Python爬虫日记02-数据可视化
Posted 大树的困惑
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python爬虫日记02-数据可视化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
PYTHON爬虫日记02-数据可视化
记录自己的学习爬虫日记
1.环境准备
linux 环境python3.6+ (这里网上的教程很多,这里选择一个比较有效的在Linux上安装Python3))
linux nginx环境 (选择自己喜欢的版本 https://nginx.org/download/)
linux gunicorn (pip 下载)
pycharm 本地项目调试
数据准备 页面展示的数据为猫眼top100,已经在上一篇博客实现有兴趣的可以跳转
2.思路
1.准备好爬虫的数据
上一步已经将数据都导入到mysql数据库中了,我们只需要将数据从数据库中导出,并展示在页面上,这样我们的简单页面可视化就实现了
2.准备好前端模板
选择有用,合适的模板可以大幅度的减少开发时间,这里找了一个简单的模板
3.模板的修改,并通过python进行部署
修改根据个人喜好,这里不过多赘述,选择python的flask作为我们的web框架
4.将项目以flask+gunicorn+nginx的形式部署到linux上面
flask单独部署也可以访问,但是存在很多限制和缺点,借助gunicorn+nginx的结合可以很好的解决
5.爬虫测试
将自己做好的页面作为爬虫的对象,自己爬自己‘^’ 为后台实现大数据反爬提供数据基础
3.开干
由于篇幅,这里的相关代码只展示相关逻辑,完整的代码https://github.com/lxw2/Flsak_Spider
-
新建Flask项目
-
因为我用的Pycharm是免费社区版的,没办法直接生成模板,所以我们需要手动创建flask项目
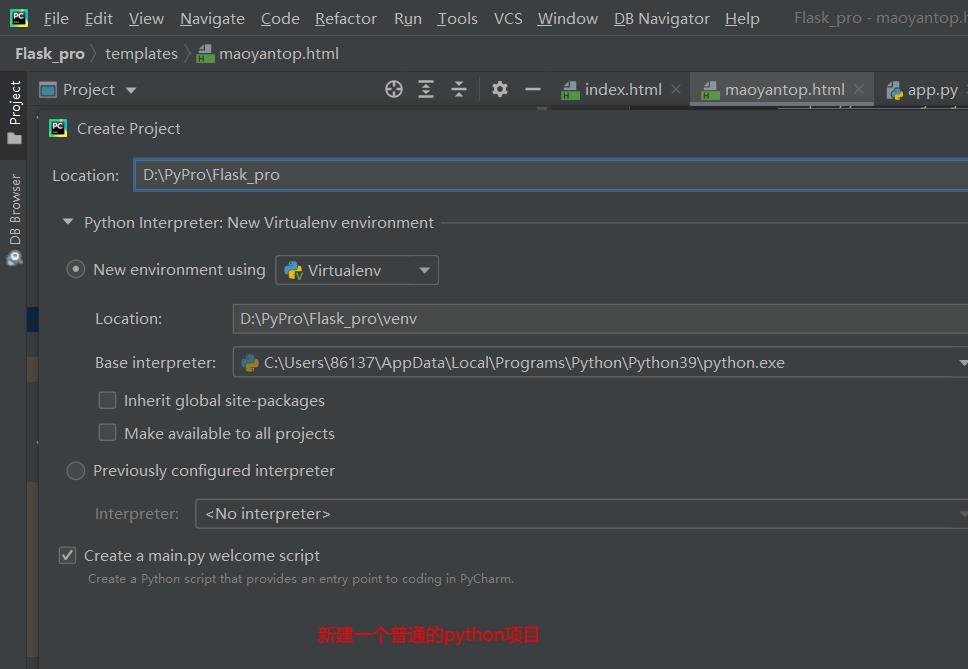
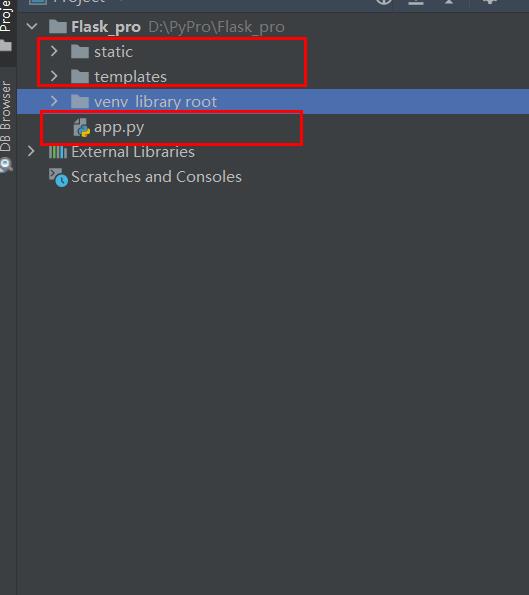
在项目的根目录下新建两个python包,并将自动生成的__INIT__.py 删除,将根目录下的__INIT__.py 也删除,新建成app.py
这样一个基本的flask的结构就建好了
static文件夹,用来存放css、javascript、image等静态资源文件
templates文件夹,该文件夹用来存放html文件
-
准备前端模板,并应用到flask项目上
前端模板-Mamba.zip-网页制作文档类资源-CSDN下载
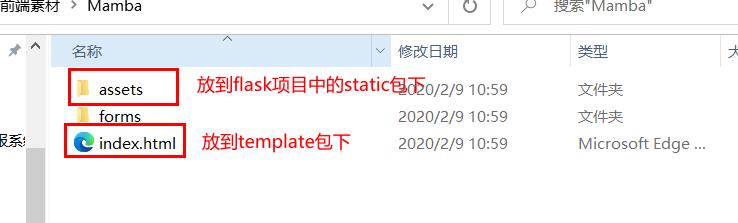
-
修改app.py
app.py
from flask import Flask, render_template,request import pymysql app = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/header") def header(): """ 主页 :return: Index.html """ return render_template('index.html') @app.route("/maoyantop") def maoyantop(): """ 猫眼页面 :return: maoyantop.html """ #获取分页偏移参数 offset=request.args.get("offset") if offset == None: offset=0 datalist = [] conn = pymysql.connect( host='xxx.xx.xx.xx', # host port=3306, # 默认端口,根据实际修改 user='root', # 用户名 passwd='123456', # 密码 db='luke_db', # DB name ) cur = conn.cursor() #查询数据 cur.execute("select * from luke_db.t_movie_top100_maoyan limit "+str(offset)+",10") data = cur.fetchall() for dat in data : datalist.append(dat) # print(dat) cur.close() conn.close() #将数据传入页面调用 return render_template("maoyantop.html",movies = datalist) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True, host='127.0.0.1', port='5000') -
html 数据的展示以及分页
<section class="counts section-bg"> <div class="container" style="max-width: 100%"> <table class="table table-striped" > <!-- 列表展示 --> <tr> <td nowrap="nowrap">排名</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">标题</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">链接</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">图片</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">评分</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">主演</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">上映时间</td> </tr> % for movie in movies % <tr > <td nowrap="nowrap">movie[0]+1</td> <td nowrap="nowrap"> <a href="movie[2]" target="_blank"> movie[1] </a> </td> <td nowrap="nowrap"> <a href="movie[2]" target="_blank"> movie[2] </a></td> <td nowrap="nowrap"> <img height=100 width=100 class="board-img" src="movie[3]"> </td> <td nowrap="nowrap">movie[4]</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">movie[5]</td> <td nowrap="nowrap">movie[6]</td> </tr> % endfor % </table> </div> <!