LeetCode 589. N 叉树的前序遍历(迭代写法) / 2049. 统计最高分的节点数目 / 590. N 叉树的后序遍历
Posted Zephyr丶J
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode 589. N 叉树的前序遍历(迭代写法) / 2049. 统计最高分的节点数目 / 590. N 叉树的后序遍历相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
589. N 叉树的前序遍历
2022.3.10 每日一题
题目描述
给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 前序遍历 。
n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[1,3,5,6,2,4]
示例 2:
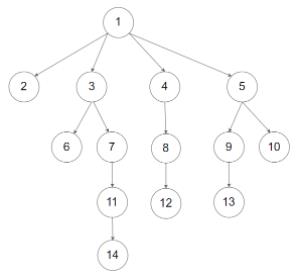
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[1,2,3,6,7,11,14,4,8,12,5,9,13,10]
提示:
节点总数在范围 [0, 10^4]内
0 <= Node.val <= 10^4
n 叉树的高度小于或等于 1000
进阶:递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-ary-tree-preorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
List<Integer> res;
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root)
res = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root);
return res;
public void inorder(Node root)
if(root == null)
return;
res.add(root.val);
List<Node> child = root.children;
for(Node node : child)
inorder(node);
迭代,无非是用栈或者队列,自己模拟一下,就出来了
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root)
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
//迭代,自己模拟了一下,需要反着加入栈中
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
//弹出底部元素
Node temp = stack.pop();
res.add(temp.val);
List<Node> child = temp.children;
if(child.isEmpty())
continue;
Collections.reverse(child);
for(Node node : child)
stack.push(node);
return res;
学习一下这种写法,就是和常规用递归写二叉树前序遍历一样
思想就是统计当前孩子节点遍历到了第几个了,然后把最新的节点放入栈中,利用栈后入先出的特性,完成迭代
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root)
//写一下和二叉树迭代一样思路的这种写法
//就是先一直往左边走,走到头了然后往右边走
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
//用双端队列代表栈,存放结点和遍历到其第几个孩子
Deque<Object[]> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.offerLast(new Object[]root, 0);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
Object[] top = stack.pollLast();
Node node = (Node)top[0];
Integer count = (Integer)top[1];
if(node == null)
continue;
//如果是第一次遍历到这个点,那么添加到结果中
if(count == 0)
res.add(node.val);
//如果还有其他孩子节点,那么添加到栈中
if(node.children.size() > count)
stack.offerLast(new Object[]node, count + 1);
stack.offerLast(new Object[]node.children.get(count), 0);
return res;
2049. 统计最高分的节点数目
2022.3.11 每日一题
题目描述
给你一棵根节点为 0 的 二叉树 ,它总共有 n 个节点,节点编号为 0 到 n - 1 。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 parents 表示这棵树,其中 parents[i] 是节点 i 的父节点。由于节点 0 是根,所以 parents[0] == -1 。
一个子树的 大小 为这个子树内节点的数目。每个节点都有一个与之关联的 分数 。求出某个节点分数的方法是,将这个节点和与它相连的边全部 删除 ,剩余部分是若干个 非空 子树,这个节点的 分数 为所有这些子树 大小的乘积 。
请你返回有 最高得分 节点的 数目 。
示例 1:
输入:parents = [-1,2,0,2,0]
输出:3
解释:
-节点 0 的分数为:3 * 1 = 3
-节点 1 的分数为:4 = 4
-节点 2 的分数为:1 * 1 * 2 = 2
-节点 3 的分数为:4 = 4
-节点 4 的分数为:4 = 4
最高得分为 4 ,有三个节点得分为 4 (分别是节点 1,3 和 4 )。
示例 2:
输入:parents = [-1,2,0]
输出:2
解释:
-节点 0 的分数为:2 = 2
-节点 1 的分数为:2 = 2
-节点 2 的分数为:1 * 1 = 1
最高分数为 2 ,有两个节点分数为 2 (分别为节点 0 和 1 )。
提示:
n == parents.length
2 <= n <= 10^5
parents[0] == -1
对于 i != 0 ,有 0 <= parents[i] <= n - 1
parents 表示一棵二叉树。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-nodes-with-the-highest-score
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
首先将一个节点相连的线删除可以把这个树分成几个部分,可以看到是三个部分,即左子树的部分,右子树的部分和父节点连接的部分,那么如果知道每个节点的大小,也就是子树的大小,那么这三个部分节点的个数就可以得到
那么怎么得到每个节点的大小呢,我想到的方法只有先构造一棵树,然后用后序遍历的方法,得到每个节点的大小,将其存储在一个哈希表中
然后遍历所有节点,计算当前结点的分数,记录最大分数及其出现的个数
需要注意的是,三个数相乘可能溢出,所以要用long类型
看了下解答,基本一样的思路,也需要先建树
class Solution
public int countHighestScoreNodes(int[] parents)
//关键问题是怎么得到每个节点的大小,也就是所包含节点的个数
//给定了所有节点的父节点,怎么才能方便的统计每个节点的大小呢
