android-----带你一步一步优化ListView
Posted 她说巷尾的樱花开了
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了android-----带你一步一步优化ListView相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上一篇介绍了通常我们优化ListView的方式,但是这点对于要加载大量图片的ListView来说显然是不够的,因为我们知道要想获取一张图片不管是本地的还是网络的,其性能上均没有从内存中获取快,所以为了提升用户的体验度,对于加载图片的ListView,通常我们会通过缓存做以下优化:基本思想:
(1)如果想要加载图片,首先先去内存缓存中查看是否有图片(内存缓存)
(2)如果内存缓存中没有,就会去本地SD卡上查找是否存在(SD卡缓存)
(3)如果本地SD卡上也没有的话,则会去网络下载了,下载完成之后将该图片存入本地缓存和内存缓存;
这篇主要从本地缓存角度介绍优化ListView显示图片的方法,接下来的几篇再从内存缓存以及本地缓存和内存缓存相结合的角度来优化ListView显示图片;
这里的本地缓存指的就是DiskLruCache,当缓存区已经满的时候他采用最近最少使用算法来替换其中的内容,当然对于本地缓存来说,这点并不是主要考虑的对象,因为毕竟SD卡的容量还是挺大的吧;
要想使用DiskLruCache,我们需要在工程中引入DiskLruCache.java文件,虽然DiskLruCache是谷歌推荐的,但是并不是谷歌开发的,下载链接:
在正式使用之前,我们先来说说使用DiskLruCache的步骤:
(1)首先当然是创建DiskLruCache对象了,因为DiskLruCache的构造函数是私有的,所以我们不能直接new出来他的实例,但是他提供了一个public static 类型的open方法,在这个方法里面是有通过new来创建DiskLruCache实例的,所以我们可以通过open方法的返回值来获得一个DiskLruCache对象;
(2)接着我们来看看要想调用open方法需要哪些参数吧
/**
* Opens the cache in {@code directory}, creating a cache if none exists
* there.
*
* @param directory a writable directory
* @param appVersion
* @param valueCount the number of values per cache entry. Must be positive.
* @param maxSize the maximum number of bytes this cache should use to store
* @throws java.io.IOException if reading or writing the cache directory fails
*/
public static DiskLruCache open(File directory, int appVersion, int valueCount, long maxSize)第一个参数directory指的是一个可写的目录,如果有SD卡或者SD卡不可移除的话,通常通过context.getExternalCacheDir().getPath()获取,对应的SD卡路径是/sdcard/android/data/包名/cache,如果没有SD卡的话,通常通过context.getCacheDir().getPath()获取,对应获取到的路径是/data/data/包名/cache;
第二个参数是app的版本号,因为我们对于图片数据的缓存很大程度上是与app的版本号有关系的,当app的版本发生更新的时候DiskLruCache会默认先删除先前所缓存的内容,其实这点是很好理解的,因为新版本会有新功能加入,而新的功能会有不同的布局内容,之前缓存的图片及视频语音之类的可能已经不再能适应新版本的界面要求啦!
