ROS_安装一个第三方仿真软件包——机器人模拟世界
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ROS_安装一个第三方仿真软件包——机器人模拟世界相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A
安装依赖:
过程图:
注意:以上命令非常重要,缺少依赖将导致软件包无法正常编译和运行。
在开始编译之前,需要确保Gazebo在7.0版本以上
接着回到catkin_ws下编译:
过程图:
过程图:
首先需要解决一个问题,不然待会儿运行时会闪退:
下面是运行过程图(是的,一开始可能会遇到一个报错 [robot_spawn.launch] is neither a launch file in package [robot_sim_demo] nor is [robot_sim_demo] a launch file name The traceback for the exception was written to the log file ,然而下面的过程图已经是从报错到解决报错成功运行的过程了):
再打开一个终端,输入以下命令,用键盘控制机器人移动,聚焦控制程序窗口,按下i、j、l等按键,控制机器人移动:
过程图如下,记得运行前要刷新环境,或者用上面的方法把刷新命令添加到脚本:
呐,对比上图,我把它移到了简介牌的右边:
ROS Gazebo使用解析
Gazebo是ROS中的一个实现物理仿真的工具包,gazebo本身就是一款机器人的仿真软件,基于ODE的物理引擎,可以模拟机器人以及环境中的很多物理特性。
类似于rviz工具,在gazebo工具中也可以加载机器人模型。
加载的步骤:
- 安装gazebo工具包
- 新建工程,将包的路径位置加入到环境变量ROS_PACKAGE_PATH中
- 新建.xacro文件并编辑内容
- 新建.world文件并编辑内容
- 新建.launch文件并编辑内容
- 显示模型及其参数
其中.xacro文件包括机器人模型信息的文件,.world是gazebo环境地图文件,.launch为启动脚本。
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:/
上述指令可以临时将包的路径位置加入到环境变量ROS_PACKAGE_PATH中
安装gazebo工具包
sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-gazebo-ros-pkgs ros-indigo-gazebo-roscontrol
安装成功后,运行测试
rosrun gazebo_ros gazebo
新建工程,将包的路径位置加入到环境变量ROS_PACKAGE_PATH中
roscreate-pkg gazebo_test urdf xacro
- 增加环境变量
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:/your_path/gazebo_test
新建.xacro文件并编辑内容
- 新建文件夹urdf
mkdir -p gazebo_test/urdf
- 在urdf文件夹下编辑robot1.xacro文件如下
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro"
xmlns:sensor="http://playerstage.sourceforge.net/gazebo/xmlschema/#sensor"
xmlns:controller="http://playerstage.sourceforge.net/gazebo/xmlschema/#controller"
xmlns:interface="http://playerstage.sourceforge.net/gazebo/xmlschema/#interface"
name="robot1">
<xacro:property name="length_wheel" value="0.05" />
<xacro:property name="radius_wheel" value="0.05" />
<xacro:macro name="default_inertial" params="mass">
<inertial>
<mass value="${mass}" />
<inertia ixx="1.0" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy="1.0" iyz="0.0"
izz="1.0" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
<link name="base_footprint">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.001 0.001 0.001"/>
</geometry>
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0"/>
</visual>
<xacro:default_inertial mass="0.0001"/>
</link>
<gazebo reference="base_footprint">
<material>Gazebo/Green</material>
<turnGravityOff>false</turnGravityOff>
</gazebo>
