Java并发编程总结4——ConcurrentHashMap在jdk1.8中的改进
Posted everSeeker
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java并发编程总结4——ConcurrentHashMap在jdk1.8中的改进相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、简单回顾ConcurrentHashMap在jdk1.7中的设计
先简单看下ConcurrentHashMap类在jdk1.7中的设计,其基本结构如图所示:
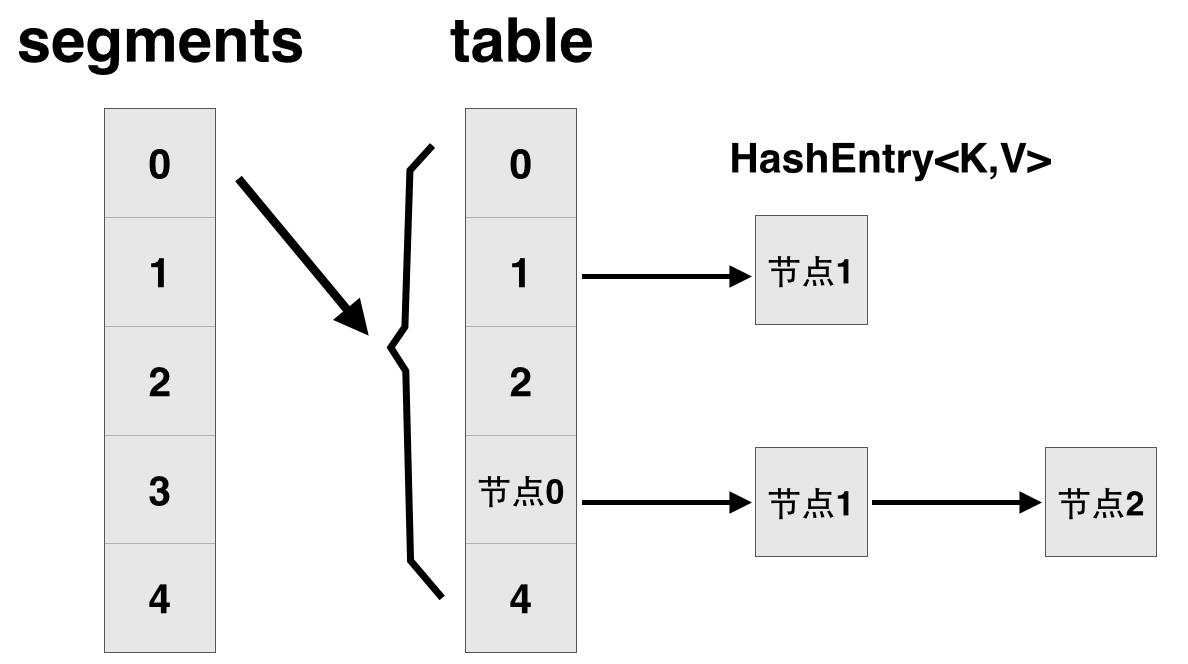
每一个segment都是一个HashEntry<K,V>[] table, table中的每一个元素本质上都是一个HashEntry的单向队列。比如table[3]为首节点,table[3]->next为节点1,之后为节点2,依次类推。
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements ConcurrentMap<K, V>, Serializable { // 将整个hashmap分成几个小的map,每个segment都是一个锁;与hashtable相比,这么设计的目的是对于put, remove等操作,可以减少并发冲突,对 // 不属于同一个片段的节点可以并发操作,大大提高了性能 final Segment<K,V>[] segments; // 本质上Segment类就是一个小的hashmap,里面table数组存储了各个节点的数据,继承了ReentrantLock, 可以作为互拆锁使用 static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable { transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; transient int count; } // 基本节点,存储Key, Value值 static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; } }
二、在jdk1.8中主要做了2方面的改进
改进一:取消segments字段,直接采用transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table保存数据,采用table数组元素作为锁,从而实现了对每一行数据进行加锁,进一步减少并发冲突的概率。
改进二:将原先table数组+单向链表的数据结构,变更为table数组+单向链表+红黑树的结构。对于hash表来说,最核心的能力在于将key hash之后能均匀的分布在数组中。如果hash之后散列的很均匀,那么table数组中的每个队列长度主要为0或者1。但实际情况并非总是如此理想,虽然ConcurrentHashMap类默认的加载因子为0.75,但是在数据量过大或者运气不佳的情况下,还是会存在一些队列长度过长的情况,如果还是采用单向列表方式,那么查询某个节点的时间复杂度为O(n);因此,对于个数超过8(默认值)的列表,jdk1.8中采用了红黑树的结构,那么查询的时间复杂度可以降低到O(logN),可以改进性能。
为了说明以上2个改动,看一下put操作是如何实现的。
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; // 如果table为空,初始化;否则,根据hash值计算得到数组索引i,如果tab[i]为空,直接新建节点Node即可。注:tab[i]实质为链表或者红黑树的首节点。 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } // 如果tab[i]不为空并且hash值为MOVED,说明该链表正在进行transfer操作,返回扩容完成后的table。 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { V oldVal = null; // 针对首个节点进行加锁操作,而不是segment,进一步减少线程冲突 synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; // 如果在链表中找到值为key的节点e,直接设置e.val = value即可。 if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } // 如果没有找到值为key的节点,直接新建Node并加入链表即可。 Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } // 如果首节点为TreeBin类型,说明为红黑树结构,执行putTreeVal操作。 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0) { // 如果节点数>=8,那么转换链表结构为红黑树结构。 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } // 计数增加1,有可能触发transfer操作(扩容)。 addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
另外,在其他方面也有一些小的改进,比如新增字段 transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells; 可方便的计算hashmap中所有元素的个数,性能大大优于jdk1.7中的size()方法。
三、ConcurrentHashMap jdk1.7、jdk1.8性能比较
测试程序如下:
