关于等高线绘制和全平面坐标节点生成
Posted xiashiwendao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于等高线绘制和全平面坐标节点生成相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
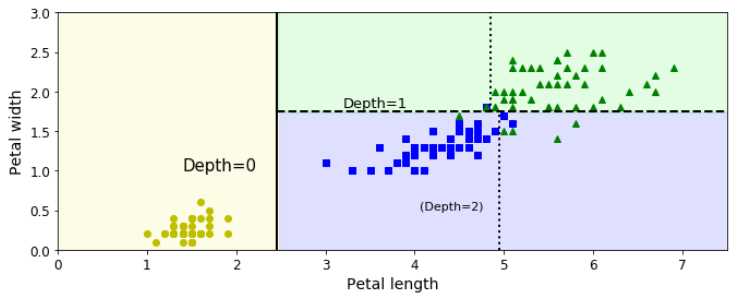
要明白机器学习画图的一个思路,就是全局生成坐标节点,然后让模型进行学习,这样可以得到一个全局的效果图(比如等高线),然后再把指定的数据扔到模型中让其学习,获取分类,然后再把这些局部点绘制出来,和整体的效果图进行比较,将会发现非常吻合。
1 from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap 2 from pprint import pprint 3 def plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, axes=[0, 7.5, 0, 3], iris=True, 4 legend=False, plot_training=True): 5 # python经典的生成全面点的实现 6 x1s = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 100) 7 x2s = np.linspace(axes[2], axes[3], 100) 8 x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(x1s, x2s) 9 X_new = np.c_[x1.ravel(), x2.ravel()] # 所有的点生成,本身是一个二维数组 10 # 预测种类,clf.repdict(X_new)其实是一个行向量(X_new每个二元坐标组将会对应一个分类,所以X_new是二维,但是y_pred是一维), 11 # reshape就是要转换成和X1相对应的形式,x1是(100, 100)的二维数组;但是,问题是为什么要reshape一下?因为在下面的等高线绘制 12 # 的内部处理中,将会生成一个(100, 100)的点集,然后根据类型进行等高线着色,那么根据每个点集的索引(比如[0][1])找到对应的 13 # 分类进行,然后决定着色种类,所以y_pred需要进行reshape为二维数组。 14 y_pred = clf.predict(X_new).reshape(x1.shape) 15 16 17 print("len(x1):{},x1.size:{}".format(len(x1), x1.size)) 18 pprint(x1) 19 print("len(x2):{},x2.size:{}".format(len(x2), x2.size)) 20 pprint(x2) 21 print("len(X_new): {}; X_new.size: {}".format(len(X_new), X_new.size)) 22 pprint(X_new) 23 tmp = clf.predict(X_new) 24 print("len(ctrl.predict(X_new)): {}; ctrl.predict(X_new).size: {}".format(len(tmp), tmp.size)) 25 pprint(tmp) 26 pprint("x1.shape:") 27 pprint(x1.shape) 28 tmp2 = tmp.reshape(x1.shape) 29 print("len(ctrl.predict(tmp2.reshape)): {}; ctrl.predict(tmp2.reshape).size: {}".format(len(tmp2), 30 tmp2.size)) 31 pprint(tmp2) 32 33 34 35 36 37 custom_cmap = ListedColormap([‘#fafab0‘,‘#9898ff‘,‘#a0faa0‘]) 38 plt.contourf(x1, x2, y_pred, alpha=0.3, cmap=custom_cmap, linewidth=10) 39 if not iris: 40 custom_cmap2 = ListedColormap([‘#7d7d58‘,‘#4c4c7f‘,‘#507d50‘]) 41 plt.contour(x1, x2, y_pred, cmap=custom_cmap2, alpha=0.8) 42 # 上面做的事情是全局的绘制等高线,那么对于指定数据(作为入参)的处理,是在下面进行的,指定数据绘制的结果应该是和等高线吻合的 43 if plot_training: 44 plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==0], X[:, 1][y==0], "yo", label="Iris-Setosa") 45 plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==1], X[:, 1][y==1], "bs", label="Iris-Versicolour") 46 plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==2], X[:, 1][y==2], "g^", label="Iris-Virginica") 47 plt.axis(axes) 48 if iris: 49 plt.xlabel("Petal length", fontsize=14) 50 plt.ylabel("Petal width", fontsize=14) 51 else: 52 plt.xlabel(r"$x_1$", fontsize=18) 53 plt.ylabel(r"$x_2$", fontsize=18, rotation=0) 54 if legend: 55 plt.legend(loc="lower right", fontsize=14) 56 57 plt.figure(figsize=(11, 4)) 58 plot_decision_boundary(tree_clf, X, y) 59 plt.plot([2.45, 2.45], [0, 3], "k-", linewidth=2) 60 plt.plot([2.45, 7.5], [1.75, 1.75], "k--", linewidth=2) 61 plt.plot([4.95, 4.95], [0, 1.75], "k:", linewidth=2) 62 plt.plot([4.85, 4.85], [1.75, 3], "k:", linewidth=2) 63 plt.text(1.40, 1.0, "Depth=0", fontsize=15) 64 plt.text(3.2, 1.80, "Depth=1", fontsize=13) 65 plt.text(4.05, 0.5, "(Depth=2)", fontsize=11) 66 67 # save_fig("decision_tree_decision_boundaries_plot") 68 plt.show()
输出内容:
len(x1):100,x1.size:10000
array([[0. , 0.07575758, 0.15151515, ..., 7.34848485, 7.42424242,
7.5 ],
[0. , 0.07575758, 0.15151515, ..., 7.34848485, 7.42424242,
7.5 ],
[0. , 0.07575758, 0.15151515, ..., 7.34848485, 7.42424242,
7.5 ],
...,
[0. , 0.07575758, 0.15151515, ..., 7.34848485, 7.42424242,
7.5 ],
[0. , 0.07575758, 0.15151515, ..., 7.34848485, 7.42424242,
7.5 ],
[0. , 0.07575758, 0.15151515, ..., 7.34848485, 7.42424242,
7.5 ]])
len(x2):100,x2.size:10000
array([[0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ],
[0.03030303, 0.03030303, 0.03030303, ..., 0.03030303, 0.03030303,
0.03030303],
[0.06060606, 0.06060606, 0.06060606, ..., 0.06060606, 0.06060606,
0.06060606],
...,
[2.93939394, 2.93939394, 2.93939394, ..., 2.93939394, 2.93939394,
2.93939394],
[2.96969697, 2.96969697, 2.96969697, ..., 2.96969697, 2.96969697,
2.96969697],
[3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. , 3. ,
3. ]])
len(X_new): 10000; X_new.size: 20000
array([[0. , 0. ],
[0.07575758, 0. ],
[0.15151515, 0. ],
...,
[7.34848485, 3. ],
[7.42424242, 3. ],
[7.5 , 3. ]])
len(ctrl.predict(X_new)): 10000; ctrl.predict(X_new).size: 10000
array([0, 0, 0, ..., 2, 2, 2])
u‘x1.shape:‘
(100L, 100L)
len(ctrl.predict(tmp2.reshape)): 100; ctrl.predict(tmp2.reshape).size: 10000
array([[0, 0, 0, ..., 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, ..., 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, ..., 1, 1, 1],
...,
[0, 0, 0, ..., 2, 2, 2],
[0, 0, 0, ..., 2, 2, 2],
[0, 0, 0, ..., 2, 2, 2]])
以上是关于关于等高线绘制和全平面坐标节点生成的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章