Java集合类详解
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合类详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
转载至:
Java集合类详解
Java的集合就像是一种容器,可以把对个对象的引用放入容器中,其中不断可以存储不等的多个对象,还可以用于保存具有映射关系的关联数组。其中Java的集合可以分为三种体系:
- Set集合:内部元素无序,并且元素不可以重复;
- List集合:内部元素有序,且元素可以重复;
- Map集合:具有映射关系的集合
(一)Collection接口:
Collection接口是List,Set和Queue接口的父接口,该接口中定义的方法可以用户操作List,Set和Queue集合;其中主要有以下的一些方法:
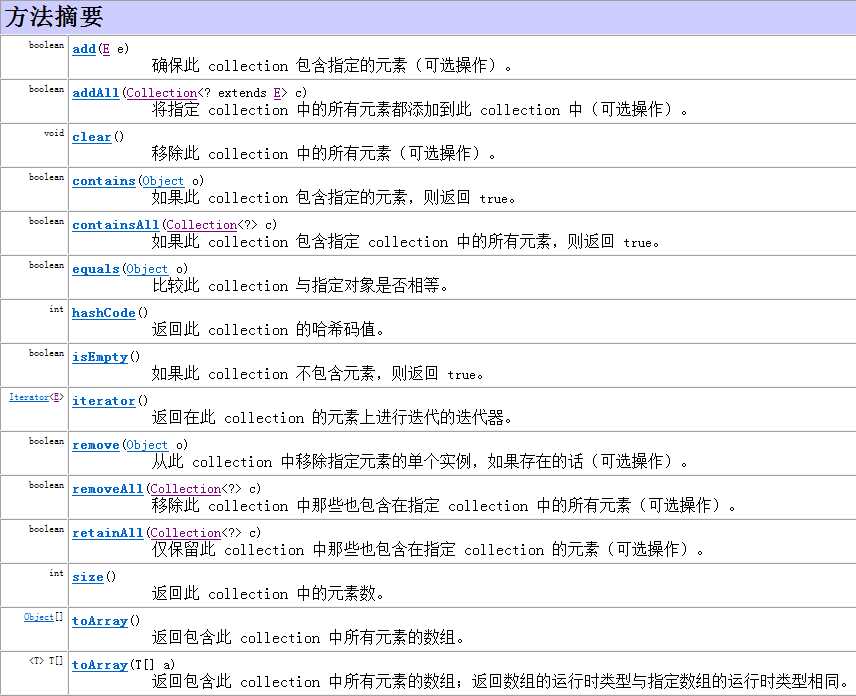
这里给出测试上述部分方法的举例:
首先给出Person类,用于放入集合中

1 package collection;
2
3 /**
4 * Created by : Zhong
5 * DATE : 2017/3/2
6 * Time : 23:06
7 * Funtion :
8 */
9 public class Person {
10 public String name;
11 public int age;
12
13
14 public Person() {
15
16 }
17
18 public Person(String name, int age) {
19 this.name = name;
20 this.age = age;
21 }
22
23
24 public String getName() {
25 return name;
26 }
27
28 public void setName(String name) {
29 this.name = name;
30 }
31
32
33 public int getAge() {
34 return age;
35 }
36
37 public void setAge(int age) {
38 this.age = age;
39 }
40
41 @Override
42 public String toString() {
43 return "Person{" +
44 "name=‘" + name + ‘\\‘‘ +
45 ", age=" + age +
46 ‘}‘;
47 }
48
49 @Override
50 public boolean equals(Object o) {
51 if (this == o) return true;
52 if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
53
54 Person person = (Person) o;
55
56 if (age != person.age) return false;
57 return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;
58
59 }
60
61 @Override
62 public int hashCode() {
63 int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
64 result = 31 * result + age;
65 return result;
66 }
67 }
然后举例说明Collection接口的相关方法:

1 package collection;
2
3 import org.junit.Test;
4
5 import java.util.ArrayList;
6 import java.util.Collection;
7 import java.util.Iterator;
8
9 /**
10 * Created by :Infaraway
11 * DATE : 2017/3/26
12 * Time : 12:35
13 * Funtion :
14 */
15 public class CollectionTest {
16
17
18
19 @Test
20 public void testTool(){
21 Collection collection = new ArrayList();
22 Collection collection2 = new ArrayList();
23 Person person = new Person("Tom", 22);
24 collection.add(person);
25 collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 25));
26 collection.add(new Person("Mike", 32));
27 collection.add("infaraway");
28
29 //1. contains(Object obj):利用equals方法比较,查看集合中有没有指定元素
30 boolean flag = collection.contains(new Person("Mike", 32));
31 System.out.println(flag);
32 flag = collection.contains(person);
33 System.out.println(flag);
34
35 //2. containsAll(Collection coll)利用equals方法比较,查看集合中有没有指定元素的集合
36 collection2.add(person);
37 collection2.add("infaraway");
38 flag = collection.containsAll(collection2);
39 System.out.println(flag);
40
41 //3. isEmpty():检查集合是否为空
42 flag = collection.isEmpty();
43 System.out.println(flag);
44
45 //4. toArray()转化集合为数组
46 Object [] object = collection.toArray();
47 System.out.println(object.length);
48
49 //toArray(T[] a)
50 }
51
52
53 /**
54 * 1. clear() 清空集合
55 * 2. remove() :移除指定的元素,通过equals() 方法在集合中查找指定的元素
56 * 如果元素存在,则移除
57 * 3. removeAll(Collection coll) 移除coll中有的元素
58 * 4. retainAll(Collection coll) 保存coll中有的元素
59 */
60 @Test
61 public void testRemove(){
62
63 Collection collection = new ArrayList();
64 Collection collection2 = new ArrayList();
