关于Linux中自动化配置服务和网络接口的一些笔记
Posted 山河已无恙
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于Linux中自动化配置服务和网络接口的一些笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前面
- 嗯,准备
RHCA,学习整理这部分知识 - 所谓自动化配置服务和网络接口,其实是使用
Ansible配置 - 关于
Ansible的一些基本操作在RHCE一门课中有涉及。 - 博文内容为对
Ansible操作回顾:Ansible的简单概述及环境配置的Demo- 使用
Ansible自动化管理配置Service unit - 使用
Ansible的rhel-system-roles.network角色来自动化配置网络接口 - 阅读本文需要了解一些基本
Ansible知识
傍晚时分,你坐在屋檐下,看着天慢慢地黑下去,心里寂寞而凄凉,感到自己的生命被剥夺了。当时我是个年轻人,但我害怕这样生活下去,衰老下去。在我看来,这是比死亡更可怕的事。--------王小波
利用Ansible我们可以实现服务和网络的自动化管理,试想如果有数十台机器搭集群,需要配置firewalld、SElinux、NetworkManager,如果一台一台配就特别麻烦,而且是需要一个交互环境,即使刷脚本我们也需要一台一台远程去看状态,但是使用Ansible就很方便。
Ansible 简述
Ansible概念和架构
Ansible是一款简洁、高效的运维自动化工具。基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,只需要将ansible安装在主控机器上,就可以通过SSH协议实现针对大量受管服务器的批量化、剧本化的管理。通过Ansible实现远程控制,,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量自动化的能力。真正具有批量自动化的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。
为了方便复杂任务(包含大批量任务操作、模板、变量等资源)的重复使用,降低playbook剧本编写难度,ansible提出角色的概念,所谓角色就是预先定义好的一套目录结构。针对每一个角色,ansible会到固定的目录去调取特定的数据,使用角色时不指定hosts: 清单主机列表,而是交给调用此角色的剧本来指定.
下面我们来看一个ansible的demo
Ansible Demo
Ansible需要配置控制节点到受管节点的SSH免密和root提权,这里我们已经配置好测试下
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ssh node1 sudo id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
对于Ansible的所有配置,命令操作,都是在一个指定文件夹下进行的,Ansible在执行临时命令或者剧本时会扫描当前工作目录,满足要求才会执行,否则会发出警告。新建ansible目录,编写主机清单inventory,主机清单用于指定要控制的主机
inventory:指定操作的主机,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机,可以是域名,IP。同时支持分组,表达式等高级特性
┌──[root@control]-[~]
└─$mkdir web;cd web
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$touch inventory
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$cat > inventory << EOF
> [webs]
> node1
> EOF
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$
当前目录编写ansible配置文件,用于指定主机清单文件,连接受管机器的远程的用户名,用户的su 提权等
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ls
ansible.cfg inventory
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$cat ansible.cfg
[defaults]
# 主机清单文件,就是要控制的主机列表
inventory=inventory
# 连接受管机器的远程的用户名
remote_user=root
# 角色目录
roles_path=roles
# 设置用户的su 提权
[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
ping 受控节点测试:管控到受控的ping命令测试
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ansible webs -m ping
node1 | SUCCESS =>
"ansible_facts":
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
,
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
只需要几步,我们就通过control来控制node1机器,当然上面我们省略了ansible装包,配置SSH免密、sudo提权。
上面的命令相当于在Control机器ping node1机器,-m指定模块,默认为command模块
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ping node1
剧本实现服务自动化配置
利用Ansible实现服务自动化管理,主要涉及模块:Service、systemd和service_facts,下面我们看一个Demo
通过编写ploybook的方式,用yum、service、firewalld模块实现httpd服务的自动配置
编写剧本 vim deploy_book_web.yaml
- name: deploy web servers
hosts: webs
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: start and enable httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: set firewall to allow httpd service
firewalld:
service: http
permanent: yes #持久放行
immediate: yes #立刻放行
state: enabled
- name: index.html write
copy:
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
content: "Hello Word !\\n"
通过 ansible-playbook --syntax-check来检测剧本语法
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-playbook deploy_book_web.yaml --syntax-check
playbook: deploy_book_web.yaml
通过 ansible-playbook 执行剧本
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-playbook deploy_book_web.yaml
PLAY [deploy web servers] **********************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [install httpd] ***************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [start and enable httpd] ******************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [set firewall to allow httpd service] *****************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [index.html write] ************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************
node1 : ok=4 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
测试httpd服务
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$curl node1
Hello Word !
