编程艺术0002_两数相加_解法
Posted 极智视界
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了编程艺术0002_两数相加_解法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
欢迎关注我的公众号 [极智视界],获取我的更多笔记分享
和大家一起 coding,享受 coding 的乐趣
大家好,我是极智视界。本文分享 0002_两数相加 的多语言解法,包括 C++、C、python、go、java、js。
leetcode 原题链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers/
github 题解链接:https://github.com/Jeremy-J-J/leetcode
文章目录
1、题目描述
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例1
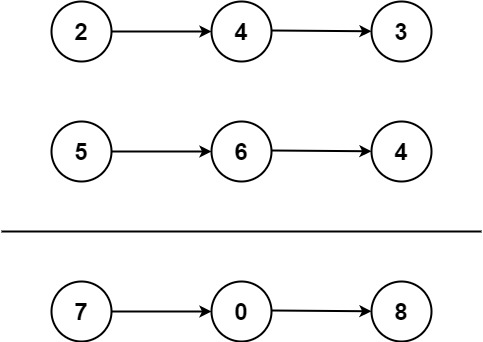
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例二
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
示例三
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 100] 内
- 0 < Node.val <= 9
- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
2、题解
2.1 C++
1> 链表 (哨兵节点)
- 执行用时 24 ms,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 76.40% 的用户
- 内存消耗 69.5 MB,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 35.15% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr)
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr)
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next)
* ;
*/
class Solution
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
ListNode* head = new ListNode(0); // 哨兵节点 head->next 是头指针
ListNode* curNode = head;
int c = 0;
while(l1 || l2 || c)
int n1 = l1 ? l1->val : 0;
int n2 = l2 ? l2->val : 0;
ListNode* node = new ListNode((n1 + n2 + c) % 10);
curNode->next = node; // 链接到下一节点
curNode = node; // 更新当前节点
l1 = l1 ? l1->next : nullptr;
l2 = l2 ? l2->next : nullptr;
c = (n1 + n2 + c) / 10;
return head->next;
;
2.2 C
1> 链表 (哨兵节点)
- 执行用时 12 ms,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 82.45% 的用户
- 内存消耗 7.7 MB,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 12.64 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ;
*/
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2)
struct ListNode *head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); // 哨兵节点 head->next 是头指针
head->next = NULL;
struct ListNode *curNode = head;
int c = 0;
while(l1 || l2 || c)
int n1 = l1 ? l1->val : 0;
int n2 = l2 ? l2->val : 0;
struct ListNode* node = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
node->next = NULL;
node->val = (n1 + n2 + c) % 10;
curNode->next = node; // 链接到下一节点
curNode = node; // 更新当前节点
l1 = l1 ? l1->next : NULL;
l2 = l2 ? l2->next : NULL;
c = (n1 + n2 + c) / 10;
return head->next;
2.3 Python
1> 链表 (哨兵节点)
- 执行用时 56 ms,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 89.04% 的用户
- 内存消耗 14.9 MB,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 79.26% 的用户
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
head = ListNode(0) # 哨兵节点 head.next是头指针
curNode = head
c = 0
while l1 or l2 or c:
n1 = l1.val if l1 else 0
n2 = l2.val if l2 else 0
node = ListNode(int((n1 + n2 + c) % 10))
curNode.next = node # 链接到下一节点
curNode = node # 更新当前节点
l1 = l1.next if l1 else None
l2 = l2.next if l2 else None
c = int((n1 + n2 + c) / 10)
return head.next
2.4 go
1> 链表 (哨兵节点)
- 执行用时 12 ms,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 44.69% 的用户
- 内存消耗 4.5 MB,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 11.70% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
*
*/
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode
var head = new(ListNode) // 哨兵节点 head.Next是头指针
head.Val = 0
var curNode = head
var c = 0
for
var n1, n2 int = 0, 0
if l1 != nil
n1 = l1.Val
if l2 != nil
n2 = l2.Val
var node = new(ListNode)
node.Val = (n1 + n2 + c) % 10
curNode.Next = node // 链接到下一节点
curNode = node // 更新当前节点
if l1 != nil
l1 = l1.Next
else
l1 = nil
if l2 != nil
l2 = l2.Next
else
l2 = nil
c = (n1 + n2 + c) / 10
if l1 == nil && l2 == nil && c == 0
break;
return head.Next
2.5 java
1> 链表 (哨兵节点)
- 执行用时 1 ms,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 100.00% 的用户
- 内存消耗 41.2 MB,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 70.99% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode()
* ListNode(int val) this.val = val;
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) this.val = val; this.next = next;
*
*/
class Solution
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
ListNode head = new ListNode(0); // 哨兵节点 head.Next是头指针
ListNode curNode = head;
int c = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null || c != 0)
int n1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int n2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
ListNode node = new ListNode((n1 + n2 + c) % 10);
curNode.next = node; // 链接到下一节点
curNode = node; // 更新到当前节点
l1 = l1 != null ? l1.next : null;
l2 = l2 != null ? l2.next : null;
c = (n1 + n2 + c) / 10;
return head.next;
2.6 js
1> 链表 (哨兵节点)
- 执行用时 96 ms,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 64.37% 的用户
- 内存消耗 45.9 MB,在所有 C++ 提交中击败了 61.34% 的用户
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next)
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
*
*/
/**
* @param ListNode l1
* @param ListNode l2
* @return ListNode
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2)
let head = new ListNode(0) // 哨兵节点 head.next是头指针
let curNode = head
let c = 0
while(l1 || l2 || c)
let n1 = l1 ? l1.val : 0
let n2 = l2 ? l2.val : 0
let node = new ListNode((n1 + n2 + c) % 10)
curNode.next = node // 链接到下一节点
curNode = node // 更新到当前节点
l1 = l1 ? l1.next : null
l2 = l2 ? l2.next : null
c = Math.floor((n1 + n2 + c) / 10)
return head.next
;
好了,以上分享和整理了 0002_两数相加 的多语言解法,希望我的分享能对你的学习有一点帮助。
【公众号传送】

扫描下方二维码即可关注我的微信公众号【极智视界】,获取我的更多经验分享,让我们用极致+极客的心态来迎接AI !
以上是关于编程艺术0002_两数相加_解法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章