读书笔记:线性表-单向链表
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了读书笔记:线性表-单向链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
链表(linklist)
单项链表可以说是数据结构里面最简单的部分,也是十分重要的部分,数据结构后面的学习中 比如说:栈,队列,树, 图 都要使用这种数据结构来表示。
不多说,进入我对链表的理解部分。
简介:
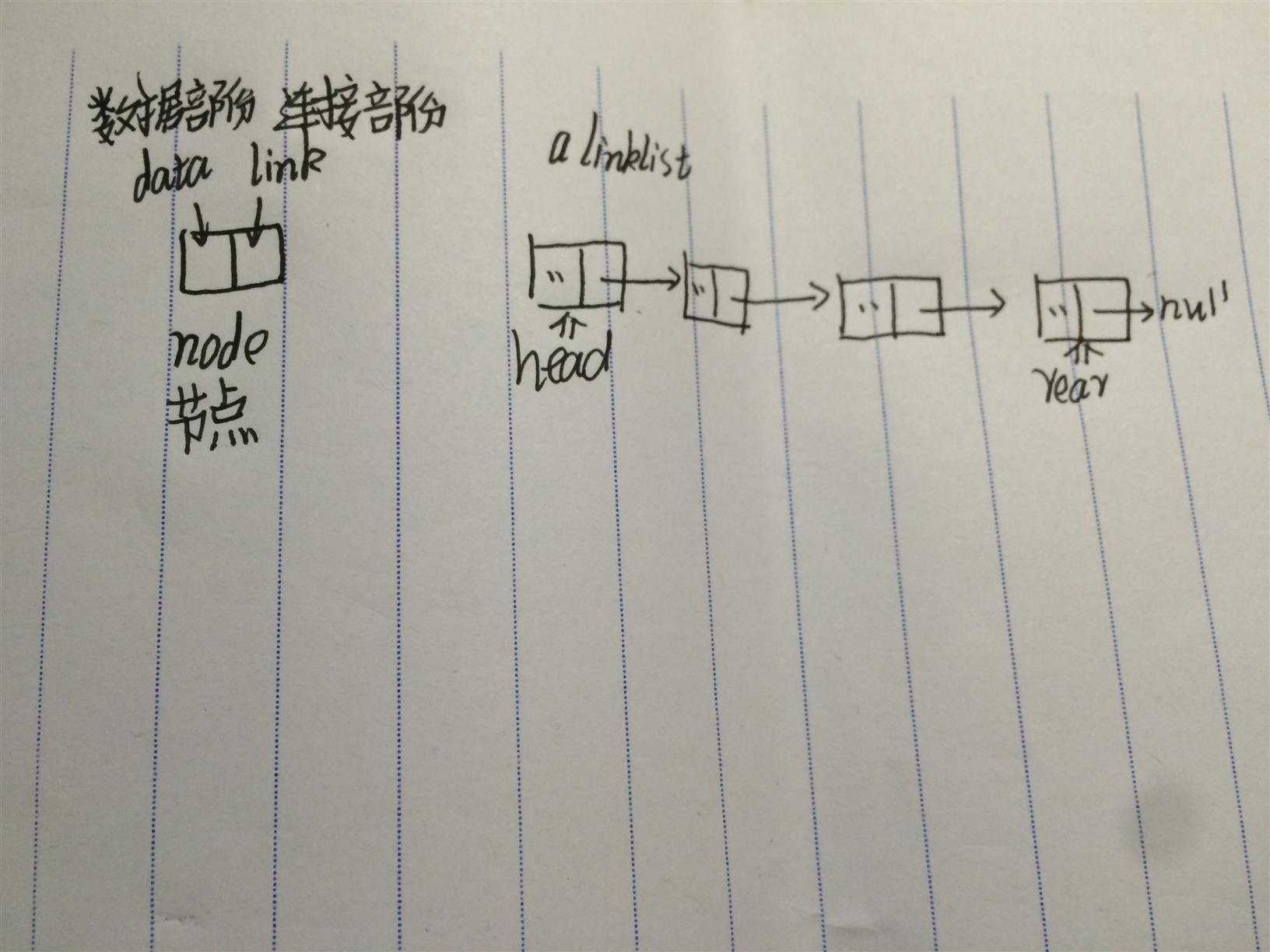
链表是一种数据结构,链表中,数据对象实例的每一个元素都用一个单元或节点来描述。每一个节点中都包含着它的数据[数据部分]和相关节点的位置信息[链接部分],我们称连通两个节点的部分为链(link)或指针(pointer)。链表的第一个节点称为头节点(head),最后一个节点为尾节点。头节点没有前驱,尾节点没有后继(我们一般将尾节点的链或指针指向一个NULL表示链表在这里完结)
通常把节点叫做node,链叫做next
如下图展示一个链表 :
接下来讲解链表的几项基本操作: 插入,删除, 查找, 遍历。
链表的插入:
如下图,我们首先利用for迭代找到待插入位置节点(node)的前一个节点(node_prev),把后一个节点叫做(node_next)。
将新节点(new_node)中的next指向 node,再将node_prev中的next指向new_node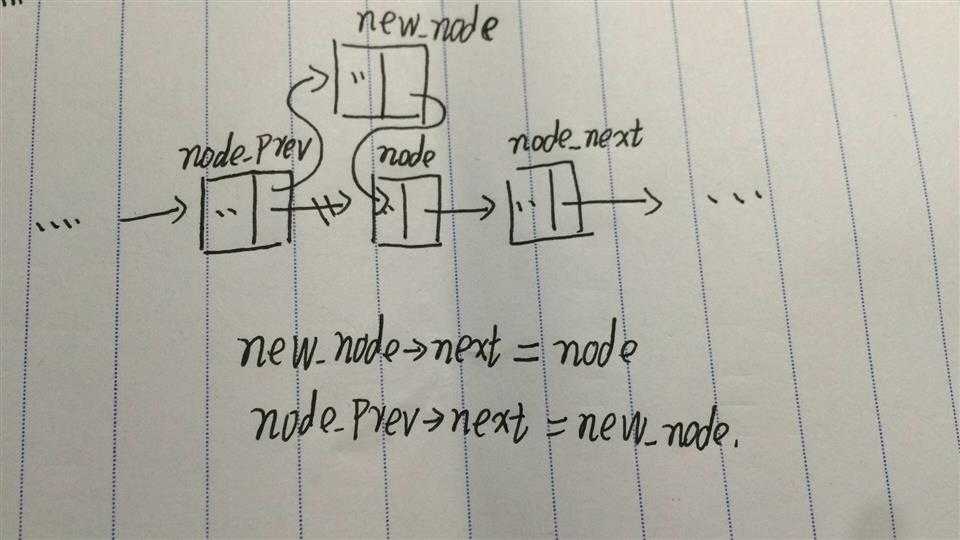
接下来post我自己写的链表代码 [简单的写了下,多多指教].