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$
服务自动化常用模块
软件管理模块(yum/dnf):yum/dnf 模块用于安装软件包,常用参数
- name:软件名、软件名-版本号、逗号分隔的列表、@组名、*通配符
- state:present、absent,
- list:软件名、installed、available
- name: install the nginx rpm from a remote repo
yum:
name: http://nginx.org/packages/centos/6/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-6-0.el6.ngx.n>
state: present
- name: install nginx rpm from a local file
yum:
name: /usr/local/src/nginx-release-centos-6-0.el6.ngx.noarch.rpm
state: present
- name: install the 'Development tools' package group
yum:
name: "@Development tools"
state: present
安全控制模块(firewalld):用于管理配置Linux防火墙服务 firewalld,常用参数:
- permanent(永久开启)
- port(端口)
- service(服务)、
- source(源端)
- state(状态)
- immediate(立即生效)
- firewalld:
service: https
permanent: yes
state: enabled
- name: Redirect port 443 to 8443 with Rich Rule
firewalld:
rich_rule: rule family=ipv4 forward-port port=443 protocol=tcp to-port=8443
zone: public
permanent: yes
immediate: yes
state: enabled
服务控制模块(service/systemd):代替systemctl 指令来控制服务的启动/停止/重启、开机自启动状态的设置
- name=服务名 //指定系统服务名(必选参数)
- state=“started|stoped|restarted|reloaded” //启动|停止|重启|重载服务
- enable=“yes|no” //是否开机自启
service模块用于执行基本的系统服务管理
- name: Enable service httpd, and not touch the state
service:
name: httpd
enabled: yes
systemd模块可以提供更多配置选项,例如daemon-reload。reload子命令重新加载的是当前service unit的配置文件。daemon-reload子命令是重新加载 systemd 程序的配置文件。而所有的 unit 配置文件都是作为 systemd 程序的配置文件存在的。所以需要执行daemon-reload命令的时候
- 新添加 unit 配置文件时需要执行 daemon-reload 子命令
- 有 unit 的配置文件发生变化时也需要执行 daemon-reload 子命令
- name: reload service httpd, in all cases
systemd:
name: httpd
state: reloaded
- name: just force systemd to reread configs (2.4 and above)
systemd:
daemon_reload: yes
service_facts模块:对于服务模块来讲,还可以通过service_facts模块收集有关系统上服务的信息,并将该信息存储在ansible_facts[services]变量中。
- name: populate service facts
service_facts:
- debug:
var: ansible_facts.services
- name: serviers facts
hosts: webs
tasks:
- name: collect service status facts
service_facts:
- name: display whether NetworkManager is running
debug:
var: ansible_facts['services']['NetworkManager.service']['state']
通过service_facts模块查看NetworkManager服务运行状态为running
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$vim service_facts.yaml
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-playbook service_facts.yaml --syntax-check
playbook: service_facts.yaml
┌──[root@control]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-playbook service_facts.yaml
.......
TASK [display whether NetworkManager is running] ***********************************************************************
ok: [node1] =>
"ansible_facts['services']['NetworkManager.service']['state']": "running"
........
角色实现网络自动化配置
使用ansible配置不但可以通过剧本的方式,也可以通过角色的方式来配置,自RHEL7.4开始,操作系统随附了多个Ansible角色,由rhel-system-roles软包提供。在RHEL8中,该软件包可从AppStream频道获取。系统角色的目的是标准化配置版本6.10及以上的任何RHEL主机。RHEL系统角色来源于开源Ansible Galaxy的Linux System Role项目。
系统角色默认安装在/usr/share/ansible/roles目录,Ansible可以直接引用这些角色。一般通过拷贝的方法,使用ansible配置网络常用模块network_connections来配置。对应的角色包为rhel-system-roles.network
下面我们使用角色rhel-system-roles.network,以及角色中network_connections变量配置网络。角色的执行,首先需要拷贝对应的角色包当前角色目录下,然后编写需要替换的变量文件(即tasks/main.yml中的变量),我们可以在host_vars主机变量文件夹下编写,之前需要编写执行角色的剧本。
角色环境配置
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~]
└─$dnf list rhel-system-roles
Last metadata expiration check: 0:00:58 ago on Thu 14 Apr 2022 11:42:34 PM CST.
Available Packages
rhel-system-roles.noarch 1.0-9.el8 rhel-8.1-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~]
└─$dnf -y install rhel-system-roles.noarch
Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:15 ago on Thu 14 Apr 2022 11:42:34 PM CST.
......
