收客户端请求时,NioEndpoint.Poller会获取事件并开始迭代执行.(一下省略部分代码)
public void run()
while (true)
.......
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext())
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
NiosocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
if (attachment == null)
iterator.remove();
else
iterator.remove();
//开始正式执行请求流程
processKey(sk, attachment);
//while
//process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
//while
getStopLatch().countDown();
2.1 Poller.processKey()
processKey方法继续调用其中的processSocket方法,并开始处理会话.
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment)
try
if ( close )
cancelledKey(sk);
else if ( sk.isValid() && attachment != null )
if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable() )
if ( attachment.getSendfileData() != null )
processSendfile(sk,attachment, false);
else
unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps());
boolean closeSocket = false;
// Read goes before write
if (sk.isReadable())
//开始处理会话
if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true))
closeSocket = true;
if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable())
if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true))
closeSocket = true;
if (closeSocket)
cancelledKey(sk);
else
//invalid key
cancelledKey(sk);
catch ( CancelledKeyException ckx )
cancelledKey(sk);
catch (Throwable t)
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error("",t);
2.2 AbstractEndpoint.processSocket()
当跟踪进processSocket时会发现调用的是AbstractEndpoint的processSocket方法.
他会首先获取Socket的处理器,并获取线程池为处理Socket单独开启一个线程.
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch)
try
if (socketWrapper == null)
return false;
//获取socket的处理器
SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop();
if (sc == null)
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
else
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
//获取到线程池
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null)
//由线程池调用一个线程来执行Socket处理器
executor.execute(sc);
else
sc.run();
catch (RejectedExecutionException ree)
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
catch (Throwable t)
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
return true;
3. NioEndpoint.SocketProcessor.doRun()
经过跟踪会最终发现,sc.run()方法实际上是在调用NioEndpoint.SocketProcessor.doRun();
protected void doRun()
NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket();
SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());
....
if (handshake == 0)
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
// Process the request from this socket
if (event == null)
//获取Handler处理器:Servlet(处理器),调度处理器的处理方法
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);
else
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);
if (state == SocketState.CLOSED)
close(socket, key);
....
4. AbstractProtocol.ConnectionHandler.process
在doRun的方法中最后会交给AbstractProtocol.ConnectionHandler.process方法执行.
@Override
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status)
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled())
getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.process",
wrapper.getSocket(), status));
if (wrapper == null)
// Nothing to do. Socket has been closed.
return SocketState.CLOSED;
//获取Socket
S socket = wrapper.getSocket();
//交给Processor处理 -> 真正开始处理请求
Processor processor = connections.get(socket);
....
do
//开始解析请求
state = processor.process(wrapper, status);
.....
while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING);
至此,请求由Endpoint组件正式转交给Processor进行处理.
主要内容为在请求转交给Coyote适配器后的流程分析,紧接上文中请求交由Processor处理.
5.AbstractProcessorLight.process()
当请求由Endpoint交由Processor处理时,首先经过的就是AbstractProcessorLight.process()
public SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status)
throws IOException
SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;
Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null;
do
if (dispatches != null)
DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next();
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled())
getLog().debug("Processing dispatch type: [" + nextDispatch + "]");
state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus());
if (!dispatches.hasNext())
state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper);
else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT)
else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END)
state = dispatch(status);
state = checkForPipelinedData(state, socketWrapper);
else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE)
// Extra write event likely after async, ignore
state = SocketState.LONG;
else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ)
//调度Http11Processor.service方法
state = service(socketWrapper);
else if (status == SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL)
logAccess(socketWrapper);
else
state = SocketState.CLOSED;
....
while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END ||
dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED);
return state;
6.Http11Processor的service方法
@Override
public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper)
....
while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null &&
sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !endpoint.isPaused())
// Parsing the request header
try
//解析socket请求数据中每一行,按照http协议解析请求头----只负责解析请求头
if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive))
if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1)
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead())
break;
if (endpoint.isPaused())
// 503 - Service unavailable
response.setStatus(503);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
else
keptAlive = true;
// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());
if (!inputBuffer.parseHeaders())
// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
// instead associate it with the socket
openSocket = true;
readComplete = false