65 Person person = new Person("Tom", 22);
66 collection.add(person);
67 collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 25));
68 collection.add(new Person("Mike", 32));
69 collection.add("infaraway");
70
71 /* System.out.println(collection.size());
72 collection.remove(person);*/
73
74 System.out.println(collection.size());
75
76 collection2.add(person);
77 collection2.add("infaraway");
78
79 collection.removeAll(collection2);
80 System.out.println(collection.size());
81 }
82
83 /**
84 * 在Collection中无法获取指定的元素,但是可以遍历所有的元素
85 * 1. 使用增强for循环遍历
86 * 2. 使用Iterator迭代器遍历
87 * 2.1 获取迭代器对象,调用Collection的iterator方法,获取Iterator接口的实现
88 * 2.2 调用Iterator接口方法进行迭代
89 */
90 @Test
91 public void testIterator(){
92
93 Collection collection = new ArrayList();
94 Collection collection2 = new ArrayList();
95 collection.add("infaraway");
96
97 Person person = new Person("Tom", 22);
98 collection.add(person);
99 collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 25));
100 collection.add(new Person("Mike", 32));
101
102 //使用addAll方法
103 collection2.addAll(collection);
104
105 /* System.out.println(collection.size());
106 for (Object o : collection) {
107 System.out.println(o);
108 }*/
109
110 Iterator it = collection2.iterator();
111 while(it.hasNext()){
112 System.out.println(it.next());
113 }
114
115
116 }
117
118 /**
119 * add()方法
120 */
121 @Test
122 public void testCollection(){
123 Collection collection = new ArrayList();
124 collection.add("infaraway");
125 collection.add(new Person("Tom", 22));
126 collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 25));
127 collection.add(new Person("Mike", 32));
128 }
129
130 }
(二)Set集合
Set集合不允许包含相同的元素,如果把两个相同的元素添加进入Set集合,则添加操作失败。Set集合中判断两个对象是否相同不是使用“==” 而是根据equals()方法的返回值决定;
2.1 HashSet
1)HashSet特点
HashSet 是 Set 接口的典型实现,大多数时候使用 Set 集合时都使用这个实现类。
HashSet 按 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取和查找性能。
HashSet 具有以下特点:
- 不能保证元素的排列顺序
- HashSet 不是线程安全的
- 集合元素可以使 null
当向 HashSet 集合中存入一个元素时,HashSet 会调用该对象的 hashCode() 方法来得到该对象的 hashCode 值,然后根据 hashCode 值决定该对象在 HashSet 中的存储位置。如果两个元素的 equals() 方法返回 true,但它们的 hashCode() 返回值不相等,hashSet 将会把它们存储在不同的位置,但依然可以添加成功。
重写 hashCode() 方法的基本原则
- 在程序运行时,同一个对象多次调用 hashCode() 方法应该返回相同的值
- 当两个对象的 equals() 方法比较返回 true 时,这两个对象的 hashCode() 方法的返回值也应相等
- 对象中用作 equals() 方法比较的 Field,都应该用来计算 hashCode 值
package collection; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; /** * Created by :Infaraway * DATE : 2017/3/26 * Time : 13:18 * Funtion : 测试HashSet * * 关于HashSet * 1. HashSet是Set的最典型的实现 * 2. HashSet中不能有重复的元素,判断两个元素相等的标准是equals()方法返回true * 3. HashSet根据hashCode()值来存储元素,因此不能保证元素的顺序 * 4. 如果两个对象通过equals()方法返回true 这两个对象的hashcode值应该是相同的 * 5. HashSet 是线程不安全的 */ public class HashSetTest { @Test public void testAdd(){ Set set = new HashSet(); set.add(new Person("AAA",22)); set.add(new Person("BBB",22)); set.add(new Person("CCC",27)); set.add(new Person("DDD",29)); System.out.println(set.size()); for (Object person : set) { System.out.println(person.toString()); } } }
2)子类 LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet 集合根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,但它同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的。