<joint name="base_footprint_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_footprint" />
<child link="base_link" />
</joint>
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.2 .3 .1"/>
</geometry>
<origin rpy="0 0 1.54" xyz="0 0 0.05"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="0.2 .3 0.1"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<xacro:default_inertial mass="10"/>
</link>
<link name="wheel_1">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
<!-- <origin rpy="0 1.5 0" xyz="0.1 0.1 0"/> -->
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0"/>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0 0 0 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<xacro:default_inertial mass="1"/>
</link>
<link name="wheel_2">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
<!-- <origin rpy="0 1.5 0" xyz="-0.1 0.1 0"/> -->
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0"/>
<material name="black"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<xacro:default_inertial mass="1"/>
</link>
<link name="wheel_3">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
<!-- <origin rpy="0 1.5 0" xyz="0.1 -0.1 0"/> -->
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0"/>
<material name="black"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<xacro:default_inertial mass="1"/>
</link>
<link name="wheel_4">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
<!-- <origin rpy="0 1.5 0" xyz="-0.1 -0.1 0"/> -->
<origin rpy="0 0 0" xyz="0 0 0" />
<material name="black"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${length_wheel}" radius="${radius_wheel}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<xacro:default_inertial mass="1"/>
</link>
<joint name="base_to_wheel1" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="wheel_1"/>
<origin rpy="1.5707 0 0" xyz="0.1 0.15 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
</joint>
<joint name="base_to_wheel2" type="continuous">
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
<anchor xyz="0 0 0" />
<limit effort="100" velocity="100" />
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="wheel_2"/>
<origin rpy="1.5707 0 0" xyz="-0.1 0.15 0"/>
</joint>
<joint name="base_to_wheel3" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
<child link="wheel_3"/>
<origin rpy="1.5707 0 0" xyz="0.1 -0.15 0"/>
</joint>
<joint name="base_to_wheel4" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
<child link="wheel_4"/>
<origin rpy="1.5707 0 0" xyz="-0.1 -0.15 0"/>
