Winform跨线程更新UI控件
Posted z415353144
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Winform跨线程更新UI控件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
首选拖几个控件,如图:
直接上代码:

1 public partial class Form3 : Form 2 { 3 public Form3() 4 { 5 InitializeComponent(); 6 } 7 8 9 //方法一开始 10 private async void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) 11 { 12 var t = Task.Run(() => 13 { 14 Thread.Sleep(5000); 15 return "Hello I am TimeConsumingMethod"; 16 }); 17 label1.Text = await t; 18 } 19 20 21 private void btnWrite_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) 22 { 23 var taskCount = 10000; //任务量为10000 24 pgbWrite.Maximum = taskCount; 25 pgbWrite.Value = 0; 26 27 var dataWrite = new DataWrite(); //实例化一个写入数据的类 28 dataWrite.UpdateUIDelegate += UpdateUiStatus; //绑定更新任务状态的委托 29 dataWrite.TaskCallBack += Accomplish; //绑定完成任务要调用的委托 30 31 var thread = new Thread(dataWrite.Write) {IsBackground = true}; 32 thread.Start(taskCount); 33 } 34 35 //更新UI 36 private void UpdateUiStatus(int step) 37 { 38 if (InvokeRequired) 39 { 40 Invoke(new AsycUpdateUi(delegate(int s) 41 { 42 pgbWrite.Value += s; 43 lblWriteStatus.Text = $"{pgbWrite.Value}/{pgbWrite.Maximum}"; 44 }), step); 45 } 46 else 47 { 48 pgbWrite.Value += step; 49 lblWriteStatus.Text = $"{pgbWrite.Value}/{pgbWrite.Maximum}"; 50 } 51 } 52 53 //完成任务时需要调用 54 private void Accomplish() 55 { 56 //还可以进行其他的一些完任务完成之后的逻辑处理 57 MessageBox.Show(@"任务完成"); 58 } 59 //方法一结束 60 61 //方法三 62 private delegate void AsycUpdateUi(int step); 63 64 65 ////方法二开始 66 //private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) 67 //{ 68 // var ResultTask = Task.Run(() => { 69 // Console.WriteLine("Helo I am TimeConsumingMethod. My Thread ID is :" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 70 // Thread.Sleep(5000); 71 // Console.WriteLine("Helo I am TimeConsumingMethod after Sleep(5000). My Thread ID is :" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 72 // return "Hello I am TimeConsumingMethod"; 73 // }); 74 75 // ResultTask.ContinueWith(OnDoSomthingIsComplete); 76 77 //} 78 79 //private void OnDoSomthingIsComplete(Task<string> t) 80 //{ 81 // Action action = () => { 82 // label1.Text = t.Result; 83 // }; 84 // label1.Invoke(action); 85 // Console.WriteLine("Continue Thread ID :" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 86 //} 87 ////方法二结束 88 }
页面设计器代码:

1 partial class Form3 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// Required designer variable. 5 /// </summary> 6 private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null; 7 8 /// <summary> 9 /// Clean up any resources being used. 10 /// </summary> 11 /// <param name="disposing">true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false.</param> 12 protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) 13 { 14 if (disposing && (components != null)) 15 { 16 components.Dispose(); 17 } 18 base.Dispose(disposing); 19 } 20 21 #region Windows Form Designer generated code 22 23 /// <summary> 24 /// Required method for Designer support - do not modify 25 /// the contents of this method with the code editor. 26 /// </summary> 27 private void InitializeComponent() 28 { 29 this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); 30 this.label1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); 31 this.textBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); 32 this.pgbWrite = new System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar(); 33 this.label2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); 34 this.lblWriteStatus = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); 35 this.btnWrite = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); 36 this.SuspendLayout(); 37 // 38 // button1 39 // 40 this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(126, 79); 41 this.button1.Name = "button1"; 42 this.button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23); 43 this.button1.TabIndex = 0; 44 this.button1.Text = "异步更新"; 45 this.button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true; 46 this.button1.