第三个参数指的是同一个key值所对应的所对应的缓存文件的个数,这个值只能是正数;
第四个参数指的是缓存区的最大字节数,当然你不能指定成大于SD卡的容量了;
(3)很多人会发现你的app安装目录下会多好多名字奇怪的文件,然而你还打不开这些文件,别担心,那些就是缓存文件了,这些文件中有一个名字为journal,这类似于我们通常程序中的日志文件,这个文件是在open方法调用DiskLruCache构造函数的时候创建的,他记录了我们对缓存的种种操作,不信我打开一个你看看:
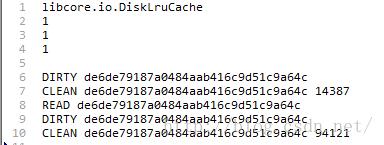
第一行表示我们使用的是DiskLruCache
第二行是DiskLruCache的版本,目前来说是恒为1的
第三行是app的版本,这个值就是上面open方法传入的第二个参数了
第四行是空行,用来分开头部和主体部分
第五行DIRTY表示后面这个名字的文件是个脏数据文件,每当我们调用DiskLruCache的edit方法的时候都会写入一条DIRTY信息
第六行CLEAN表示后面这个名字的文件已经成为了缓存文件,每当我们调用DiskLruCache的commit方法之后都会在journal文件中加入这么一条记录
有时候你还会看到开头是REMOVE名字的一行,这是在调用DiskLruCache abort方法的时候写入日志的一条记录
(4)好了,现在有了DiskLruCache对象了,通过他我们可以获取到Editor对象,他是DiskLruCache的内部类,注意这个才是真正写缓存的对象,我们可以通过他的commit、abort、close、flush等方法来进行写缓存操作
(5)有了写缓存的介绍,那么读缓存呢?读缓存是通过Snapshot来完成的,同样,他也是DiskLruCache的内部类
好了,DiskLruCache的大致操作过程介绍完毕了,接下来通过实例来完成带有本地缓存的ListView加载图片:
首先定义Activity布局文件listView.xml,用来显示ListView
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/imageView"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_marginRight="70dp"
/>
</RelativeLayout>上面两个布局文件都很好理解,在此不做过多解释;
因为创建DiskLruCache需要用到一个可写的目录以及app的版本号,因此我们实现了一个工具类Utils,其中两个方法如下:
/**
* 获取磁盘缓存的存储路径
* @param context
* @param uniqueName
* @return
*/
public static File getDiskCacheDir(Context context,String uniqueName)
{
String filePath = "";
if(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(Environment.getExternalStorageState()) || !Environment.isExternalStorageRemovable())
{
//表示SD卡存在或者不可移除
try {
filePath = context.getExternalCacheDir().getPath();//获得缓存路径
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}else
{
filePath = context.getCacheDir().getPath();
}
System.out.println(filePath+File.separator+uniqueName);
return new File(filePath+File.separator+uniqueName);
}
/**
* 获取app的版本号
* @param context
*/
public static int getAppVersion(Context context)
{
PackageInfo info;
try {
info = context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(context.getPackageName(), 0);
return info.versionCode;
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
} 接下来就是最关键的ListViewAdapter了,代码有点长,先贴出来再解释:
public class ListViewAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
public List<String> list;
public DiskLruCache diskCache;
public LayoutInflater inflater;
public ListView listView;
public Set<ImageAsyncTask> tasks;
public int reqWidth;
public int reqHeight;
public ListViewAdapter() {
}
public ListViewAdapter(Context context,List<String> list,DiskLruCache diskCache,ListView listView,ImageView imageView) {
this.list = list;
this.diskCache = diskCache;
this.inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
this.listView = listView;
tasks = new HashSet<ImageAsyncTask>();
//获得ImageView的宽和高
LayoutParams params = imageView.getLayoutParams();
this.reqWidth = params.width;
this.reqHeight = params.height;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
@Override
public String getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view = null;
ViewHolder holder = null;
if(convertView == null)
{
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.imageView = (ImageView)view.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
holder.textView = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.textView);
view.setTag(holder);//为了复用holder
}else
{
view = convertView;
holder = (ViewHolder) view.getTag();
}
//为ImageView设置标志,防止乱序
holder.imageView.setTag(position);
holder.textView.setTag(position+"#");
return view;
}
/**
* 加载图片
* @param url
* @param key
* @param holder
*/
public void loadImage(String url,String key,final int index)
{