-- 分页的简单实现 --> <div class="page" style="max-width: 100%"> <ul style="max-width: 100%"> <li class="prev"><a id="uppage" href="" >上一页</a></li> <li><a id="page_1" href="?offset=0">1</a></li> <li><a id="page_2" href="?offset=10">2</a></li> <li><a id="page_3" href="?offset=20">3</a></li> <li><a id="page_4" href="?offset=30">4</a></li> <li><a id="page_5" href="?offset=40">5</a></li> <li><a id="page_6" href="?offset=50">6</a></li> <li><a id="page_7" href="?offset=60">7</a></li> <li><a id="page_8" href="?offset=70">8</a></li> <li><a id="page_9" href="?offset=80">9</a></li> <li><a id="page_10" href="?offset=90">10</a></li> <li class="next"><a id="downpage" href="">下一页</a></li> </ul> </div> </section> <!-- 分页相关的几个js脚本 --> <script type="text/javascript"> var page = location.search.substr(1).split('=')[1] if (isNaN(page)) page=0 if (parseInt(page)!=0) page=parseInt(page)-10 document.getElementById("uppage").href="?offset="+page+"" </script> <script type="text/javascript"> var page = location.search.substr(1).split('=')[1] if (isNaN(page)) page=10 page=parseInt(page)+10 document.getElementById("downpage").href="?offset="+page+"" </script> <script> var page_num = location.search.substr(1).split('=')[1] /10 if (isNaN(page_num)) page_num=1 else page_num=page_num+1 var page_id="page_"+page_num document.getElementById(page_id).setAttribute('class','active') </script>相关代码已经上传github,可以根据自己需求进行修改
修改后就可以进行启动调试
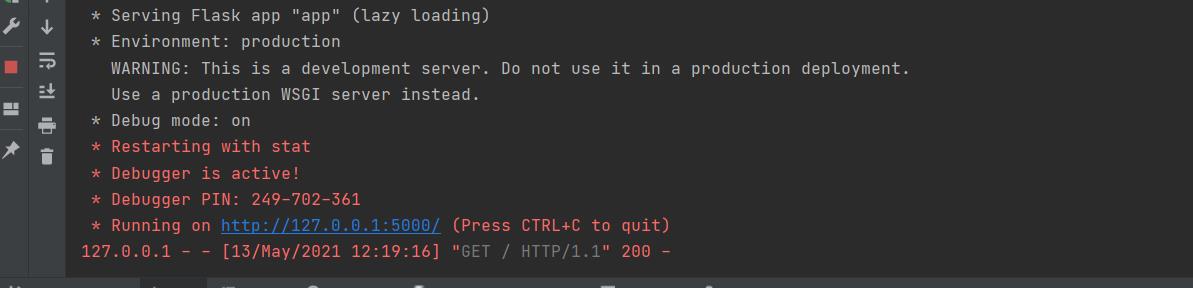
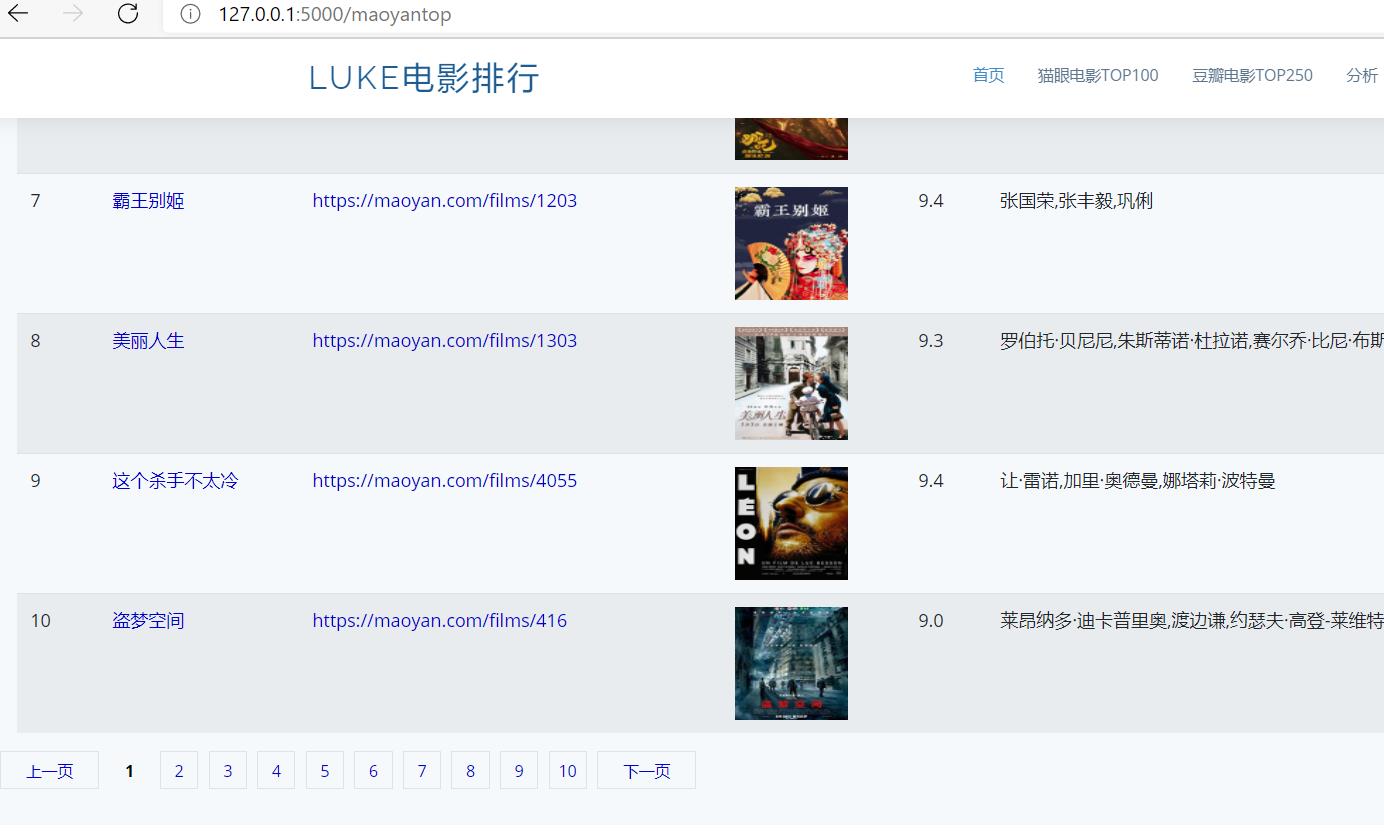
注意将数据库路径进行修改
-
-
部署到linux上,通过gunicorn+nginx辅助部署
我这边直接将整个包上传到linux上面去了
执行