</joint>
</robot>
新建.world文件并编辑内容
- 新建文件夹worlds
mkdir -p gazebo_test/worlds
- worlds 文件夹下新建并编辑robot.world文件
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<sdf version="1.4">
<!-- We use a custom world for the rrbot so that the camera angle is launched correctly -->
<world name="default">
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
<!-- Global light source -->
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<!-- Focus camera on tall pendulum -->
<gui fullscreen=‘0‘>
<camera name=‘user_camera‘>
<pose>4.927360 -4.376610 3.740080 0.000000 0.275643 2.356190</pose>
<view_controller>orbit</view_controller>
</camera>
</gui>
</world>
</sdf>
world文件的参数就是配置些灯光视角参数
新建.launch文件并编辑内容
- 新建lauch文件夹并新建gazebo.lauch如下
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<!-- these are the arguments you can pass this launch file, for example paused:=true -->
<arg name="paused" default="true"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" default="false"/>
<arg name="gui" default="true"/>
<arg name="headless" default="false"/>
<arg name="debug" default="true"/>
<!-- We resume the logic in empty_world.launch, changing only the name of the world to be launched -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find gazebo_test)/worlds/robot.world"/>
<arg name="debug" value="$(arg debug)" />
<arg name="gui" value="$(arg gui)" />
<arg name="paused" value="$(arg paused)"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" value="$(arg use_sim_time)"/>
<arg name="headless" value="$(arg headless)"/>
</include>
<!-- Load the URDF into the ROS Parameter Server -->
<arg name="model" />
<param name="robot_description"
command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py $(arg model)" />
<!-- Run a python script to the send a service call to gazebo_ros to spawn a URDF robot -->
<node name="urdf_spawner" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" respawn="false" output="screen"
args="-urdf -model robot1 -param robot_description -z 0.05"/>
</launch>
注意着行代表表示加载的.world文件位置,(find gazebo_test)返回的是包的绝对路径。
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find gazebo_test)/worlds/robot.world"/>
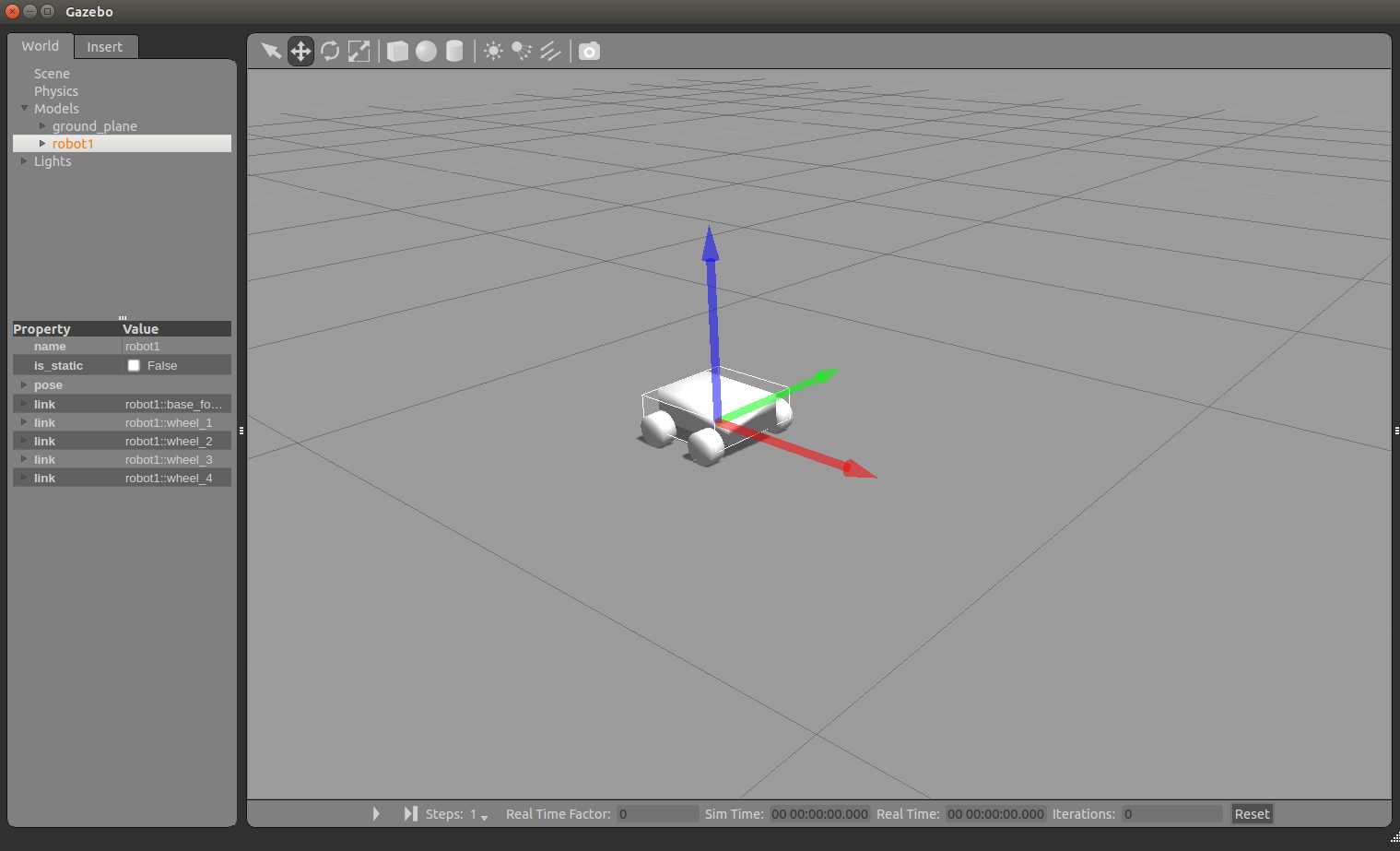
显示效果
roslaunch gazebo_test gazebo.launch model:="$(rospack find gazebo_test)/urdf/robot1.xacro" //或者使用绝对路径命令 roslaunch gazebo_test gazebo.launch model:="your_workspace/gazebo_test/urdf/robot1.xacro"
以上是关于ROS_安装一个第三方仿真软件包——机器人模拟世界的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章