仿真环境下移动机器人的导航
Posted hloay
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了仿真环境下移动机器人的导航相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、导航功能包简介
导航的关键包含机器人定位和路径规划两大部分,针对这两部分核心内容,ROS提供了以下两个功能包:
(1)move_base: 实现机器人导航中最优路径规划。
(2)amcl: 实现二维地图中的机器人定位。
在上述两个功能包的基础上,ROS提供一套完整的导航功能框架,如下图所示:
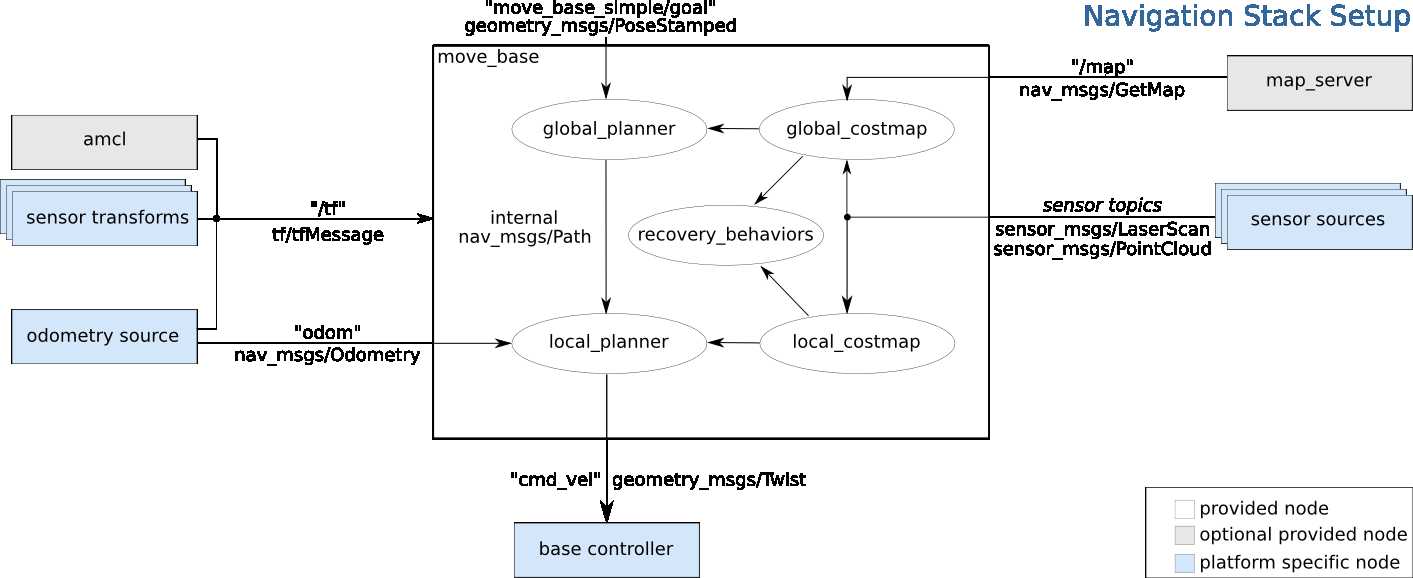
导航框架所包含的功能包很多,可以直接利用以下指令进行完整安装:
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-navigation
2、创建move_base启动文件move_base.launch,其内容如下:

