Android屏幕适配
Posted Dufre.WC
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android屏幕适配相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
这篇文章来源于最近遇到的一个问题:微博在我们的平台上crash。查看log,一开始怀疑的点在找不到资源文件上,但是反编译发现资源文件存在。
android.content.res.Resources$NotFoundException: Drawable com.sina.weibo:drawable/divider_horizontal_timeline with resource ID #0x7f020664
Caused by: android.content.res.Resources$NotFoundException: File res/drawable-xxhdpi-v4/divider_horizontal_timeline.png from drawable resource ID #0x7f020664
再看Runtime Error部分的信息:
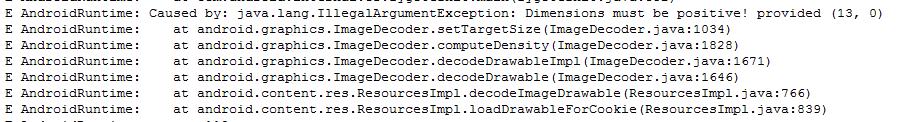
可以看到Crash发生在ImageDecoder的setTargetSize()函数,再来看代码。从这个函数,可以看到是width or height小于等于0,造成了IllegalArgumentException。这两个参数是传进来的参数。
/frameworks/base/graphics/java/android/graphics/ImageDecoder.java
public void setTargetSize(@Px @IntRange(from = 1) int width,
@Px @IntRange(from = 1) int height)
if (width <= 0 || height <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Dimensions must be positive! "
+ "provided (" + width + ", " + height + ")");
mDesiredWidth = width;
mDesiredHeight = height;
接着往下分析,从AndroidRuntime可以看到是computeDensity()调用了setTargetSize()函数,在函数底部可以看到this.setTargetSize(scaledWidth, scaledHeight);,因此scaledWidth和scaledHeight这里小于等于0。那这两个参数是怎么计算的呢?如下所示,其中mWidth和mHeight是APP传进来的资源文件的参数,系统无法修改。
int scaledWidth = (int) (mWidth * scale + 0.5f);int scaledHeight = (int) (mHeight * scale + 0.5f);
所以问题出在了scale上,其计算公式如下,其中srcDensity是APP传进来的参数(480),dstDensity(160)是系统设置的(ro.sf.lcd_density)。所以最终追到是ro.sf.lcd_density的值没有设置正确。
float scale = (float) dstDensity / srcDensity;
/frameworks/base/graphics/java/android/graphics/ImageDecoder.java
// This method may modify the decoder so it must be called prior to performing the decode
private int computeDensity(@NonNull Source src)
// if the caller changed the size then we treat the density as unknown
if (this.requestedResize())
return Bitmap.DENSITY_NONE;
final int srcDensity = src.getDensity();
if (srcDensity == Bitmap.DENSITY_NONE)
return srcDensity;
// Scaling up nine-patch divs is imprecise and is better handled
// at draw time. An app won't be relying on the internal Bitmap's
// size, so it is safe to let NinePatchDrawable handle scaling.
// mPostProcessor disables nine-patching, so behave normally if
// it is present.
if (mIsNinePatch && mPostProcessor == null)
return srcDensity;
// Special stuff for compatibility mode: if the target density is not
// the same as the display density, but the resource -is- the same as
// the display density, then don't scale it down to the target density.
// This allows us to load the system's density-correct resources into
// an application in compatibility mode, without scaling those down
// to the compatibility density only to have them scaled back up when
// drawn to the screen.
Resources res = src.getResources();
if (res != null && res.getDisplayMetrics().noncompatDensityDpi == srcDensity)
return srcDensity;
final int dstDensity = src.computeDstDensity();
if (srcDensity == dstDensity)
return srcDensity;
// For P and above, only resize if it would be a downscale. Scale up prior
// to P in case the app relies on the Bitmap's size without considering density.
if (srcDensity < dstDensity && sApiLevel >= Build.VERSION_CODES.P)
return srcDensity;
float scale = (float) dstDensity / srcDensity;
int scaledWidth = (int) (mWidth * scale + 0.5f);
int scaledHeight = (int) (mHeight * scale + 0.5f);
this.setTargetSize(scaledWidth, scaledHeight);
return dstDensity;
查看屏幕分辨率和density的值。(注意这里的density其实是dpi值,之后会解释)

基本概念
screen size
屏幕尺寸,一般指对角线的长度,单位是英寸。
For example:13.3英寸≈33.782cm
4:3长27.03cm,宽20.27cm16:9长29.44cm,宽16.56cm16:10长28.64cm,宽17.91cm
px
像素,构成图片的最小单位,1px相当于屏幕的一个像素点。两个物理尺寸相同的屏幕,像素点的个数不一定相同。
screen resolution
屏幕分辨率,屏幕的宽度上的像素点 * 高度上的像素点,例如1920*1080。表示屏幕水平方向有1920个像素点,垂直方向有1080个像素点。可以通过adb命令查看:adb shell wm size。
dpi
dpi:dots-per-inch,屏幕像素密度,指1英寸对应的像素点个数。dpi越高,画面越清晰。如下图所示。
dpi的值可以通过adb shell wm density或者adb shell getprop ro.sf.lcd_density获取。

APP的资源文件,会根据dpi区分不同的Drawable。

dp(dip)
dp(dip):Density-independent pixel,独立像素密度。这是谷歌为了方便开发人员适配而做的一个单位。谷歌规定,当dpi为160的时候,1dp = 1px。也就是说,160dpi是一个基准线。
px和dp的计算公式:
px = dp * (dpi / 160)
为什么要提出这个概念呢?举个例子,假设一个手势,使用px为单位,手机移动16px,才能识别到。
- 160dpi的设备:需要移动的长度是
16 pixels / 160 dpi = 1/10 inch = 2.5mm - 240dpi的设备:需要移动的长度是
16 pixels / 240 dpi = 1/15 inch = 1.7mm
用户会认为240dpi的设备更灵敏,但如果使用dp,会根据比例缩放,就不会有这个问题。
Density(dpi)
回到开始提出的问题,系统density的值如何计算的?
举个例子:
屏幕分辨率是1920*1080,13.3英寸。
1920 * 1080,代表对角线的像素点是(19202 + 10802)开根号,约等于2202.9。
因此dpi等于2202.9/13.3 = 165.6。
前言中提到的例子:
dstDensity== 160(ro.sf.lcd_density)srcDensity== 480(App传进来)
float scale = (float) dstDensity / srcDensity;
int scaledWidth = (int) (mWidth * scale + 0.5f);
int scaledHeight = (int) (mHeight * scale + 0.5f);
this.setTargetSize(scaledWidth, scaledHeight);
return dstDensity;
可以得出两个可能性:
- 屏幕的
density值有误(可计算) - app的
density值有误
这个问题经常发生在手机的apk装载到车机屏幕或者平板屏幕上,某些apk crash。比如apk传进来的density是适配手机的,同样的分辨率1920*1080。手机的尺寸是5 inch,但是车机或者平板的尺寸是13.3英寸左右,从而造成density的不同:
- phone:480dpi
- car or tablet:160dpi
因此在测试第三方apk的时候,最好选用适配平台的版本。
以上是关于Android屏幕适配的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章