查看预先设置好的角色包位置。
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~]
└─$ansible-galaxy list
# /usr/share/ansible/roles
- linux-system-roles.kdump, (unknown version)
- linux-system-roles.network, (unknown version)
.......
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~]
└─$
拷贝角色到当前的roles目录下
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$mkdir roles
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-galaxy list
# /root/web/roles
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$cp -r /usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.network/ roles/network
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$cd roles/network/
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web/roles/network]
└─$ls
defaults library LICENSE meta module_utils pylintrc README.html README.md tasks tests tox.ini
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web/roles/network]
└─$
查看当前目录的ansible环境拥有的角色
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-galaxy list
# /root/web/roles
- network, (unknown version)
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$
查看network角色执行的任务剧本,这是一个写好的模板,我们配置网络只需要在文件中定向最下面的network_connections变量即可
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$cat roles/network/tasks/main.yml
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
# get service facts, used in defaults/main.yml
---
- name: Check which services are running
service_facts:
no_log: true
# needed for ansible_facts.packages
- name: Check which packages are installed
package_facts:
no_log: true
- name: Print network provider
debug:
msg: "Using network provider: network_provider "
# Depending on the plugins, checking installed packages might be slow
# for example subscription manager might slow this down
# Therefore install packages only when rpm does not find them
- name: Install packages
package:
name: " network_packages "
state: present
when:
- not network_packages is subset(ansible_facts.packages.keys())
- name: Enable and start NetworkManager
service:
name: " network_service_name "
state: started
enabled: true
when:
- network_provider == "nm"
- name: Enable network service
service:
name: " network_service_name "
enabled: true
when:
- network_provider == "initscripts"
- name: Ensure initscripts network file dependency is present
copy:
dest: /etc/sysconfig/network
content: "# Created by network system role"
force: false
when:
- network_provider == "initscripts"
- name: Configure networking connection profiles
network_connections:
provider: " network_provider | mandatory "
ignore_errors: " network_ignore_errors | default(omit) "
force_state_change: " network_force_state_change | default(omit) "
connections: " network_connections | default([]) "
- name: Re-test connectivity
ping:
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$
编写变量文件
在host_vars文件夹下定义变量