1 <launch> 2 3 <param name="use_sim_time" value="true" /> 4 5 <!-- 设置地图的配置文件 --> 6 <arg name="map" default="gmapping_map.yaml" /> 7 8 <!-- 运行地图服务器,并且加载设置的地图--> 9 <node name="map_server" pkg="map_server" type="map_server" args="$(find slam_robot)/maps/$(arg map)"/> 10 11 12 <!-- fake_move_base.launch中的内容,用来加载地图的配置文件 --> 13 <node pkg="move_base" type="move_base" respawn="false" name="move_base" output="screen" clear_params="true"> 14 <rosparam file="$(find slam_robot)/config/fake/costmap_common_params.yaml" command="load" ns="global_costmap" /> 15 <rosparam file="$(find slam_robot)/config/fake/costmap_common_params.yaml" command="load" ns="local_costmap" /> 16 <rosparam file="$(find slam_robot)/config/fake/local_costmap_params.yaml" command="load" /> 17 <rosparam file="$(find slam_robot)/config/fake/global_costmap_params.yaml" command="load" /> 18 <rosparam file="$(find slam_robot)/config/fake/base_local_planner_params.yaml" command="load" /> 19 </node> 20 21 <!-- 运行虚拟定位,兼容AMCL输出 --> 22 <node pkg="fake_localization" type="fake_localization" name="fake_localization" output="screen" /> --> 23 24 25 <!-- 加入amcl启动文件,此处有了上面的节点,因此不用开启,此处注释掉 26 <include file = "$(find mrobot_navigation)/launch/amcl.launch" /> 27 --> 28 29 <!-- 对于虚拟定位,需要设置一个/odom与/map之间的静态坐标变换 --> 30 <node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="map_odom_broadcaster" args="0 0 0 0 0 0 /map /odom 100" /> 31 32 33 </launch>
其中需要加载几个导航过程的配置文件,其文件内容分别为:
(a)base_local_planner_params.yaml:

1 controller_frequency: 3.0 2 recovery_behavior_enabled: false 3 clearing_rotation_allowed: false 4 5 TrajectoryPlannerROS: 6 max_vel_x: 0.5 7 min_vel_x: 0.1 8 max_vel_y: 0.0 # zero for a differential drive robot 9 min_vel_y: 0.0 10 max_vel_theta: 1.0 11 min_vel_theta: -1.0 12 min_in_place_vel_theta: 0.4 13 escape_vel: -0.1 14 acc_lim_x: 1.5 15 acc_lim_y: 0.0 # zero for a differential drive robot 16 acc_lim_theta: 1.2 17 18 holonomic_robot: false 19 yaw_goal_tolerance: 0.1 # about 6 degrees 20 xy_goal_tolerance: 0.05 # 5 cm 21 latch_xy_goal_tolerance: false 22 pdist_scale: 0.4 23 gdist_scale: 0.8 24 meter_scoring: true 25 26 heading_lookahead: 0.325 27 heading_scoring: false 28 heading_scoring_timestep: 0.8 29 occdist_scale: 0.05 30 oscillation_reset_dist: 0.05 31 publish_cost_grid_pc: false 32 prune_plan: true 33 34 sim_time: 1.0 35 sim_granularity: 0.05 36 angular_sim_granularity: 0.1 37 vx_samples: 8 38 vy_samples: 0 # zero for a differential drive robot 39 vtheta_samples: 20 40 dwa: true 41 simple_attractor: false
(b)costmap_common_params.yaml:

1 obstacle_range: 2.5 2 raytrace_range: 3.0 3 #footprint: [[0.175, 0.175], [0.175, -0.175], [-0.175, -0.175], [-0.175, 0.175]] 4 #footprint_inflation: 0.01 5 robot_radius: 0.3 6 inflation_radius: 0.4 7 max_obstacle_height: 0.6 8 min_obstacle_height: 0.0 9 observation_sources: scan 10 scan: {data_type: LaserScan, topic: /scan, marking: true, clearing: true, expected_update_rate: 0}
(c)global_costmap_params.yaml:

1 global_costmap: 2 global_frame: map 3 robot_base_frame: base_footprint 4 update_frequency: 1.0 5 publish_frequency: 1.0 6 static_map: true 7 rolling_window: false 8 resolution: 0.01 9 transform_tolerance: 1.0 10 map_type: costmap
(d)local_costmap_params.yaml:

1 local_costmap: 2 global_frame: map 3 robot_base_frame: base_footprint 4 update_frequency: 3.0 5 publish_frequency: 1.0 6 static_map: true 7 rolling_window: false 8 width: 6.0 9 height: 6.0 10 resolution: 0.01 11 transform_tolerance: 1.0
3、启动move_base.launch文件:
sudo roslaunch slam_robot move_base.launch
4、开启rviz
以上是关于仿真环境下移动机器人的导航的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Nvidia Isaac Sim ROS机器人仿真和AMR开发环境
在ROS中开始自主机器人仿真 - 3 让turtlebot自主导航