LinkedHashSet 性能插入性能略低于 HashSet,但在迭代访问 Set 里的全部元素时有很好的性能。
LinkedHashSet 不允许集合元素重复。
2.2 TreeSet
TreeSet 是 SortedSet 接口的实现类,TreeSet 可以确保集合元素处于排序状态。
其中TreeSet还有以下的一些常用的操作:这里就不一一列举实现了
- Comparator comparator()
- Object first() 获取第一个元素
- Object last() 获取最后一个元素
- Object lower(Object e)
- Object higher(Object e)
- SortedSet subSet(fromElement, toElement)
- SortedSet headSet(toElement)
- SortedSet tailSet(fromElement)
TreeSet 支持两种排序方法:自然排序和定制排序。默认情况下,TreeSet 采用自然排序。
1)自然排序
排序:TreeSet 会调用集合元素的 compareTo(Object obj) 方法来比较元素之间的大小关系,然后将集合元素按升序排列,如果试图把一个对象添加到 TreeSet 时,则该对象的类必须实现 Comparable 接口。实现 Comparable 的类必须实现 compareTo(Object obj) 方法,两个对象即通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法的返回值来比较大小。
实现Compareable接口代码示例:
1 package collection;
2
3 /**
4 * Created by : Zhong
5 * DATE : 2017/3/2
6 * Time : 23:06
7 * Funtion :
8 */
9 public class PersonCompare implements Comparable{
10 public String name;
11 public int age;
12 public PersonCompare() {
13 }
14 public PersonCompare(String name, int age) {
15 this.name = name;
16 this.age = age;
17 }
18 public String getName() {
19 return name;
20 }
21 public void setName(String name) {
22 this.name = name;
23 }
24 public int getAge() {
25 return age;
26 }
27 public void setAge(int age) {
28 this.age = age;
29 }
30 @Override
31 public String toString() {
32 return "Person{" +
33 "name=‘" + name + ‘\\‘‘ +
34 ", age=" + age +
35 ‘}‘;
36 }
37
38 @Override
39 public boolean equals(Object o) {
40 if (this == o) return true;
41 if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
42
43 PersonCompare person = (PersonCompare) o;
44
45 if (age != person.age) return false;
46 return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;
47
48 }
49 @Override
50 public int hashCode() {
51 int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
52 result = 31 * result + age;
53 return result;
54 }
55
56 @Override
57 public int compareTo(Object o) {
58
59 if (o instanceof PersonCompare){
60 PersonCompare personCompare = (PersonCompare) o;
61 return this.name.compareTo(personCompare.name);
62 }else{
63 throw new ClassCastException("转换类型失败!");
64 }
65 }
66 }
自然排序方法的使用示例:
/** * 自然排序情况 * * 默认情况下TreeSet要求集合中的元素必须实现Comparable接口 * Comparable接口中只有一个方法: * public int compareTo(T o) * 如果返回0 代表两个元素相等 * 如果返回正数,代表当前元素大 * 如果返回负数,代表当前元素小 * TreeSet 会调用每个元素的compareTo()方法去和集合中的每个已经有的元素比较,进而决定当前元素在集合中的位置 * */ @Test public void testTreeSet(){ TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(); treeSet.add(new PersonCompare("AAA",16)); treeSet.add(new PersonCompare("BBB",13)); treeSet.add(new PersonCompare("CCC",11)); treeSet.add(new PersonCompare("DDD",15)); for (Object o : treeSet) { System.out.println(o.toString()); } }
Comparable 的典型实现:
- BigDecimal、BigInteger 以及所有的数值型对应的包装类:按它们对应的数值大小进行比较
- Character:按字符的 UNICODE 值来进行比较
- Boolean:true 对应的包装类实例大于 false 对应的包装类实例
- String:按字符串中字符的 UNICODE 值进行比较
- Date、Time:后边的时间、日期比前面的时间、日期大
因为只有相同类的两个实例才会比较大小,所以向 TreeSet 中添加的应该是同一个类的对象。当需要把一个对象放入 TreeSet 中,重写该对象对应的 equals() 方法时,应保证该方法与 compareTo(Object obj) 方法有一致的结果:如果两个对象通过 equals() 方法比较返回 true,则通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法比较应返回 0
2)定制排序
如果需要实现定制排序,则需要在创建 TreeSet 集合对象时,提供一个 Comparator 接口的实现类对象。由该 Comparator 对象负责集合元素的排序逻辑。定制排序的优点就是让需要排序的对象不需要实现Compareable接口,减少了耦合性,是程序更加简单。