python3 app.py # 正常输出 那么即可访问 * Serving Flask app "app" (lazy loading) * Environment: production WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead. * Debug mode: on * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) * Restarting with stat * Debugger is active! * Debugger PIN: 298-358-626 #如果报错,缺少某个模块,那么执行相应的 pip install XXX即可 #接下来安装 gunicorn pip install gunicorn #然后在项目的目录下执行 gunicorn -w 2 -b localhost:5000 app:app #成功输出即可通过浏览器访问 #可以让程序后台执行 gunicorn -w 2 -b localhost:5000 app:app 1> /dev/null 2>&1 &gunicorn部署成功后,就可以使用nginx,因为后续需要反爬,作为反爬的数据源,我们需要采集别人请求页面的数据,所以我们需要采集日志落地到文件中去
在安装完nginx之后
先准备好对应的nginx.conf
server模块中是主要修改的部分,添加了对本地端口的代理,然后打开日志采集的注释
将日志定向到我们指定的目录中去
#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events worker_connections 1024; http include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; # log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; log_format main '$remote_addr"#csc#"-"#csc#"$remote_user"#csc#"[$time_local]"#csc#""$request""#csc#"' '$status"#csc#"$body_bytes_sent"#csc#""$http_referer""#csc#"' '"$http_user_agent""#csc#""$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log logs/user_access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; root html; index index.html index.htm; location / proxy_pass http://localhost:5000/; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $http_post; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html root html;芜湖~就可以启动了
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf这个是后台启动的
-
部署成功之后,我们直接在本地访问一下页面
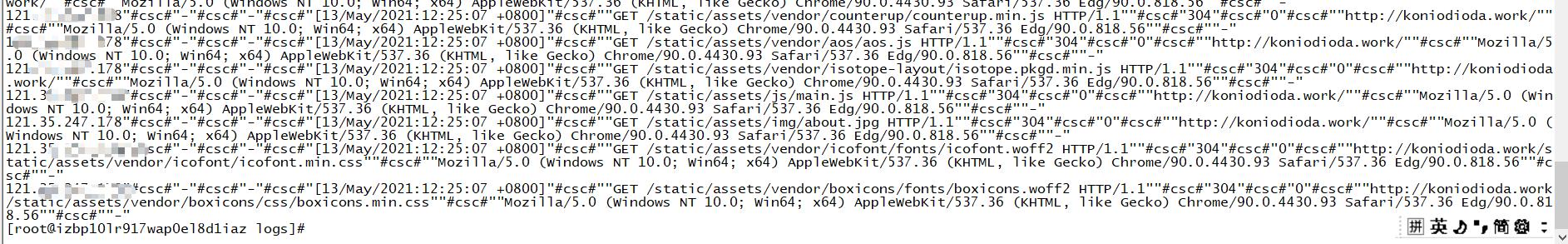
可以看到对应的请求数据已经拿到了,后续会进行实时性的采集请求数据进行分析,用目前比较流行的大数据框架进行搭建反爬工程
欢迎交流~
以上是关于Python爬虫日记02-数据可视化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章