基于周志华西瓜书数据的简单决策树(信息增益)的python代码实现
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于周志华西瓜书数据的简单决策树(信息增益)的python代码实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
数据集如下:
1 色泽 根蒂 敲声 纹理 脐部 触感 好瓜 2 青绿 蜷缩 浊响 清晰 凹陷 硬滑 是 3 乌黑 蜷缩 沉闷 清晰 凹陷 硬滑 是 4 乌黑 蜷缩 浊响 清晰 凹陷 硬滑 是 5 青绿 蜷缩 沉闷 清晰 凹陷 硬滑 是 6 浅白 蜷缩 浊响 清晰 凹陷 硬滑 是 7 青绿 稍蜷 浊响 清晰 稍凹 软粘 是 8 乌黑 稍蜷 浊响 稍糊 稍凹 软粘 是 9 乌黑 稍蜷 浊响 清晰 稍凹 硬滑 是 10 乌黑 稍蜷 沉闷 稍糊 稍凹 硬滑 否 11 青绿 硬挺 清脆 清晰 平坦 软粘 否 12 浅白 硬挺 清脆 模糊 平坦 硬滑 否 13 浅白 蜷缩 浊响 模糊 平坦 软粘 否 14 青绿 稍蜷 浊响 稍糊 凹陷 硬滑 否 15 浅白 稍蜷 沉闷 稍糊 凹陷 硬滑 否 16 乌黑 稍蜷 浊响 清晰 稍凹 软粘 否 17 浅白 蜷缩 浊响 模糊 平坦 硬滑 否 18 青绿 蜷缩 沉闷 稍糊 稍凹 硬滑 否
基于信息增益的ID3决策树的原理这里不再赘述,读者如果不明白可参考西瓜书对这部分内容的讲解。
python实现代码如下:
1 from math import log2 2 import pandas as pd 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties 5 6 # 统计label出现次数 7 def get_counts(data): 8 total = len(data) 9 results = {} 10 for d in data: 11 results[d[-1]] = results.get(d[-1], 0) + 1 12 return results, total 13 14 # 计算信息熵 15 def calcu_entropy(data): 16 results, total = get_counts(data) 17 ent = sum([-1.0*v/total*log2(v/total) for v in results.values()]) 18 return ent 19 20 # 计算每个feature的信息增益 21 def calcu_each_gain(column, update_data): 22 total = len(column) 23 grouped = update_data.iloc[:, -1].groupby(by=column) 24 temp = sum([len(g[1])/total*calcu_entropy(g[1]) for g in list(grouped)]) 25 return calcu_entropy(update_data.iloc[:, -1]) - temp 26 27 # 获取最大的信息增益的feature 28 def get_max_gain(temp_data): 29 columns_entropy = [(col, calcu_each_gain(temp_data[col], temp_data)) for col in temp_data.iloc[:, :-1]] 30 columns_entropy = sorted(columns_entropy, key=lambda f: f[1], reverse=True) 31 return columns_entropy[0] 32 33 # 去掉数据中已存在的列属性内容 34 def drop_exist_feature(data, best_feature): 35 attr = pd.unique(data[best_feature]) 36 new_data = [(nd, data[data[best_feature] == nd]) for nd in attr] 37 new_data = [(n[0], n[1].drop([best_feature], axis=1)) for n in new_data] 38 return new_data 39 40 # 获得出现最多的label 41 def get_most_label(label_list): 42 label_dict = {} 43 for l in label_list: 44 label_dict[l] = label_dict.get(l, 0) + 1 45 sorted_label = sorted(label_dict.items(), key=lambda ll: ll[1], reverse=True) 46 return sorted_label[0][0] 47 48 # 创建决策树 49 def create_tree(data_set, column_count): 50 label_list = data_set.iloc[:, -1] 51 if len(pd.unique(label_list)) == 1: 52 return label_list.values[0] 53 if all([len(pd.unique(data_set[i])) ==1 for i in data_set.iloc[:, :-1].columns]): 54 return get_most_label(label_list) 55 best_attr = get_max_gain(data_set)[0] 56 tree = {best_attr: {}} 57 exist_attr = pd.unique(data_set[best_attr]) 58 if len(exist_attr) != len(column_count[best_attr]): 59 no_exist_attr = set(column_count[best_attr]) - set(exist_attr) 60 for nea in no_exist_attr: 61 tree[best_attr][nea] = get_most_label(label_list) 62 for item in drop_exist_feature(data_set, best_attr): 63 tree[best_attr][item[0]] = create_tree(item[1], column_count) 64 return tree 65 66 # 决策树绘制这部分基本参考《机器学习实战》书内的代码以及博客 => http://blog.csdn.net/c406495762/article/details/76262487 67 # 获取树的叶子节点数目 68 def get_num_leafs(decision_tree): 69 num_leafs = 0 70 first_str = next(iter(decision_tree)) 71 second_dict = decision_tree[first_str] 72 for k in second_dict.keys(): 73 if isinstance(second_dict[k], dict): 74 num_leafs += get_num_leafs(second_dict[k]) 