Kafka 温故:Kafka的消费编程模型
Posted pony1223
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kafka 温故:Kafka的消费编程模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Kafka的消费模型分为两种:
1.分区消费模型
2.分组消费模型
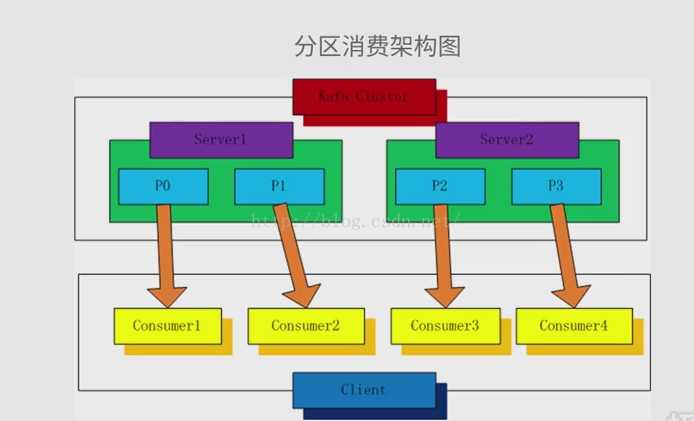
一.分区消费模型
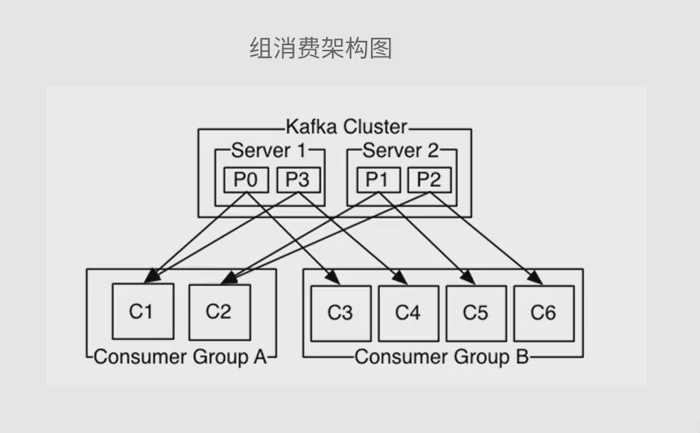
二、分组消费模型
Producer :
package cn.outofmemory.kafka; import java.util.Properties; import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer; import kafka.producer.KeyedMessage; import kafka.producer.ProducerConfig; /** * Hello world! * */ public class KafkaProducer { private final Producer<String, String> producer; public final static String TOPIC = "TEST-TOPIC"; private KafkaProducer(){ Properties props = new Properties(); //此处配置的是kafka的端口 props.put("metadata.broker.list", "192.168.193.148:9092"); //配置value的序列化类 props.put("serializer.class", "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder"); //配置key的序列化类 props.put("key.serializer.class", "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder"); //request.required.acks //0, which means that the producer never waits for an acknowledgement from the broker (the same behavior as 0.7). This option provides the lowest latency but the weakest durability guarantees (some data will be lost when a server fails). //1, which means that the producer gets an acknowledgement after the leader replica has received the data. This option provides better durability as the client waits until the server acknowledges the request as successful (only messages that were written to the now-dead leader but not yet replicated will be lost). //-1, which means that the producer gets an acknowledgement after all in-sync replicas have received the data. This option provides the best durability, we guarantee that no messages will be lost as long as at least one in sync replica remains. props.put("request.required.acks","-1"); producer = new Producer<String, String>(new ProducerConfig(props)); } void produce() { int messageNo = 1000; final int COUNT = 10000; while (messageNo < COUNT) { String key = String.valueOf(messageNo); String data = "hello kafka message " + key; producer.send(new KeyedMessage<String, String>(TOPIC, key ,data)); System.out.println(data); messageNo ++; } } public static void main( String[] args ) { new KafkaProducer().produce(); } }
Consumer
package cn.outofmemory.kafka; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import kafka.consumer.ConsumerConfig; import kafka.consumer.ConsumerIterator; import kafka.consumer.KafkaStream; import kafka.javaapi.consumer.ConsumerConnector; import kafka.serializer.StringDecoder; import kafka.utils.VerifiableProperties; public class KafkaConsumer { private final ConsumerConnector consumer; private KafkaConsumer() { Properties props = new Properties(); //zookeeper 配置 props.put("zookeeper.connect", "192.168.193.148:2181"); //group 代表一个消费组 props.put("group.id", "jd-group"); //zk连接超时 props.put("zookeeper.session.timeout.ms", "4000"); props.put("zookeeper.sync.time.ms", "200"); props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000"); props.put("auto.offset.reset", "smallest"); //序列化类 props.put("serializer.class", "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder"); ConsumerConfig config = new ConsumerConfig(props); consumer = kafka.consumer.Consumer.createJavaConsumerConnector(config); } void consume() { Map<String, Integer> topicCountMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); topicCountMap.put(KafkaProducer.TOPIC, new Integer(1)); StringDecoder keyDecoder = new StringDecoder(new VerifiableProperties()); StringDecoder valueDecoder = new StringDecoder(new VerifiableProperties()); //获取到的输入流 Map<String, List<KafkaStream<String, String>>> consumerMap = consumer.createMessageStreams(topicCountMap,keyDecoder,valueDecoder); KafkaStream<String, String> stream = consumerMap.get(KafkaProducer.TOPIC).get(0); ConsumerIterator<String, String> it = stream.iterator(); //输出接受到的消息 while (it.hasNext()) System.out.println(it.next().message()); } public static void main(String[] args) { new KafkaConsumer().consume(); } }
kafka 学习告一段落,后面进入的为Spring 温习。
以上是关于Kafka 温故:Kafka的消费编程模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章