构造,关键字,代码块,封装。
Posted -relife
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了构造,关键字,代码块,封装。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
构造方法:
[修饰符] 类名(){
}
分为有参构造/无参构造。
无参构造:
构造里没有赋值的方法为无参。无参构造会赋予默认参数。
public class Dog{
String name;
int health;
int love;
String strain;
public Dog(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
health = 100;
love = 0;
}
…
}
有参构造:
向构造方法中赋予参数为有参构造。
[修饰符] 类名(Type arg1,Type arg2,…){
// 初始化代码
}
局部变量和成员变量的优先级:
成员变量和局部变量重名时,局部变量优先级更高。
public class Dog{
String name;
int health;
int love;
String strain;
/*
public Dog(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
health = 100;
love = 0;
}
public Dog(String _name,int _health,int _love,String _strain){
name = _name;
health = _health;
love = _love;
strain = _strain;
}
public void showInfo(){
System.out.print("我的名字叫"+name);
System.out.print(",健康值"+health);
System.out.print(",亲密度"+love);
System.out.println(",我是一只"+strain);
}
}
有参构造和无参构造是方法重载的关系。
有参构造常见问题:
如果一个类提供了有参构造方法,jvm不再给类默认分配无参构造。
在开发过程中,如果开发者提供了有参构造方法,一定要习惯性的提供无参构造。
This 关键字:
this关键字表示对象本身/引用对象本身。
this访问对象属性可以解决局部变量和成员变量的同名问题。
|
public Dog2(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ System.out.println("this:"+this); this.name = name; this.health = health; this.love = love; this.strain = strain; } |
|
public class Test04{ public static void main(String[] args){
Dog2 dog = new Dog2("二狗",100,0,"土狗"); System.out.println("dog:"+dog); dog.showInfo(); } } |
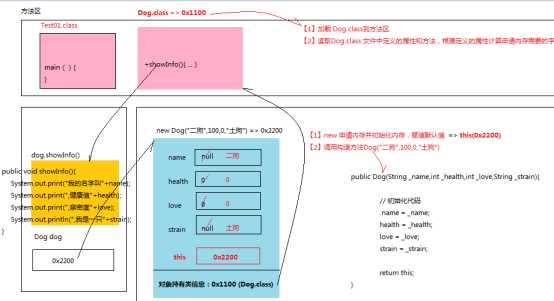
通过打印this中的引用,可以看出对象dog和this指向同一内存。
一般而言,dog用于类的外部,this用于类的内部。因为类的内部根本不知道dog变量名的存在。
方法调用内存图:
优化方法代码
|
public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字叫"+this.name); System.out.print(",健康值"+this.health); System.out.print(",亲密度"+this.love); System.out.println(",我是一只"+this.strain); } |
Static:
Static(静态,可修改变量/修饰方法)。
静态变量:
static 修饰的变量称为静态变量/静态属性,形式
|
static 类型 变量名称 [= 初始值] |
静态变量归类所有,也叫类变量,访问方式
类名.静态变量:
|
public class Car{ String brand; String type; float price;
static int count = 0;
public Car(){ Car.count++; }
public Car(String brand,String type,float price){ this.brand = brand; this.type = type; this.price = price; Car.count++; }
public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("车辆信息:"); System.out.println("品牌:"+this.brand); System.out.println("型号:"+this.type); System.out.println("价格:"+this.price); System.out.println("我是第"+Car.count+"辆车"); }
} |
|
public class Test01{ public static void main(String[] args){ Car car1 = new Car("奔驰","漏油GL300",66); car1.showInfo();
Car car2 = new Car("奔驰","漏油GL400",66); car2.showInfo();
System.out.println(Car.count); System.out.println(car1.count); System.out.println(car2.count);
} } |
静态方法访问非静态成员:
public class Car{
String brand;
String type;
float price;
static int count = 0;
public Car(){
Car.count++;
}
public Car(String brand,String type,float price){
this.brand = brand;
this.type = type;
this.price = price;
Car.count++;
}
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println("车辆信息:");
System.out.println("品牌:"+this.brand);
System.out.println("型号:"+this.type);
System.out.println("价格:"+this.price);
System.out.println("我是第"+Car.count+"辆车");
}
public static int getCarCount(){
// 在静态方法中访问实例变量
// System.out.println("品牌:"+brand);
//showInfo();
//this.showInfo();
return Car.count;
}
}
实例方法可以访问静态成员。
静态方法不能访问非静态成员。
1.1.1 类加载机制
Car car = new Car(…);
当实例化一个对象时,jvm首先把Car.class加载到方法区
[1]读取Car.class 根据声明的成员变量计算申请内存需要的字节数
[2]读取Car.class 中的静态成员,给静态变量分配空间并初始化。
new Car 申请内存得到一个car对象,此时才有对象的空间。showInfo才可以通过car对象调用。
以上是关于构造,关键字,代码块,封装。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章