Python 中的 classmethod 和 staticmethod
Posted xiaohuhu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python 中的 classmethod 和 staticmethod相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
类中最常用的方法是实例方法, 即通过通过实例作为第一个参数的方法。
输出:
Reset done for: 12
DB connection made for: 12
如果使用@staticmethod就能把相关的代码放到对应的位置了.
下面这个图解释了以上代码是怎么运行的:
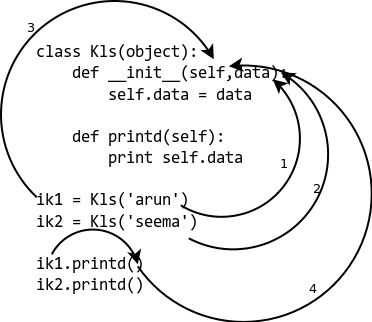
举个例子,一个基本的实例方法就向下面这个:
class Kls(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
def printd(self):
print(self.data)
ik1 = Kls(‘arun‘)
ik2 = Kls(‘seema‘)
ik1.printd()
ik2.printd()
这会给出如下的输出:
arun
seema
然后看一下代码和示例图片:

- 1,2参数传递给方法.
- 3 self参数指向当前实例自身.
- 4 我们不需要传递实例自身给方法,Python解释器自己会做这些操作的.
如果现在我们想写一些仅仅与类交互而不是和实例交互的方法会怎么样呢?
可以使用@classmethod装饰器来创建类方法.
class Kls(object):
no_inst = 0
def __init__(self):
Kls.no_inst = Kls.no_inst + 1
@classmethod
def get_no_of_instance(cls_obj):
return cls_obj.no_inst
ik1 = Kls()
ik2 = Kls()
print ik1.get_no_of_instance()
print Kls.get_no_of_instance()
输出:
2
2
这样的好处是: 不管这个方式是从实例调用还是从类调用,它都用第一个参数把类传递过来.
@staticmethod
经常有一些跟类有关系的功能但在运行时又不需要实例和类参与的情况下需要用到静态方法. 比如更改环境变量或者修改其他类的属性等能用到静态方法. 这种情况可以直接用函数解决, 但这样同样会扩散类内部的代码,造成维护困难.
比如这样:
IND = ‘ON‘
def checkind():
return (IND == ‘ON‘)
class Kls(object):
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data
def do_reset(self):
if checkind():
print(‘Reset done for:‘, self.data)
def set_db(self):
if checkind():
self.db = ‘new db connection‘
print(‘DB connection made for:‘,self.data)
ik1 = Kls(12)
ik1.do_reset()
ik1.set_db()
输出:
Reset done for: 12
DB connection made for: 12
如果使用@staticmethod就能把相关的代码放到对应的位置了.
IND = ‘ON‘
class Kls(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
@staticmethod
def checkind():
return (IND == ‘ON‘)
def do_reset(self):
if self.checkind():
print(‘Reset done for:‘, self.data)
def set_db(self):
if self.checkind():
self.db = ‘New db connection‘
print(‘DB connection made for: ‘, self.data)
ik1 = Kls(12)
ik1.do_reset()
ik1.set_db()
输出:
Reset done for: 12
DB connection made for: 12
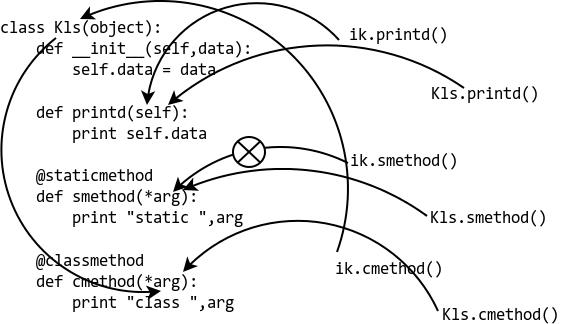
下面这个更全面的代码和图示来展示这两种方法的不同
@staticmethod 和 @classmethod的不同
class Kls(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
def printd(self):
print(self.data)
@staticmethod
def smethod(*arg):
print(‘Static:‘, arg)
@classmethod
def cmethod(*arg):
print(‘Class:‘, arg)
>>> ik = Kls(23)
>>> ik.printd()
23
>>> ik.smethod()
Static: ()
>>> ik.cmethod()
Class: (<class ‘__main__.Kls‘>,)
>>> Kls.printd()
TypeError: unbound method printd() must be called with Kls instance as first argument (got nothing instead)
>>> Kls.smethod()
Static: ()
>>> Kls.cmethod()
Class: (<class ‘__main__.Kls‘>,)
下面这个图解释了以上代码是怎么运行的:

以上是关于Python 中的 classmethod 和 staticmethod的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
python中@classmethod @staticmethod区别
Python 中的 classmethod 和 staticmethod
Python中的 @staticmethod@classmethod方法