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$mkdir host_vars;cd host_vars
定义一个静态IP的网络接口配置的变量文件
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$cat host_vars/servera.yaml
通过network_connections还可以配置网桥,VLAN等其他的一些配置,更多见附录
---
network_connections:
- name: ethO-static
type: ethernet
interface_name: eth0
persistent_state: present
autoconnect: yes #自动连接
state: up
ip:
address:
- 172.25.250.10/24
- 172.25.254.10/24
gateway4: 172.25.250.254
dns:
- 172.25.250.254
- 172.25.254.254
dns_search:
- lab.example.com
- example.com
通过debug模块来测试变量
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible servera -m debug -a 'var=network_connections'
servera | SUCCESS =>
"network_connections": [
"autoconnect": true,
"interface_name": "eth0",
"ip":
"address": [
"172.25.250.10/24",
"172.25.254.10/24"
],
"dns": [
"172.25.250.254",
"172.25.254.254"
],
"dns_search": [
"lab.example.com",
"example.com"
],
"gateway4": "172.25.250.254"
,
"name": "ethO-static",
"persistent_state": "present",
"state": "up",
"type": "ethernet"
]
编写执行角色剧本
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$vim config_network.yaml
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$cat config_network.yaml
---
- name: config eth0 on servea
hosts: servara
roles:
- network
查看原本的eth0接口配置
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible servera -m shell -a "ip addr show eth0"
servera | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:00:fa:0a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.25.250.10/24 brd 172.25.250.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::984:87d2:dba7:1007/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
执行剧本
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible-playbook config_network.yaml
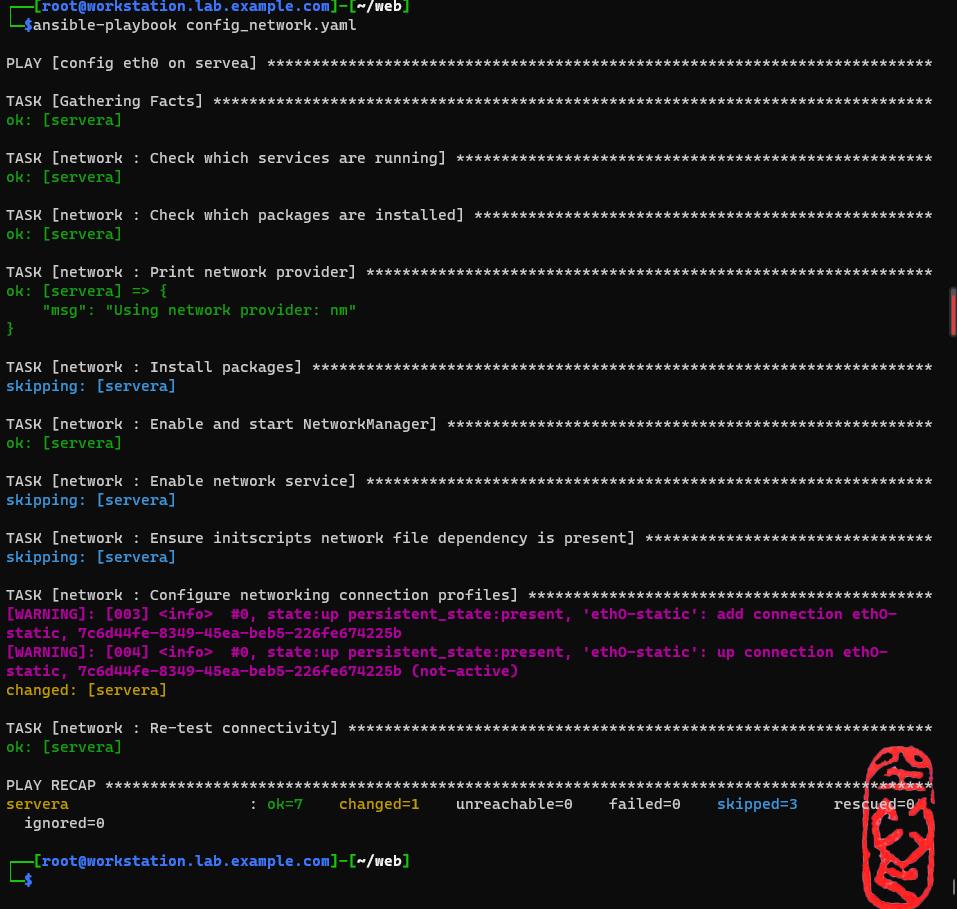
查看执行之后的网络状态
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible servera -m shell -a "ip addr show eth0"
servera | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:00:fa:0a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.25.250.10/24 brd 172.25.250.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 172.25.254.10/24 brd 172.25.254.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::e88f:e7dd:6595:4edf/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
ipv4的地址信息
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible servera -m setup -a "filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses"
servera | SUCCESS =>
"ansible_facts":
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"172.25.250.10",
"172.25.254.10"
],
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
,
"changed": false
dns信息
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible servera -m setup -a "filter=ansible_dns"
servera | SUCCESS =>
"ansible_facts":
"ansible_dns":
"nameservers": [
"172.25.250.254",
"172.25.254.254"
],
"search": [
"lab.example.com",
"example.com"
]