1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class LinkListNode 6 { 7 public: 8 // data mumber 9 int element; 10 LinkListNode *next; 11 12 13 //construcion function 14 LinkListNode() = default; 15 16 LinkListNode(const int theElement, LinkListNode *next) 17 { 18 this->element = theElement; 19 this->next = next; 20 } 21 }; 22 23 class LinkList 24 { 25 friend void operator << (ostream &os, LinkList &x); 26 public: 27 LinkList() 28 { 29 ListSize = 0; 30 head = NULL; 31 } 32 33 // Function 34 void insert(int theIndex, const int theElement); 35 void erase(int theIndex); 36 void erase(int firstIndex, int lastIndex); 37 void output(ostream &os) const; 38 39 40 int& operator [] (int theIndex); 41 private: 42 LinkListNode *head; 43 int ListSize; 44 }; 45 46 void operator << (ostream &os, LinkList &x) 47 { 48 x.output(os); 49 } 50 51 void LinkList::output(ostream &os) const 52 { 53 LinkListNode *p = head; 54 while (p != NULL) { 55 os << p->element << ‘ ‘; 56 p = p->next; 57 } 58 } 59 60 // insert Function, you can insert element into List in all place, 61 // and if the Index of your input is out of list‘range, the program will making some error information to tell you, and 62 // you can change the Index ,so that make it right 63 void LinkList::insert(int theIndex, const int theElement) 64 { 65 char c = ‘y‘; 66 while (c != ‘n‘) { 67 try { 68 if (0 > theIndex || theIndex > ListSize) 69 throw range_error("the Index is out of LinkList‘ range "); 70 //main of function body 71 else { 72 if(theIndex == 0) 73 head = new LinkListNode(theElement, head); 74 else { 75 LinkListNode *p = head; 76 for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++) 77 p = p->next; 78 p->next = new LinkListNode(theElement, p->next); 79 } 80 ListSize++; 81 c = ‘n‘; 82 } 83 } 84 catch (range_error err) { 85 cout << err.what() 86 << endl << "input Index again ? \\n" << "y or n" << endl; 87 cin >> c; 88 if (c == ‘y‘) 89 cin >> theIndex; 90 } 91 } 92 } 93 94 // Erase function, use it , you can delete a Node form list, but your Index can‘t out ou the list‘range too, and 95 // the funciton also has a error imformation unit 96 void LinkList::erase(int theIndex) 97 { 98 LinkListNode * delNode; 99 try { 100 if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= ListSize) 101 throw range_error("error Index \\n[No erase]"); 102 else { 103 if (theIndex == 0) { 104 delNode = head; 105 head = head->next; 106 } 107 else { 108 LinkListNode *p = head; 109 for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++) 110 p = p->next; 111 delNode = p->next; 112 p->next = p->next->next; 113 } 114 } 115 ListSize--; 116 delete delNode; 117 } 118 catch (range_error err) { 119 cout << err.what(); 120 } 121 } 122 123 // This is Erase funciton too, in deffrent to last function, this can delete a range of elements, and it has Error checking too 124 void LinkList::erase(int firstIndex, int lastIndex) 125 { 126 LinkListNode *fNode; 127 LinkListNode *tNode; 128 try { 129 if (firstIndex < 0 || lastIndex >= ListSize) 130 throw range_error("the range of your input is error"); 131 else { 132 LinkListNode *p = head; 133 int i; 134 for (i = 0; i < firstIndex - 1; i++) 135 p = p->next; 136 fNode = p->next; 137 LinkListNode *q = p; 138 for (; i < lastIndex - 1; i++) 139 p = p->next; 140 tNode = p->next; 141 142 if (firstIndex == 0) 143 head = tNode->next; 144 else q->next = tNode->next; 145 } 146 while (fNode != tNode) { 147 LinkListNode *temp = fNode->next; 148 delete fNode; 149 fNode = temp; 150 ListSize--; 151 } 152 } catch(range_error err){ 153 cout << err.what(); 154 } 155 } 156 157 // this is a operator, you can input index ,and you will get the element of the list‘index 158 int& LinkList::operator[] (int theIndex) 159 { 160 LinkListNode *p = head; 161 for (int i = 0; i < theIndex; i++) 162 p = p->next; 163 return p->element; 164 }
未完[...]
以上是关于读书笔记:线性表-单向链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章