netty为什么非阻塞
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了netty为什么非阻塞相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A netty 的非阻塞 到底是指的什么netty的非阻塞指的是nio
多路复用器是阻塞的 其提供 非阻塞调用 阻塞调用 阻塞一段时间 的调用
也就是我们采用多路复用器操作io的时候 如果是bio 存在2个阻塞 一个是io的本身阻塞
还有一个是多路复用器本身的阻塞,有一个阻塞 就会阻塞
netty使用nio 所以不会发生 io阻塞 netty依靠多路复用器 在没有任何任务的时候 会阻塞调用
当有任务进入队列的时候多路复用器会从阻塞回复
Netty——网络编程(非阻塞理解及代码示例)
目录
一、非阻塞概述
- 非阻塞模式下,相关方法都会不会让线程暂停。
(1)、在 ServerSocketChannel.accept 在没有连接建立时,会返回 null,继续运行;
(2)、SocketChannel.read 在没有数据可读时,会返回 0,但线程不必阻塞,可以去执行其它 SocketChannel 的 read 或是去执行 ServerSocketChannel.accept;
(3)、写数据时,线程只是等待数据写入 Channel 即可,无需等 Channel 通过网络把数据发送出去; - 非阻塞模式下,即使没有连接建立和可读数据,线程仍然在不断运行,白白浪费了 cpu。
- 数据复制过程中,线程实际还是阻塞的(AIO 改进的地方)。
二、非阻塞模式服务端代码示例(使用nio实现)
-
服务端代码
package com.example.nettytest.nio.day3; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import static com.example.nettytest.nio.day1.ByteBufferUtil.debugRead; /** * @description: 非阻塞模式服务端代码示例(使用nio实现) * @author: xz * @create: 2022-08-16 21:21 */ @Slf4j public class