//查看DiskLruCache缓存中是否存在对应key值得缓存文件,如果存在的话,则直接从缓存中取出图片即可,如果不存在的话,则需要从网络中加载,加载完成同时写到缓存中
//读缓存是通过DiskLruCache的Snaphot来实现的
final ImageView imageView;
final TextView textView;
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot = null;
FileInputStream in = null;
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
snapshot = diskCache.get(key);
if(snapshot != null)
{
imageView = (ImageView)listView.findViewWithTag(index);
textView = (TextView)listView.findViewWithTag(index+"#");
//非空表示缓存中存在该缓存文件
//通过Snapshot直接从缓存中取出写入到内存的输入流,随后调用BitmapFactory工厂方法来将其转变成为Bitmap对象显示在ImageView上面,同时将TextView设置为是从缓存中读取的数据
in = (FileInputStream) snapshot.getInputStream(0);//这里的0指的是key对应的第1个缓存文件,因为在创建DiskLruCache的时候,第三个参数我们会用来输入一个key对应几个缓存文件,之前我们创建的DiskLruCache的第三个参数输入的是1
//对流中的图片进行压缩处理操作
bitmap = decodeSampleBitmapFromStream(in, reqWidth, reqHeight);
if(imageView != null)
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
if(textView != null)
textView.setText("从缓存中获取的");
}else
{
//否则的话需要开启线程,从网络中获取图片,获取成功后返回该图片,并且将其设置为ImageView显示的图片,同时将TextView的值设置成是从网络中获取的
//这里我们使用的是AsyncTask,因为可以很方便的获取到我们要的图片,当然也可以通过Handler的方式来获取图片
ImageAsyncTask task = new ImageAsyncTask(listView,diskCache,index);
task.setOnImageLoadListener(new OnImageLoadListener() {
@Override
public void onSuccessLoad(Bitmap bitmap) {
System.out.println("已经使用的缓存大小: "+((float)diskCache.size())/(1024*1024)+" M");
System.out.println("加载图片成功.......");
}
@Override
public void onFailureLoad() {
System.out.println("加载图片失败.......");
}
});
tasks.add(task);//将任务加入到线程池中
task.execute(url);//执行加载图片的线程
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 暂停所有任务(为了防止在滑动的时候仍然有线程处于请求状态)
*/
public void cancelTask()
{
if(tasks != null)
{
for(ImageAsyncTask task: tasks)
task.cancel(false);//暂停任务
}
}
/**
* 对图片进行压缩处理
* @param in
* @param reqWidth
* @param reqHeight
* @return
*/
public static Bitmap decodeSampleBitmapFromStream(FileInputStream in,int reqWidth,int reqHeight)
{
//设置BitmapFactory.Options的inJustDecodeBounds属性为true表示禁止为bitmap分配内存
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
byte[] data = inputStreamToByteArray(in);
//这次调用的目的是获取到原始图片的宽、高,但是这次操作是没有写内存操作的
Bitmap beforeBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, options);
options.inSampleSize = calculateInSampleSize(options, reqWidth, reqHeight);
//设置这次加载图片需要加载到内存中
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
Bitmap afterBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, options);
return afterBitmap;
}
/**
* 计算出压缩比
* @param options
* @param reqWith
* @param reqHeight
* @return
*/
public static int calculateInSampleSize(BitmapFactory.Options options,int reqWidth,int reqHeight)
{
//通过参数options来获取真实图片的宽、高
int width = options.outWidth;
int height = options.outHeight;
int inSampleSize = 1;//初始值是没有压缩的
if(width > reqWidth || height > reqHeight)
{
//计算出原始宽与现有宽,原始高与现有高的比率
int widthRatio = Math.round((float)width/(float)reqWidth);
int heightRatio = Math.round((float)height/(float)reqHeight);
//选出两个比率中的较小值,这样的话能够保证图片显示完全
inSampleSize = widthRatio < heightRatio ? widthRatio:heightRatio;
}
return inSampleSize;
}
/**
* 将InputStream转换为Byte数组
* @param in
* @return
*/
public static byte[] inputStreamToByteArray(InputStream in)
{
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
try {
while((len = in.read(buffer)) != -1)
{
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
in.close();
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return outputStream.toByteArray();
}
static class ViewHolder
{
ImageView imageView;
TextView textView;
}
//这里为了能够获知ImageAsyncTask网络加载图片成功与否,我们定义了一个接口OnImageLoadListener,里面有两个方法onSuccessLoad