定制排序方法代码示例:
/** * 定制排序 * */ @Test public void testTreeSet2(){ //创建comparator接口的实现类对象 Comparator comparator = new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if (o1 instanceof Person && o2 instanceof Person){ Person p1 = (Person)o1; Person p2 = (Person)o2; return p1.getAge() - p2.getAge(); } throw new ClassCastException("类型转换异常"); } }; //创建TreeSet对象,传入Comparator接口的实现类对象 TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(comparator); treeSet.add(new Person("AAA",16)); treeSet.add(new Person("BBB",13)); treeSet.add(new Person("CCC",11)); treeSet.add(new Person("DDD",15)); for (Object person : treeSet) { System.out.println(person.toString()); } }
(三)List集合
3.1 概述
- List 代表一个元素有序、且可重复的集合,集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引
- List 允许使用重复元素,可以通过索引来访问指定位置的集合元素。
- List 默认按元素的添加顺序设置元素的索引。
- List 集合里添加了一些根据索引来操作集合元素的方法
- void add(int index, Object ele) 把元素添加到指定的位置 原来的元素被后移
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles) 把一组元素添加到指定的位置
- Object get(int index) 获取指定索引的元素
- int indexOf(Object obj) 获取指定对象的索引,如果元素不存在,则返回-1
- int lastIndexOf(Object obj) 获取重复的元素的最后一个索引
- Object remove(int index) 移除指定索引的元素
- Object set(int index, Object ele) 设置指定索引的元素,原来的元素被替换
- List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
3.2 ArrayList 和 Vector
ArrayList 和 Vector 是 List 接口的两个典型实现
区别:
- 是一个古老的集合,通常建议使用 ArrayList
- ArrayList 是线程不安全的,而 Vector 是线程安全的。
- 即使为保证 List 集合线程安全,也不推荐使用 Vector
Arrays.asList(…) 方法返回的 List 集合即不是 ArrayList 实例,也不是 Vector 实例。 Arrays.asList(…) 返回值是一个固定长度的 List 集合。
(四)Map集合
4.1 概述
- Map 用于保存具有映射关系的数据,因此 Map 集合里保存着两组值,一组值用于保存 Map 里的 Key,另外一组用于保存 Map 里的 Value
- Map 中的 key 和 value 都可以是任何引用类型的数据
- Map 中的 Key 不允许重复,即同一个 Map 对象的任何两个 Key 通过 equals 方法比较中返回 false
- Key 和 Value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 Key 总能找到唯一的,确定的 Value。
常用方法:
- void clear() 清空map
- boolean containsKey(Object key) 检测是否包含key值
- boolean containsValue(Object value) 检测是否包含value值
- Set<Mao.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 得到剪枝对对应的Entry 的Set
- V get(Object key)
- Set<K> keySet()
- V put(K key, V value)
- V remove(Object key) 移除指定key 的键值对
4.2 HashMap 和 Hashtable
- HashMap 和 Hashtable 是 Map 接口的两个典型实现类
- 区别:
- Hashtable 是一个古老的 Map 实现类,不建议使用
- Hashtable 是一个线程安全的 Map 实现,但 HashMap 是线程不安全的。
- Hashtable 不允许使用 null 作为 key 和 value,而 HashMap 可以
- 与 HashSet 集合不能保证元素的顺序的顺序一样,Hashtable 、HashMap 也不能保证其中 key-value 对的顺序
- Hashtable 、HashMap 判断两个 Key 相等的标准是:两个 Key 通过 equals 方法返回 true,hashCode 值也相等。
- Hashtable 、HashMap 判断两个 Value相等的标准是:两个 Value 通过 equals 方法返回 true
4.3 LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类
LinkedHashMap 可以维护 Map 的迭代顺序:迭代顺序与 Key-Value 对的插入顺序一致
1 @Test
2 public void testLinkedHashMap(){
3 Map map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
4
5 map.put("CC", new Person("CC", 18));
6 map.put("AA", new Person("AA", 10));
7 map.put("DD", new Person("DD", 12));
8 map.put("BB", new Person("BB", 16));
9
10 /*Iterator it = map.keySet().iterator();
11 while (it.hasNext()){
12 Object key = it.next();
13 Object value = map.get(key);
14 System.out.println(key+":"+value);
15 }
16 System.out.println();*/
17
18 for (Object key : map.keySet()){