TestServer public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException nioNoBlockServer(); /** * 使用nio来理解非阻塞模式(单线程服务端) * */ private static void nioNoBlockServer() throws IOException //1、创建ByteBuffer,容量16 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16); //2、创建服务器 ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ssc.configureBlocking(false);//ssc设置为非阻塞模式 //3、绑定监听端口 ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080)); //4、连接集合 ArrayList<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>(); while(true) //5、accept() 建立与客户端连接, SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信 SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();//启动服务端,非阻塞方法,线程会继续运行。如果没有建立连接 sc=null if(sc !=null) log.info("create connected SocketChannel... ", sc); sc.configureBlocking(false);//sc设置为非阻塞模式 //6、建立的客户端连接sc 添加到 连接集合channels中 channels.add(sc); //7、遍历连接集合 for(SocketChannel channel : channels) // 8、 接收客户端发送的数据,从channel中读取数据写入到byteBuffer中 int read = channel.read(byteBuffer);// 启动客户端,非阻塞方法,线程会继续运行,read 返回 0 if(read>0) //切换读模式 byteBuffer.flip(); //打印可读取内容(从byteBuffer中读取数据内容) debugRead(byteBuffer); //切换回写模式 byteBuffer.clear(); log.info("after read channel ... ", channel);
三、非阻塞模式客户端代码示例(使用nio实现)
-
客户端代码
package com.example.nettytest.nio.day3; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketAddress; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; /** * @description: * @author: xz * @create: 2022-08-16 21:45 */ public class TestClient public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open(); sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)); SocketAddress address = sc.getLocalAddress(); //debug模式后,点击src参数,右键选择 输入表达式sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello"));然后执行 System.out.println("waiting...");
四、工具类代码示例
-
工具类,打印输入、输出数据使用
package com.example.nettytest.nio.day1; import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import static io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil.isOutOfBounds; import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE; public