//是不是还需要先构造一棵树啊
//先构造树,然后用遍历统计每个节点的大小
int n = parents.length;
Node root = new Node(0);
Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, root);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
int p = parents[i];
Node pp = map.getOrDefault(p, new Node(p));
Node temp = map.getOrDefault(i, new Node(i));
if(pp.left == null)
pp.left = temp;
else
pp.right = temp;
map.put(p, pp);
map.put(i, temp);
//到这里构建好了一颗二叉树
//然后开始遍历,记录每个节点的大小,具体来说就是用一个哈希表记录每个节点的子节点个数
Map<Node, Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
dfs(count, root);
count.put(root, n);
//到这里,统计了所有节点的大小,然后可是统计分数
long max = 0;
int res = 0;
//对于任意一个节点删除以后,可以将树分为三个部分,左节点,右节点,还有福接地那的部分
//而左右节点的个数已经被统计出来,如果为空的话,置为1
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Node temp = map.get(i);
int ll = count.getOrDefault(temp.left, 0);
int rr = count.getOrDefault(temp.right, 0);
int pp = n - 1 - ll - rr;
ll = ll == 0 ? 1 : ll;
rr = rr == 0 ? 1 : rr;
pp = pp == 0 ? 1 : pp;
long grade = (long)ll * rr * pp;
if(grade > max)
max = grade;
res = 1;
else if(grade == max)
res++;
return res;
public int dfs(Map<Node, Integer> count, Node root)
if(root == null)
return 0;
int t = dfs(count, root.left) + dfs(count, root.right);
count.put(root, t + 1);
return t + 1;
class Node
int val;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int v)
val = v;
left = null;
right = null;
590. N 叉树的后序遍历
2022.3.12 每日一题
题目描述
给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 后序遍历 。
n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[5,6,3,2,4,1]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[2,6,14,11,7,3,12,8,4,13,9,10,5,1]
提示:
节点总数在范围 [0, 10^4] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 10^4
n 叉树的高度小于或等于 1000
进阶:递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-ary-tree-postorder-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
和前天一样的题
递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root)
//先递归
hou(root);
return res;
public void hou(Node root)
if(root == null)
return;
List<Node> list = root.children;
for(Node node : list)
hou(node);
res.add(root.val);
迭代
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root)
//迭代
//左右根,反过来就根右左
//所以和前序遍历反过来就行了
//先将根放进去,然后正序将子节点放在stack中
//例如第二个例子中,放入了2345,弹出5,放入9 10 ,弹出10...
//最后把结果翻过来就行了
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.offerLast(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
Node temp = stack.pollLast();
res.add(temp.val);
if(temp.children == null)
continue;
for(Node node : temp.children)
stack.offerLast(node);
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
通用的迭代方法:
和前序遍历的关键区别在于添加到结果集中的时机
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root)
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
Deque<Object[]> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.offerLast(new Object[]root, 0);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
Object[] top = stack.pollLast();
Integer cnt = (Integer)top[1];
Node temp = (Node)top[0];
if(temp == null)
continue;
List<Node> list = temp.children;
//如果遍历到最后一个了,加入集合中
if(cnt == list.size())
res.add(temp.val);
if(cnt < list.size())
stack.offerLast(new Object[]temp, cnt + 1);
stack.offerLast(new Object[]list.get(cnt), 0);
return res;
以上是关于LeetCode 589. N 叉树的前序遍历(迭代写法) / 2049. 统计最高分的节点数目 / 590. N 叉树的后序遍历的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
LeetCode 589. N叉树的前序遍历(N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal)
LeetCode 589. N 叉树的前序遍历(迭代写法) / 2049. 统计最高分的节点数目 / 590. N 叉树的后序遍历