19 Object value = map.get(key);
20 System.out.println(key+":"+value);
21 }
22 }
4.4 TreeMap
TreeMap 存储 Key-Value 对时,需要根据 Key 对 key-value 对进行排序。TreeMap 可以保证所有的 Key-Value 对处于有序状态。
TreeMap 的 Key 的排序:
- 自然排序:TreeMap 的所有的 Key 必须实现 Comparable 接口,而且所有的 Key 应该是同一个类的对象,否则将会抛出 ClasssCastException
- 定制排序:创建 TreeMap 时,传入一个 Comparator 对象,该对象负责对 TreeMap 中的所有 key 进行排序。此时不需要 Map 的 Key 实现 Comparable 接口
同样这里的key值也需要具有可比性
1 @Test
2 public void testTreeMap(){
3 Map map = new TreeMap<>();
4
5 //这里使用加入Compareable接口的Person类,这样才可以进行排序
6 map.put(new PersonCompare("CC", 18),"CC");
7 map.put(new PersonCompare("AA", 10),"AA");
8 map.put(new PersonCompare("DD", 12),"DD");
9 map.put(new PersonCompare("BB", 16),"BB");
10
11 for (Object key : map.keySet()){
12 Object value = map.get(key);
13 System.out.println(key+":"+value);
14 }
15 }
(五)操作集合的工具类:Collections
Collections 是一个操作 Set、List 和 Map 等集合的工具类
Collections 中提供了大量方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法
5.1 排序操作:
- reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序
- shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
- sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
- sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
- swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
5.2 查找、替换
- Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object min(Collection)
- Object min(Collection,Comparator)
- int frequency(Collection,Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
- boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
5.3 同步控制
Collections 类中提供了多个 synchronizedXxx()方法,该方法可使将指定集合包装成线程同步的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题
代码示例:
1 package collection;
2
3 import org.junit.Test;
4
5 import java.util.*;
6
7 /**
8 * Created by :Infaraway
9 * DATE : 2017/3/26
10 * Time : 16:39
11 * Funtion :
12 */
13 public class CollectionsTest {
14
15 @Test
16 public void testList(){
17 List list = new ArrayList<>();
18 list.add(new Person("AAA",16));
19 list.add(new Person("BBB",13));
20 list.add(new Person("CCC",11));
21 list.add(new Person("DDD",15));
22
23 for (Object o : list) {
24 System.out.println(o.toString());
25 }
26 //按年龄升序排列
27 //实现Comparator类进行排序操作
28 Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
29 @Override
30 public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
31 if (o1 instanceof Person && o2 instanceof Person){
32 Person p1 = (Person)o1;
33 Person p2 = (Person)o2;
34 return p1.getAge() - p2.getAge();
35 }
36 throw new ClassCastException("类型转换异常");
37 }
38 });
39
40 System.out.println();
41 for (Object o : list) {
42 System.out.println(o.toString());
43 }
44
45
46 //获取list中最小的元素
47 //要求集合中的元素都实现Compareable接口
48 Set set = new HashSet();
49
50 set.add(new PersonCompare("AAA",20));
51 set.add(new PersonCompare("BBB",34));
52 set.add(new PersonCompare("CCC",27));
53 set.add(new PersonCompare("DDD",29));
54
55 for (Object person : set) {
56 System.out.println(person.toString());
57 }
58 System.out.println();
59
60 Object object = Collections.min(set);
61 System.out.println(object.toString());
62 }
63
64 }
本文所涉及的代码可以在这里找到: https://git.oschina.net/infaraway/basisJava/tree/master/src/collection
以上是关于Java集合类详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