class ByteBufferUtil private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256]; private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4]; private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16]; private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4]; private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256]; private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16]; static final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F]; HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F]; int i; // Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3); for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) buf.append(" "); HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString(); // Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB). for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12); buf.append(NEWLINE); buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L)); buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|'); buf.append('|'); HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString(); // Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i); // Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i; StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding); for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) buf.append(' '); BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString(); // Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.'; else BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i; /** * 打印所有内容 * @param buffer */ public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) int oldlimit = buffer.limit(); buffer.limit(buffer.capacity()); StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256); appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity()); System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+"); System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit); System.out.println(origin); buffer.limit(oldlimit); /** * 打印可读取内容 * @param buffer */ public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256); appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position()); System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+"); System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit()); System.out.println(builder); public static void main(String[] args) ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); buffer.put(new byte[]97, 98, 99, 100); debugAll(buffer); private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length + ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')'); if (length == 0) return; dump.append( " +-------------------------------------------------+" + NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" + NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+"); final int startIndex = offset; final int fullRows = length >>> 4; final int remainder = length & 0xF; // Dump the rows which have 16 bytes. for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex; // Per-row prefix. appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex); // Hex dump int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16; for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); dump.append(" |"); // ASCII dump for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); dump.append('|'); // Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes. if (remainder != 0) int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex; appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex); // Hex dump int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder; for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]); dump.append(" |"); // Ascii dump for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]); dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]); dump.append('|'); dump.append(NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+"); private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]); else dump.append(NEWLINE); dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L)); dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|'); dump.append('|'); public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