75 else: 76 num_leafs += 1 77 return num_leafs 78 79 # 获取树的深度 80 def get_tree_depth(decision_tree): 81 max_depth = 0 82 first_str = next(iter(decision_tree)) 83 second_dict = decision_tree[first_str] 84 for k in second_dict.keys(): 85 if isinstance(second_dict[k], dict): 86 this_depth = 1 + get_tree_depth(second_dict[k]) 87 else: 88 this_depth = 1 89 if this_depth > max_depth: 90 max_depth = this_depth 91 return max_depth 92 93 # 绘制节点 94 def plot_node(node_txt, center_pt, parent_pt, node_type): 95 arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle=‘<-‘) 96 font = FontProperties(fname=r‘C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\STXINGKA.TTF‘, size=15) 97 create_plot.ax1.annotate(node_txt, xy=parent_pt, xycoords=‘axes fraction‘, xytext=center_pt, 98 textcoords=‘axes fraction‘, va="center", ha="center", bbox=node_type, 99 arrowprops=arrow_args, FontProperties=font) 100 101 # 标注划分属性 102 def plot_mid_text(cntr_pt, parent_pt, txt_str): 103 font = FontProperties(fname=r‘C:\\Windows\\Fonts\\MSYH.TTC‘, size=10) 104 x_mid = (parent_pt[0] - cntr_pt[0]) / 2.0 + cntr_pt[0] 105 y_mid = (parent_pt[1] - cntr_pt[1]) / 2.0 + cntr_pt[1] 106 create_plot.ax1.text(x_mid, y_mid, txt_str, va="center", ha="center", color=‘red‘, FontProperties=font) 107 108 # 绘制决策树 109 def plot_tree(decision_tree, parent_pt, node_txt): 110 d_node = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8") 111 leaf_node = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc=‘0.8‘) 112 num_leafs = get_num_leafs(decision_tree) 113 depth = get_tree_depth(decision_tree) 114 first_str = next(iter(decision_tree)) 115 cntr_pt = (plot_tree.xoff + (1.0 +float(num_leafs))/2.0/plot_tree.totalW, plot_tree.yoff) 116 plot_mid_text(cntr_pt, parent_pt, node_txt) 117 plot_node(first_str, cntr_pt, parent_pt, d_node) 118 second_dict = decision_tree[first_str] 119 plot_tree.yoff = plot_tree.yoff - 1.0/plot_tree.totalD 120 for k in second_dict.keys(): 121 if isinstance(second_dict[k], dict): 122 plot_tree(second_dict[k], cntr_pt, k) 123 else: 124 plot_tree.xoff = plot_tree.xoff + 1.0/plot_tree.totalW 125 plot_node(second_dict[k], (plot_tree.xoff, plot_tree.yoff), cntr_pt, leaf_node) 126 plot_mid_text((plot_tree.xoff, plot_tree.yoff), cntr_pt, k) 127 plot_tree.yoff = plot_tree.yoff + 1.0/plot_tree.totalD 128 129 def create_plot(dtree): 130 fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor=‘white‘) 131 fig.clf() 132 axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[]) 133 create_plot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) 134 plot_tree.totalW = float(get_num_leafs(dtree)) 135 plot_tree.totalD = float(get_tree_depth(dtree)) 136 plot_tree.xoff = -0.5/plot_tree.totalW 137 plot_tree.yoff = 1.0 138 plot_tree(dtree, (0.5, 1.0), ‘‘) 139 plt.show() 140 141 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 142 my_data = pd.read_csv(‘./watermelon2.0.csv‘, encoding=‘gbk‘) 143 column_count = dict([(ds, list(pd.unique(my_data[ds]))) for ds in my_data.iloc[:, :-1].columns]) 144 d_tree = create_tree(my_data, column_count) 145 create_plot(d_tree)
绘制的决策树如下:
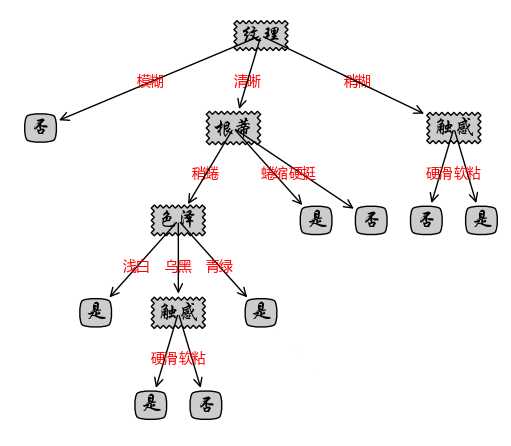
以上是关于基于周志华西瓜书数据的简单决策树(信息增益)的python代码实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Datewhale一起吃瓜 Task1周志华西瓜书第一章+第二章