public class CompareConcurrentHashMap { private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer>(40000); public static void putPerformance(int index, int num) { for (int i = index; i < (num + index) ; i++) map.put(String.valueOf(i), i); } public static void getPerformance2() { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 400000; i++) map.get(String.valueOf(i)); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("get: it costs " + (end - start) + " ms"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); final CountDownLatch cdLatch = new CountDownLatch(4); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { final int finalI = i; new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { CompareConcurrentHashMap.putPerformance(100000 * finalI, 100000); cdLatch.countDown(); } }).start(); } cdLatch.await(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("put: it costs " + (end - start) + " ms"); CompareConcurrentHashMap.getPerformance2(); } }
程序运行多次后取平均值,结果如下:

四、Collections.synchronizedList和CopyOnWriteArrayList性能分析
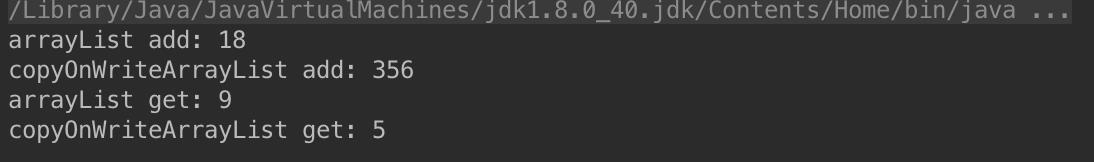
CopyOnWriteArrayList在线程对其进行变更操作的时候,会拷贝一个新的数组以存放新的字段,因此写操作性能很差;而Collections.synchronizedList读操作采用了synchronized,因此读性能较差。以下为测试程序:
public class App { private static List<String> arrayList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<String>()); private static List<String> copyOnWriteArrayList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(); private static CountDownLatch cdl1 = new CountDownLatch(2); private static CountDownLatch cdl2 = new CountDownLatch(2); private static CountDownLatch cdl3 = new CountDownLatch(2); private static CountDownLatch cdl4 = new CountDownLatch(2); static class Thread1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) arrayList.add(String.valueOf(i)); cdl1.countDown(); } } static class Thread2 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) copyOnWriteArrayList.add(String.valueOf(i)); cdl2.countDown(); } } static class Thread3 extends Thread1 { @Override public void run() { int size = arrayList.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) arrayList.get(i); cdl3.countDown(); } } static class Thread4 extends Thread1 { @Override public void run() { int size = copyOnWriteArrayList.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) copyOnWriteArrayList.get(i); cdl4.countDown(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); new Thread1().start(); new Thread1().start(); cdl1.await(); System.out.println("arrayList add: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start1)); long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); new Thread2().start(); new Thread2().start(); cdl2.await(); System.out.println("copyOnWriteArrayList add: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start2)); long start3 = System.currentTimeMillis(); new Thread3().start(); new Thread3().start(); cdl3.await(); System.out.println("arrayList get: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start3)); long start4 = System.currentTimeMillis(); new Thread4().start(); new Thread4().start(); cdl4.await(); System.out.println("copyOnWriteArrayList get: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start4)); } }
结果如下:
以上是关于Java并发编程总结4——ConcurrentHashMap在jdk1.8中的改进的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Java并发编程总结5——ThreadPoolExecutor