五、非阻塞模式代码示例本地调试
-
先启动服务端,然后在启动2个客户端,在服务端控制台可以看到服务端接收到了2个客户端的连接,accept方法为非阻塞方法,线程会继续运行。如下图所示:
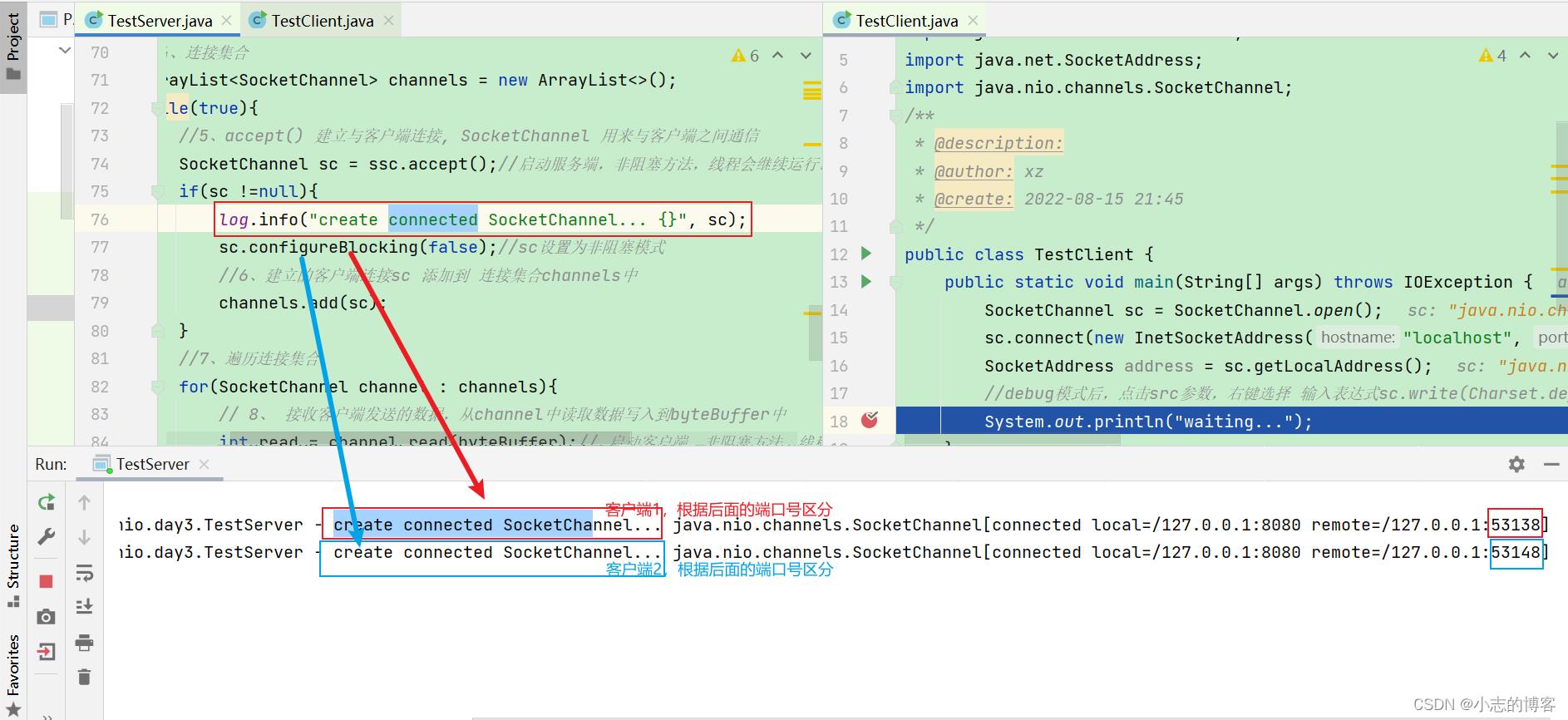
-
客户端1选择sc参数右键,点击【Evaluate Expression…】,弹出的窗口输入sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode(“111111”));表示客户端1发送数据。如下图所示:
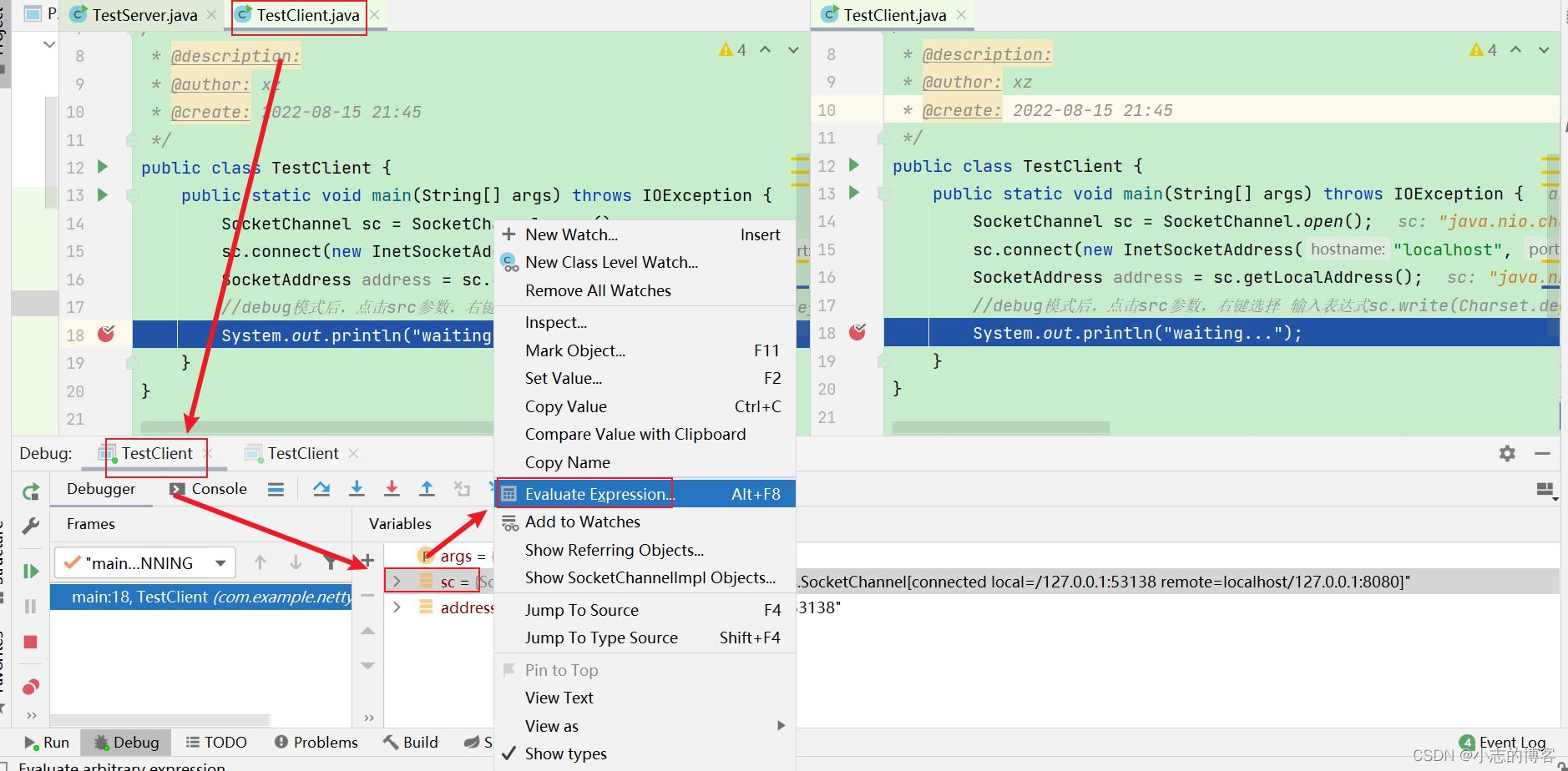
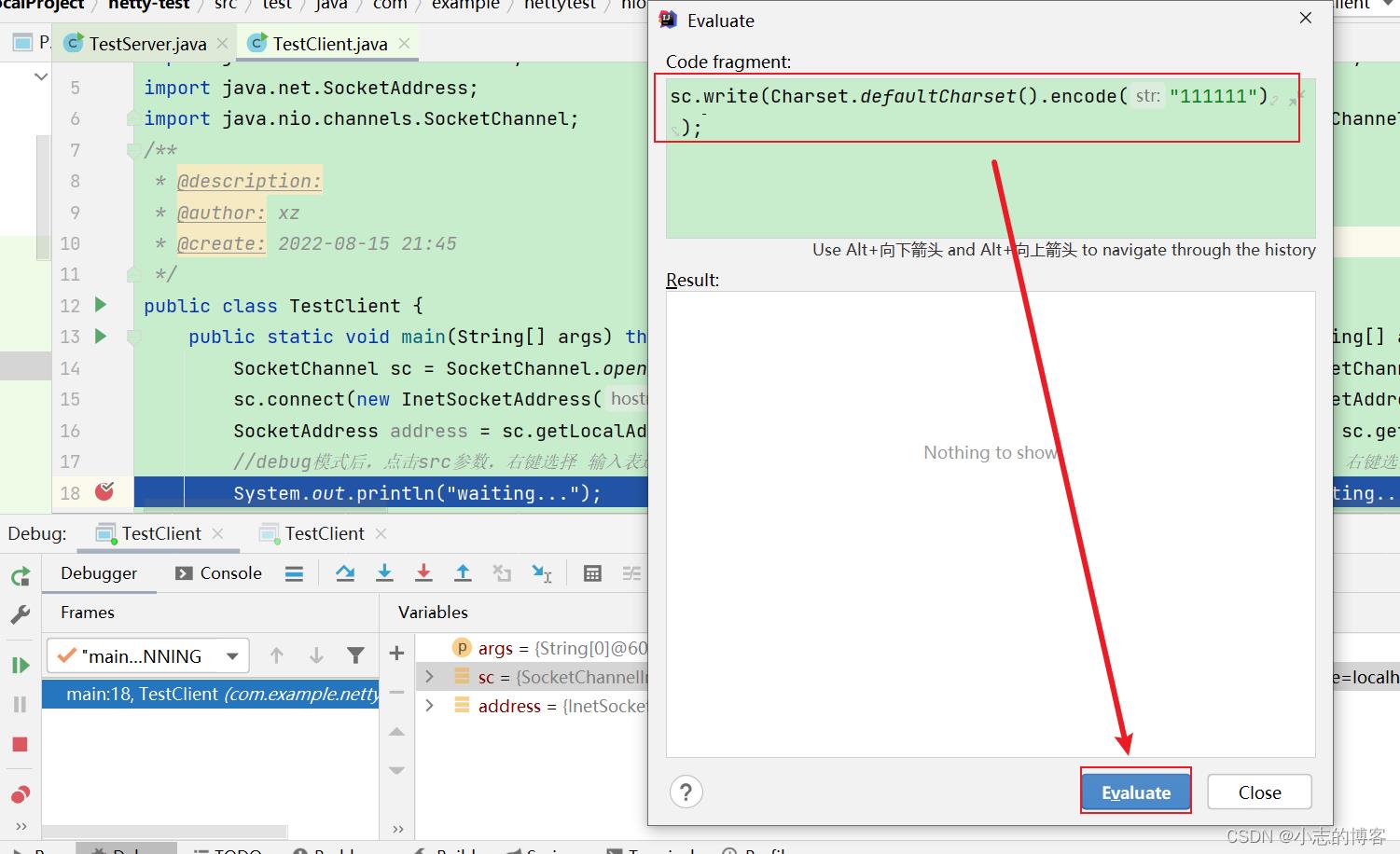
-
查看服务端,已经接收到了客户端1发送的111111数据,服务端程序已执行到完成,但是线程仍会继续运行,等待客户端发送数据。如下图所示:
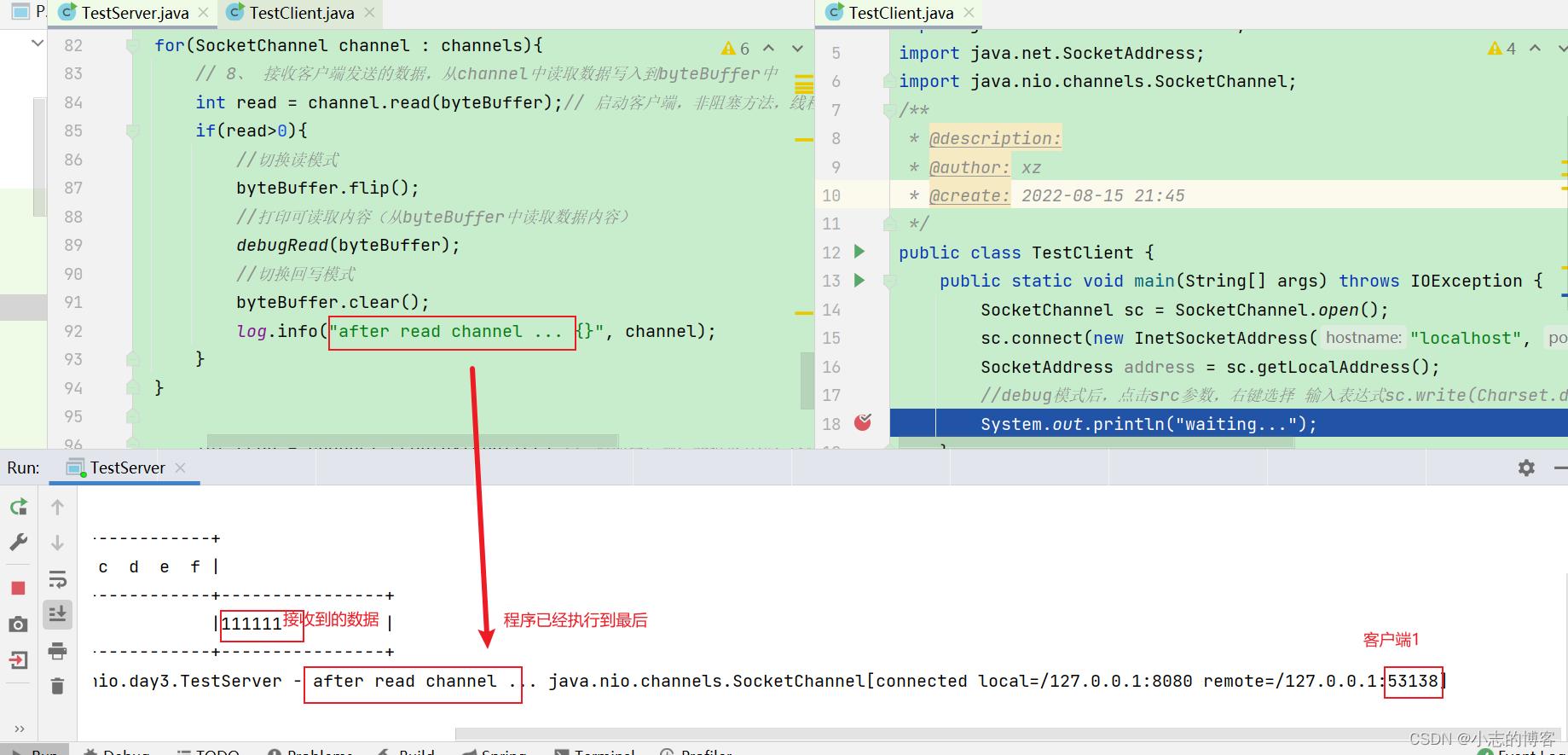
-
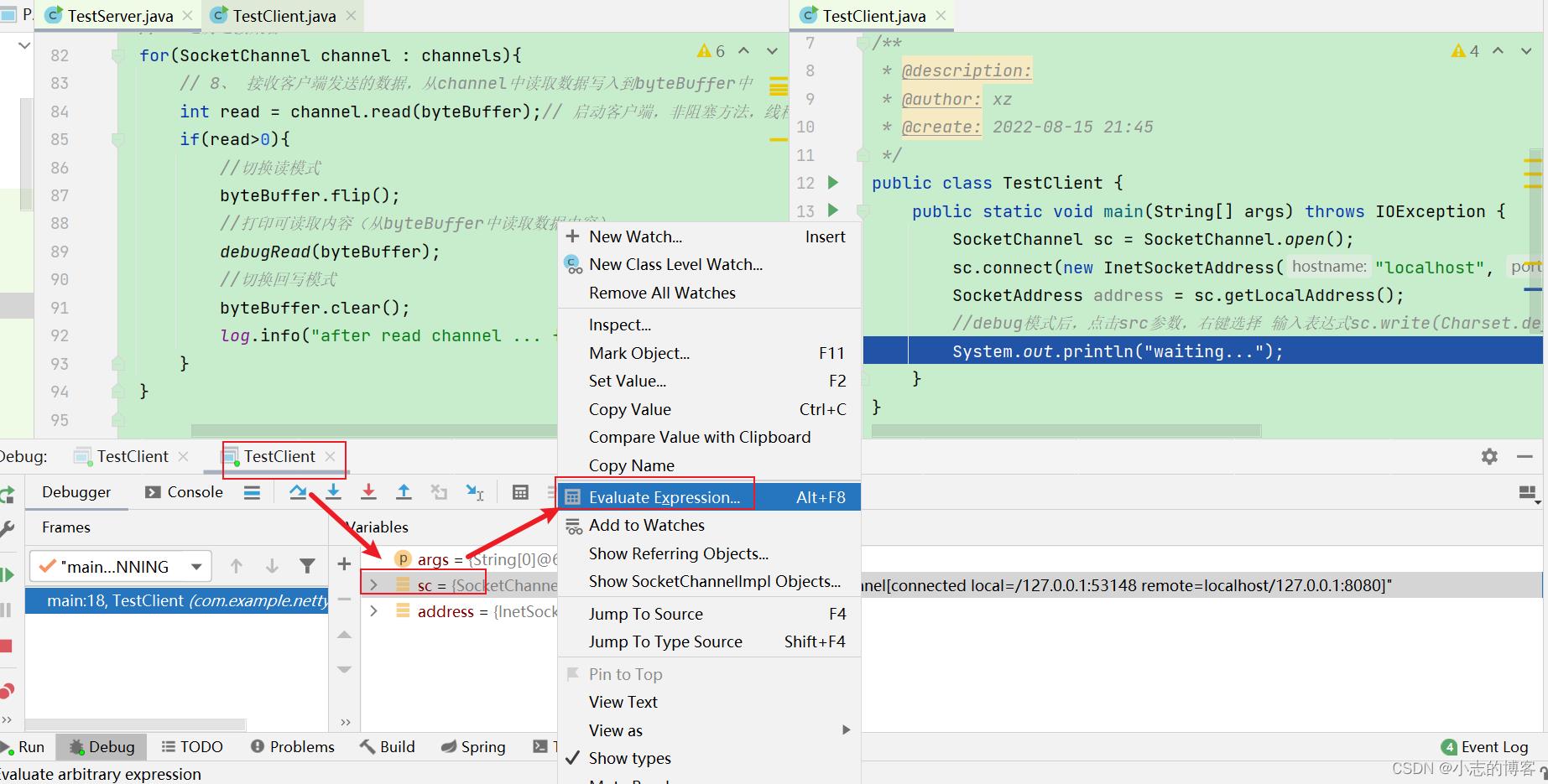
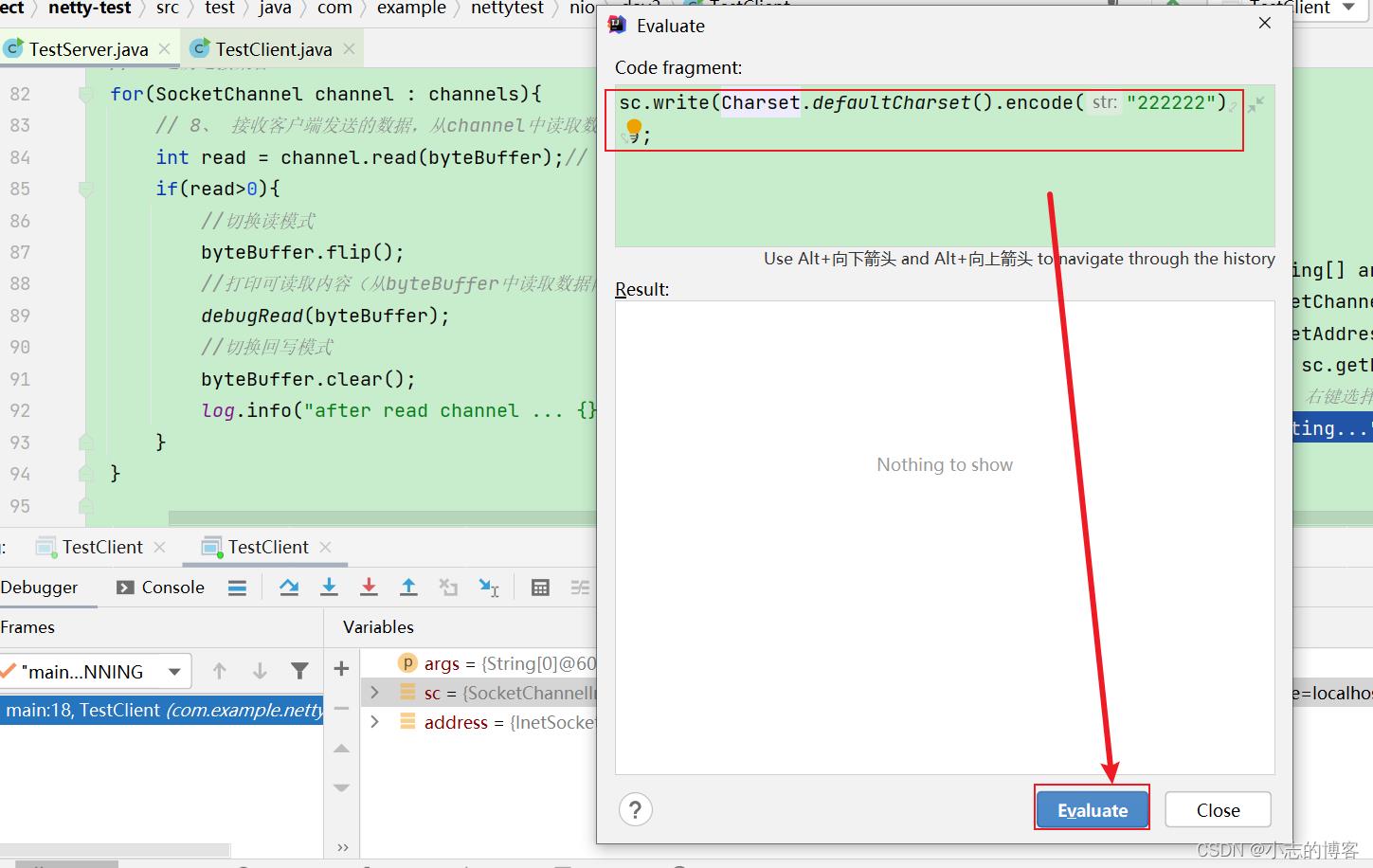
客户端2选择sc参数右键,点击【Evaluate Expression…】,弹出的窗口输入sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode(“222222”));表示客户端2发送数据。如下图所示:
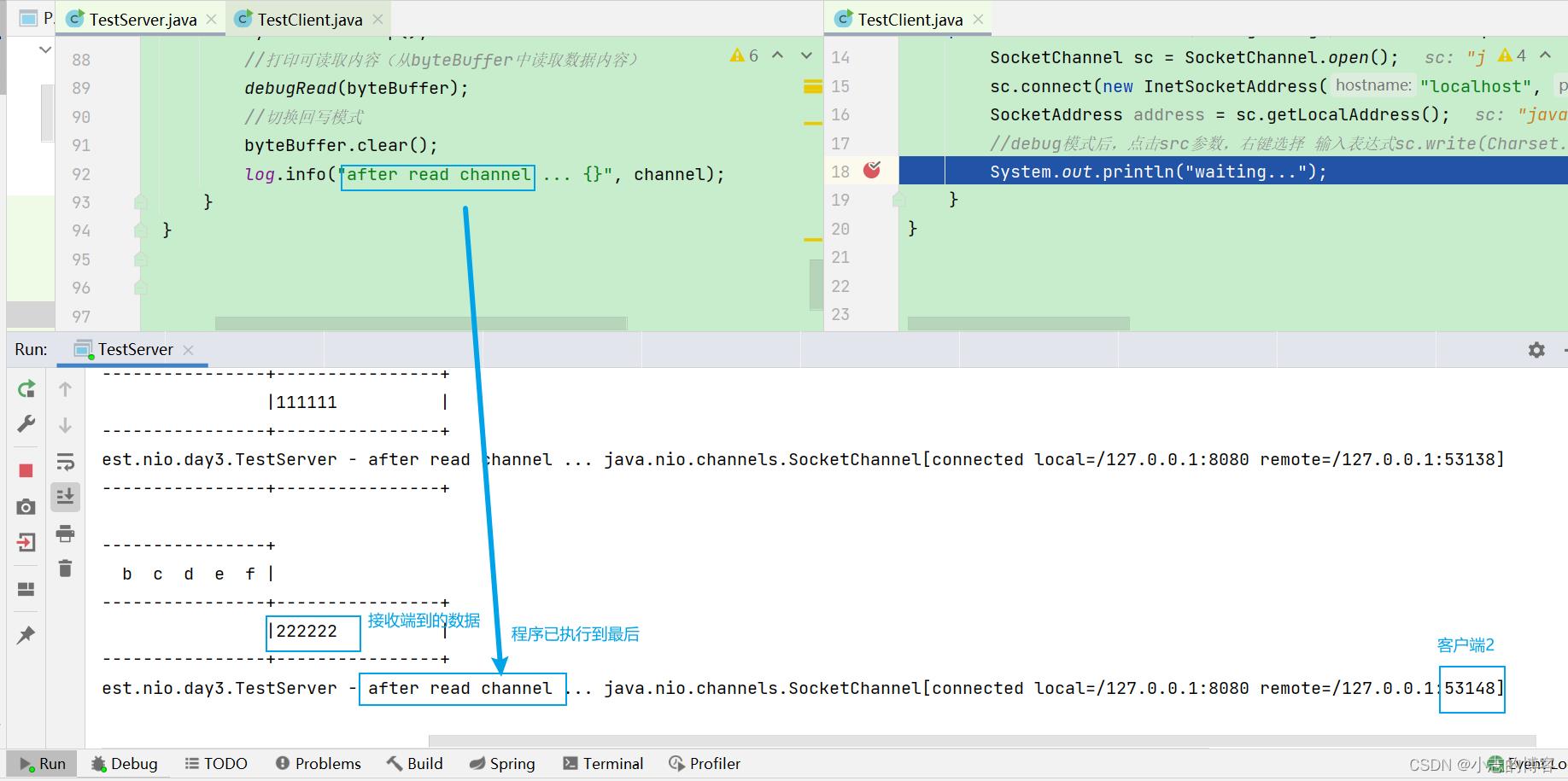
- 此时,再次查看服务端,已经接收到了客户端2发送的222222数据,服务端程序已执行到完成,但是线程仍会继续运行,等待客户端发送数据。如下图所示:
以上是关于netty为什么非阻塞的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章