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button1_Click); 47 // 48 // label1 49 // 50 this.label1.AutoSize = true; 51 this.label1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(141, 34); 52 this.label1.Name = "label1"; 53 this.label1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(41, 12); 54 this.label1.TabIndex = 1; 55 this.label1.Text = "label1"; 56 // 57 // textBox1 58 // 59 this.textBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(126, 120); 60 this.textBox1.Name = "textBox1"; 61 this.textBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 21); 62 this.textBox1.TabIndex = 2; 63 // 64 // pgbWrite 65 // 66 this.pgbWrite.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(143, 288); 67 this.pgbWrite.Name = "pgbWrite"; 68 this.pgbWrite.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(152, 23); 69 this.pgbWrite.TabIndex = 3; 70 // 71 // label2 72 // 73 this.label2.AutoSize = true; 74 this.label2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(84, 293); 75 this.label2.Name = "label2"; 76 this.label2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(53, 12); 77 this.label2.TabIndex = 4; 78 this.label2.Text = "进度条:"; 79 // 80 // lblWriteStatus 81 // 82 this.lblWriteStatus.AutoSize = true; 83 this.lblWriteStatus.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(298, 294); 84 this.lblWriteStatus.Name = "lblWriteStatus"; 85 this.lblWriteStatus.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(41, 12); 86 this.lblWriteStatus.TabIndex = 5; 87 this.lblWriteStatus.Text = "百分比"; 88 // 89 // btnWrite 90 // 91 this.btnWrite.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(143, 318); 92 this.btnWrite.Name = "btnWrite"; 93 this.btnWrite.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23); 94 this.btnWrite.TabIndex = 6; 95 this.btnWrite.Text = "开始执行"; 96 this.btnWrite.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true; 97 this.btnWrite.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnWrite_Click); 98 // 99 // Form3 100 // 101 this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 12F); 102 this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font; 103 this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(587, 388); 104 this.Controls.Add(this.btnWrite); 105 this.Controls.Add(this.lblWriteStatus); 106 this.Controls.Add(this.label2); 107 this.Controls.Add(this.pgbWrite); 108 this.Controls.Add(this.textBox1); 109 this.Controls.Add(this.label1); 110 this.Controls.Add(this.button1); 111 this.Name = "Form3"; 112 this.Text = "Form3"; 113 this.ResumeLayout(false); 114 this.PerformLayout(); 115 116 } 117 118 #endregion 119 120 private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1; 121 private System.Windows.Forms.Label label1; 122 private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textBox1; 123 private System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar pgbWrite; 124 private System.Windows.Forms.Label label2; 125 private System.Windows.Forms.Label lblWriteStatus; 126 private System.Windows.Forms.Button btnWrite; 127 }
其它类:

public class DataWrite { public delegate void UpdateUI(int step);//声明一个更新主线程的委托 public UpdateUI UpdateUIDelegate; public delegate void AccomplishTask();//声明一个在完成任务时通知主线程的委托 public AccomplishTask TaskCallBack; public void Write(object lineCount) { StreamWriter writeIo = new StreamWriter("text.txt", false, Encoding.GetEncoding("gb2312")); string head = "编号,省,市"; writeIo.Write(head); for (int i = 0; i < (int)lineCount; i++) { writeIo.WriteLine(i.ToString() + ",北京,顺义"); //写入一条数据,调用更新主线程ui状态的委托 UpdateUIDelegate(1); } //任务完成时通知主线程作出相应的处理 TaskCallBack(); writeIo.Close(); } }