,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
,
"changed": false
Ansible facts
我们上面使用setup模块,这里简单介绍下,Ansible使用facts向控制节点检索有关受管主机配置的信息。一般叫系统变量,或者系统指标。通过变量,我们可以查看系统的一些详细信息,剧本的信息的收集是通过gather_facts=yes自动搜集,临时命令调用setup模块,剧本默认会调用。
# ansible 清单主机 -m setup [-a 'filter=系统指标名']
┌──[root@workstation.lab.example.com]-[~/web]
└─$ansible servera -m setup -a "filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses"
常见的网络方面的系统变量
| 网络相关系统指标 | 网络相关系统指标 |
|---|---|
| ansible_interfaces | ansible_all_ipv4_addresses |
| ansible_domain | ansible_all_ipv6_addresses |
| ansible_interfacename | ansible_default_ipv4 |
| ansible_eth0.active | ansible_default_ipv4.address |
| ansible_eth0.device | ansible default ipv4.interface |
| ansible_eth0.features | ansible_default_ipv4.gateway |
| ansible_eth0.ipv4 | ansible_default_ipv4.netmask |
| ansible_eth0.ipv6 | ansible_default_ipv4.type |
| ansible eth0.macaddress | ansible_default_ipv6 |
| ansible_fqdn | ansible_dns |
| ansible_hostname | ansible_dns.nameservers |
facts应用
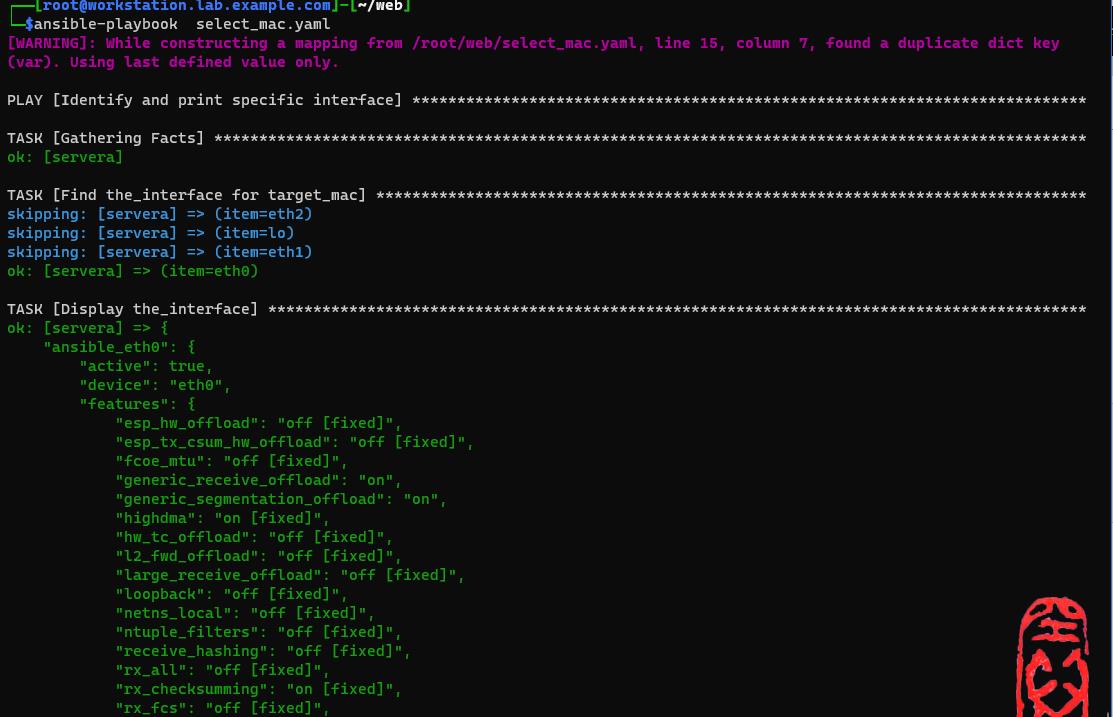
如果我们知道网络端口的MAC地址,使用Ansible来检索该接口的名称。
- name: Identify and print specific interface
hosts: servera
vars:
target_mac: "52:54:00:00:fa:0a"
tasks:
- name: Find the_interface for target_mac
set_fact: #定义变量
the_interface: "item"
when:
- ansible_facts[item]['macaddress'] is defined
- ansible_facts[item]['macaddress']==target_mac
loop: "ansible_facts['interfaces']"
- name: Display the_interface
debug:
var: the_interface
var: ansible_the_interface
附录
下面是一些网络配置角色帮助文档中的一些Demo
多次设置相同的连接配置文件:
network_connections:
- name: Wired0
type: ethernet
interface_name: eth0
ip:
dhcp4: yes
- name: Wired0
state: up
激活一个已存在的连接配置文件
network_connections:
- name: eth0
state: up
取消激活一个已存在的连接配置文件:
network_connections:
- name: eth0
state: down
创建持久连接配置文件:
network_connections:
- name: eth0
#persistent_state: present # default
type: ethernet
autoconnect: yes
mac: 00:00:5e:00:53:5d
ip:
dhcp4: yes
删除一个名为“eth0”的连接配置文件(如果它存在):
network_connections:
- name: eth0
persistent_state: absent
配置Ethernet链路:
network_connections:
- name: eth0
type: ethernet
ethernet:
autoneg: no
speed: 1000
duplex: full
创建网桥连接:
network_connections:
- name: br0
type: bridge
#interface_name: br0 # defaults to the connection name
配置网桥连接:
network_connections:
- name: internal-br0
interface_name: br0
type: bridge
ip:
dhcp4: no
auto6: no
设置 master 和 slave_type:
network_connections:
- name: br0-bond0
type: bond
interface_name: bond0
master: internal-br0
slave_type: bridge
- name: br0-bond0-eth1
type: ethernet
interface_name: eth1
master: br0-bond0
slave_type: bond
配置 VLAN:
network_connections:
- name: eth1-profile
autoconnet: no
type: ethernet
interface_name: eth1
ip:
dhcp4: no
auto6: no
- name:以上是关于关于Linux中自动化配置服务和网络接口的一些笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
关于Linux中通过 Systemd Path Unit 监听配置更新自动重启服务的一些笔记
关于Linux中网络连接配置(NetworkManager)的一些笔记