//与onFailureLoad,并且通过setOnImageLoadListener来将其绑定到指定的ImageAsyncTask中
class ImageAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<String, Void, Bitmap>
{
public OnImageLoadListener listener;
public DiskLruCache diskCache;
public int index;
public ListView listView;
public void setOnImageLoadListener(OnImageLoadListener listener)
{
this.listener = listener;
}
public ImageAsyncTask(ListView listView,DiskLruCache diskCache,int index)
{
this.listView = listView;
this.diskCache = diskCache;
this.index = index;
}
@Override
protected Bitmap doInBackground(String... params) {
String url = params[0];
String key = Utils.md5(url);
DiskLruCache.Editor editor;
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot;
OutputStream out;
FileInputStream in;
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
editor = diskCache.edit(key);
out = editor.newOutputStream(0);
if(Utils.downloadToStream(url, out))
{
//写入缓存
editor.commit();
}else
{
editor.abort();
}
diskCache.flush();//刷新到缓存中
//从缓存中将图片转换成Bitmap
snapshot = diskCache.get(key);
if(snapshot != null)
{
in = (FileInputStream) snapshot.getInputStream(0);
bitmap = ListViewAdapter.decodeSampleBitmapFromStream(in, reqWidth, reqHeight);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bitmap;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Bitmap result) {
if(result != null)
{
listener.onSuccessLoad(result);
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) listView.findViewWithTag(index);
TextView textView = (TextView)listView.findViewWithTag(index+"#");
if(imageView != null)
imageView.setImageBitmap(result);
if(textView != null)
textView.setText("从网络获取的");
}
else
listener.onFailureLoad();
tasks.remove(this);//加载结束移除任务(这点要特别注意,加载结束一定要记得移出任务)
}
}
}
第14行我们在创建ListViewAdapter的时候同时传入了DiskLruCache、ListView和ImageView对象,ImageView对象主要用来获得当前显示图片的ImageView宽和高分别是多少的,这样方便我们压缩图片;
再看getView,第58,59行这里我们防止图片以及文本乱序,分别对其添加了Tag标志;其他部分就是复用convertView以及viewHolder了,这没什么可以讲的;
第69行的loadImage用于加载第index位置上的图片,首先第79行,他会利用Snapshot对象去SD卡缓存里面查找是否存在指定key值的图片缓存是否存在,如果存在的话,则通过findViewWithTag获取到对应于index位置的ImageView和TextView对象,并且调用decodeSampleBitmapFromStream对图片进行适当的压缩处理,如果你对图片压缩不是很了解的话,可以看看我的另外一篇博客android-----解决Bitmap内存溢出的一种方法(图片压缩技术),89--92行则判断获得的ImageView和TextView是否为空并且对其进行相应赋值;如果缓存中不存在的话,则开启线程去网络加载图片,同时第111行将该线程加入到Set<ImageAsyncTask>类型的tasks中,便于我们对线程进行控制,这里我们实现了一个回调接口OnImageLoadListener,便于我们获知加载图片是否成功,这个接口很简单
public interface OnImageLoadListener {
public void onSuccessLoad(Bitmap bitmap);
public void onFailureLoad();
} 第122行是用于暂停当前所有线程的,很简单,因为我们把当前所有开启的子线程都加到了Set<ImageAsyncTask>类型的tasks中了;
那么接下来关键就是实现图片加载了,第230行开始就是比较关键的代码,首先通过params[0]获得当前传入需要加载的图片的url,随后调用md5算法计算出缓存文件的名字,md5实现代码:
/**
* 对指定URL进行MD5编码,生成缓存文件的名字
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static String md5(String str)
{
MessageDigest md5 = null;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "";
}
char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();
byte[] byteArray = new byte[charArray.length];
for(int i = 0;i < charArray.length;i++)
{
byteArray[i] = (byte) charArray[i];
}
byte[] md5Bytes = md5.digest(byteArray);
StringBuffer hexValue = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0;i < md5Bytes.length;i++)
{
int val = ((int) md5Bytes[i]) & 0xff;
if(val < 16)
{
hexValue.append("0");
}
hexValue.append(Integer.toHexString(val));
}
return hexValue.toString();
}
/**
* 根据url路径将对应图片缓存到本地磁盘
* @param urlString
* @param outputStream
* @return
*/
public static boolean downloadToStream(String urlString,OutputStream outputStream)
{
HttpURLConnection connection = null;
BufferedInputStream in = null;