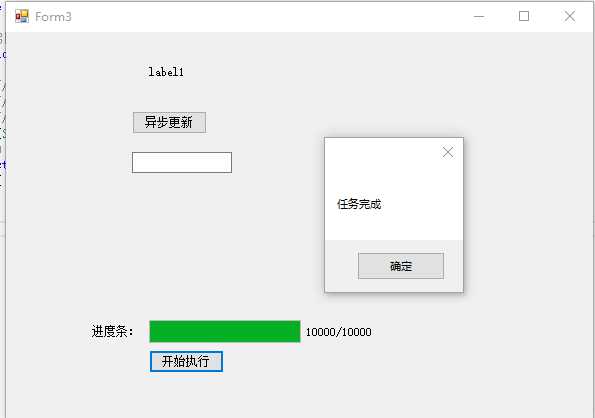
效果图:
其它方式还有:
- 通过BackgroundWorker取代Thread执行异步操作
//共分三步
//第一步:定义BackgroundWorker对象,并注册事件(执行线程主体、执行UI更新事件)
private BackgroundWorker backgroundWorker1 =null;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
backgroundWorker1 = new System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker();
//设置报告进度更新
backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
//注册线程主体方法
backgroundWorker1.DoWork += new DoWorkEventHandler(backgroundWorker1_DoWork);
//注册更新UI方法
backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged += new ProgressChangedEventHandler(backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged);
//backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted += new System.ComponentModel.RunWorkerCompletedEventHandler(this.backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted);
}
//第二步:定义执行线程主体事件
//线程主体方法
public void backgroundWorker1_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
//...执行线程任务
//在线程中更新UI(通过ReportProgress方法)
backgroundWorker1.ReportProgress(50, "This text was set safely by BackgroundWorker.");
//...执行线程其他任务
}
//第三步:定义执行UI更新事件
//UI更新方法
public void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
this.textBox1.Text = e.UserState.ToString();
}
//之后,启动线程
//启动backgroundWorker
private void setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync();
}
/*
说明:C# Winform中执行异步任务时,BackgroundWorker是个不错的选择。它是EAP(Event based Asynchronous Pattern)思想的产物,DoWork用来执行异步任务,在任务执行过程中/执行完成后,我们可以通过ProgressChanged,ProgressCompleteded事件进行线程安全的UI更新。
需要注意的是://设置报告进度更新
backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
默认情况下BackgroundWorker是不报告进度的,需要显示设置报告进度属性。
*/
- UI线程的SynchronizationContext的Post/Send方法更新

1 //共分三步 2 //第一步:获取UI线程同步上下文(在窗体构造函数或FormLoad事件中) 3 /// <summary> 4 /// UI线程的同步上下文 5 /// </summary> 6 SynchronizationContext m_SyncContext = null; 7 public Form1() 8 { 9 InitializeComponent(); 10 //获取UI线程同步上下文 11 m_SyncContext = SynchronizationContext.Current; 12 //Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false; 13 } 14 //第二步:定义线程的主体方法 15 /// <summary> 16 /// 线程的主体方法 17 /// </summary> 18 private void ThreadProcSafePost() 19 { 20 //...执行线程任务 21 22 //在线程中更新UI(通过UI线程同步上下文m_SyncContext) 23 m_SyncContext.Post(SetTextSafePost, "This text was set safely by SynchronizationContext-Post."); 24 25 //...执行线程其他任务 26 } 27 //第三步:定义更新UI控件的方法 28 /// <summary> 29 /// 更新文本框内容的方法 30 /// </summary> 31 /// <param name="text"></param> 32 private void SetTextSafePost(object text) 33 { 34 this.textBox1.Text = text.ToString(); 35 } 36 //之后,启动线程 37 /// <summary> 38 /// 启动线程按钮事件 39 /// </summary> 40 /// <param name="sender"></param> 41 /// <param name="e"></param> 42 private void setSafePostBtn_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) 43 { 44 this.demoThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.ThreadProcSafePost)); 45 this.demoThread.Start(); 46 } 47 /* 48 说明:三处加粗部分是关键。该方法的主要原理是:在线程执行过程中,需要更新到UI控件上的数据不再直接更新,而是通过UI线程上下文的Post/Send方法,将数据以异步/同步消息的形式发送到UI线程的消息队列;UI线程收到该消息后,根据消息是异步消息还是同步消息来决定通过异步/同步的方式调用SetTextSafePost方法直接更新自己的控件了。 49 50 在本质上,向UI线程发送的消息并是不简单数据,而是一条委托调用命令。 51 52 //在线程中更新UI(通过UI线程同步上下文m_SyncContext) 53 m_SyncContext.Post(SetTextSafePost, "This text was set safely by SynchronizationContext-Post."); 54 可以这样解读这行代码:向UI线程的同步上下文(m_SyncContext)中提交一个异步消息(UI线程,你收到消息后以异步的方式执行委托,调用方法SetTextSafePost,参数是“this text was ....”). 55 */
部分内容参考自:C# Winform 跨线程更新UI控件常用方法汇总
以上是关于Winform跨线程更新UI控件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