BufferedOutputStream out = null;
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
URL url = new URL(urlString);
connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
InputStream instream = connection.getInputStream();
in = new BufferedInputStream(instream);
out = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = in.read(buf)) != -1)
{
out.write(buf, 0, len);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally
{
if(connection != null)
connection.disconnect();
try {
if(out != null)
{
out.close();
out = null;
}
if(in != null)
{
in.close();
in = null;
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
如果写入流成功的话,第244行用于将流中的内容写入到缓存文件中,这时候你会发现SD卡上缓存文件的大小并没有发生变化,所以最后还得调用249行的flush方法刷新缓存内容到文件,如果写入流失败的话,第247行则调用abort方法关闭了缓存;之后和上面的方法一样,我们会使用Snapshot对象去缓存中对指定key的缓存文件,如果存在的话,则会对其进行压缩,并且将其返回,注意在doInBackground里面是不可以进行更新UI操作的,因为他属于子线程,更新UI操作的方法应该在第264行的onPostExecute中实现,这里的代码就应该很好理解了吧,之前有讲过啦,同时这里还进行了OnImageLoadListener回调处理,result不为空的话调用onSuccessLoad方法,为空的话调用onFailureLoad方法;
最后就是我们的MainActivity了:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnScrollListener {
public ListView listView = null;
public ListViewAdapter adapter = null;
public int start_index;
public int end_index;
public List<String> list;
public boolean isInit = true;
public ImageView imageView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.listview);
//首先创建存储缓存文件的地方
File directory = Utils.getDiskCacheDir(this, "bitmap");
if(!directory.exists())
{
//目录不存在的话
directory.mkdirs();
}
//获取app的版本信息
int appVersion = Utils.getAppVersion(this);
//此处的参数1表示每个key对应于一个缓存文件,1024*1024*100表示缓存大小为100M
DiskLruCache diskCache = null;
try {
diskCache = DiskLruCache.open(directory, appVersion, 1, 1024*1024*100);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//创建用于传递给ListViewAdapter的数据
list = new ArrayList<String>();
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 50;i++)
{
index = i % Utils.images.length;
list.add(Utils.images[index]);
}
listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item, null,false);
imageView = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
//创建Adapter对象
adapter = new ListViewAdapter(this, list, diskCache,listView,imageView);
listView.setOnScrollListener(this);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount, int totalItemCount) {
start_index = firstVisibleItem;
end_index = start_index + visibleItemCount;
if(isInit == true && visibleItemCount > 0)
{
String url = "";
String key = "";
for(int i = start_index;i < end_index;i++)
{
url = list.get(i);
key = Utils.md5(url);
adapter.loadImage(url,key,i);
}
isInit = false;
}
}
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
if(scrollState == AbsListView.OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE)
{
//表示停止滑动,这时候就可以加载图片
String url = "";
String key = "";
for(int i = start_index;i < end_index;i++)
{
url = list.get(i);
key = Utils.md5(url);
adapter.loadImage(url,key,i);
}
}else
{
adapter.cancelTask();
}
}
}
首先第27行调用open方法创建了DiskLruCache,第44行创建了ListViewAdapter对象,同时将该对象设置到了ListView上面;
为了防止在滑动的时候仍然有线程加载图片导致OOM异常,我们为ListView设置了滑动事件,第66行的onScrollStateChanged会在滑动停止的时候调用loadImage方法去加载图片的,否则的话会调用cancelTask停止所有正在执行加载图片的子线程,至于start_index以及end_index是通过第49行的onScroll获取的,还有一点需要注意的是,我们在首次加载的时候也是需要调用loadImage来加载图片的,这就是我们设置isInit标志的原因,因为首次加载你是没有滑动屏幕的,那么他就不会在onScrollStateChanged里面调用loadImage去加载图片,这时候你会发现首次加载ListView上面是没有图片的,当你滑动后再停止才会有图片出现,这显然是不合理的,所以首次加载的时候也应该让他能够调用loadImage方法;
好了,采用DiskLruCache来实现ListView图片加载讲解结束啦,之后我们将会从内存缓存的角度对ListView进行进一步优化,谢谢大家!
以上是关于android-----带你一步一步优化ListView的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章