React 学习笔记总结
Posted IT_Holmes
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了React 学习笔记总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
针对React拓展相关的学习。
文章目录
- 一. React 项目打包
- 二. React扩展 之 setState两种写法
- 三. React扩展 之 lazyLoad(懒加载)
- 四、React的 stateHook
- 五、React 的 Effect Hook
- 六、React 的 RefHook
- 七、React 的 Fragment
- 八、React 的 Context
- 九、React 的 PureComponent
- 十、React 的 render props
- 十一、React 的 ErrorBoundary
- 十二、React 组件通信方式总结
一. React 项目打包
安装serve,该库的作用可以将一个静态页面作为一台服务器启动。方便测试打包后的html页面。
# 安装serve
npm i serve
# 执行serve,在对应打包后的目录下,执行serve命令
serve
二. React扩展 之 setState两种写法
第一种写法:就是传对象。

setState方法的两个参数:
import React, Component from 'react';
export default class Demo extends Component
state = count:0
add = () =>
const count = this.state
// 更新状态 , 第二个参数callback是回调函数
this.setState(count:count+1,() =>
// fixme state状态改完,render页面刷新完,才调用该回调函数
)
// 因为,setState所调用的形式是异步的。
console.log('此时state中的count值并没有变化:',this.state.count)
render()
return (
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:this.state.count</h1>
<button onClick=this.add>加1</button>
</div>
);
第二种写法:传递函数。
- 函数式setState: 好处拿到了state和props。也方便维护。
import React, Component from 'react';
export default class Demo extends Component
state = count:0
add = () =>
const count = this.state
// 函数式setState: 好处拿到了state和props
this.setState((state,props) =>
console.log('state',state)
console.log('props',props)
return
count:count+1
)
console.log('此时state中的count值并没有变化:',this.state.count)
render()
return (
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:this.state.count</h1>
<button onClick=this.add>加1</button>
</div>
);
使用原则:
- 如果新状态不依赖于原来状态。 推荐使用对象方式。
- 如果新状态依赖与原来状态。 推荐使用函数方式。(例如:上面自动+1效果)。
注意:如果需要在setState()执行后获取最新的状态数据,要在第二个callback函数中进行读取操作取。
三. React扩展 之 lazyLoad(懒加载)
一般项目特别大,组件特别多,都会用到懒加载这个东西。
例如:一个页面涉及到了20多个路由页面,但是用户仅仅用了3个,然而,加载的时候缺加载了20多个路由页面,这样就不太好。
所以,就要用懒加载。
案例如下:
- 通过使用lazy和Suspense来进行操作。
// fixme 1. 引入lazy,Suspense
import React, Component,lazy,Suspense from 'react';
import NavLink, Route from 'react-router-dom'
// fixme 2. 路由组件不要用引入的方式
// import About from '../2_lazyLoad/About'
// import Home from '../2_lazyLoad/Home'
// fixme 注意: fallback中的内容组件必须是就位的,不能又使用import()函数,所以最好是提前引入
import Load from '../components/Load/Load'
// fixme 3. 定义成函数并且使用import()函数操作
const Home = lazy(() =>
// 使用import()函数来引入
return import('../2_lazyLoad/Home')
)
const About = lazy(() =>
// 使用import()函数来引入
return import('../2_lazyLoad/About')
)
class Demo extends Component
render()
return (
<div style=textAlign:"center">
<div style=textAlign:"center">
<h1>React Router Demo</h1>
</div>
<div style=textAlign:"center">
/*React靠路由跳转*/
<NavLink to="/about">
About
</NavLink>
<br/>
<NavLink to="/home">
Home
</NavLink>
</div>
<div style=textAlign:"center">
/* fixme 4. 使用Suspense来包裹Route,fallback显示的是加载完成前的操作。注意:fallback中的内容组件必须是就位的,不能又使用import()函数 */
<Suspense fallback=<Load/>>
/* 注册路由: 注意route和Router区分 */
<Route path="/about" component=About/>
<Route path="/home" component=Home/>
</Suspense>
</div>
</div>
);
export default Demo;
四、React的 stateHook
Hook是
React 16.8.0版本新增加的一个特性。
可以让函数组件中使用state以及其他的React属性(例如:生命周期钩子函数之类的。)。
三个常用的Hook:
- State Hook: React.useState()
- Effect Hook:React.useEffect()
- Ref Hook:React.useRef()
State Hook的使用:
import React from 'react';
/**
* 函数式组件
*/
function Index()
console.log('组件调用次数是 n + 1 次,第一次进入页面1次,之后render渲染n次。')
/**
* React.useState(0): 第一个参数代表初始值
* 返回值是个数组:第一个是状态state值,第二个是函数(负责更新状态state值)。
*/
const [count,setCount] = React.useState(0)
const [name,setName] = React.useState("Tom")
function add()
console.log('+++')
// setCount第一种写法:(值写法)
setCount(count + 1)
// setCount第二种写法:(函数写法) 可以更好维护
setCount(preCount => (preCount + 1))
function update()
setName('Jerry')
return (
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:count</h2>
<h2>我的名字是:name</h2>
<button onClick=add>点我 + 1</button>
<button onClick=update>修改名字</button>
</div>
)
export default Index;
五、React 的 Effect Hook
Effect Hook的使用:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
/**
* 函数式组件
*/
function Index()
const [count,setCount] = React.useState(0)
/**
* React.useEffect函数作用:就是实现了类函数中的componentDidMount之类的钩子函数了。
* 但是用法很不同: 第一个参数(函数):是要执行的函数。 第二个参数(数组):是要监听哪个状态值。
*/
React.useEffect(()=>
let timer = setInterval(()=>
setCount(count => count + 1)
,1000)
// fixme 此处的返回值就是等于componentWillUnmount
return () =>
console.log('@@@')
clearInterval(timer)
,[count])
/**
* 还有一种情况,像定时器之类的,在离开页面前需要关闭定时器。
* 一般对象组件就直接在使用componentWillUnmount组件就可以了。
*
*/
function unmount()
// 通过使用ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode来卸载组件
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('root'))
function add()
setCount(preCount => (preCount + 1))
return (
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:count</h2>
<button onClick=add>点我 + 1</button>
<button onClick=unmount>卸载Root</button>
</div>
)
export default Index;
可以把 useEffect Hook 看做对象组件如下三个钩子函数的组合:
- componentDidMount()
- componentDidUpdate()
- componentWillUnmount()
语法和说明:
useEffect(() =>
// 在此可以执行任何带副作用操作
return () => // 在组件卸载前执行
// 在此做一些收尾工作, 比如清除定时器/取消订阅等
, [stateValue]) // 如果指定的是[], 回调函数只会在第一次render()后执行
六、React 的 RefHook
类式组件使用ref:
/**
* 类式组件:
*/
class Index extends React.Component
state = count:0
// fixme 创建一个ref
myRef = React.createRef()
alertRef = () =>
alert(this.myRef.current.value)
add = ()=>
this.setState(state => (count:state.count + 1))
render()
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref=this.myRef/>
<h2>当前求和为:this.state.count</h2>
<button onClick=this.add>点我 + 1</button>
<button onClick=this.alertRef>提示</button>
</div>
);
RefHook的使用:
(1). Ref Hook可以在函数组件中存储/查找组件内的标签或任意其它数据
(2). 语法: const refContainer = useRef()
(3). 作用:保存标签对象,功能与React.createRef()一样
七、React 的 Fragment
Frgament用法:
import React, Component,Fragment from 'react';
class Index extends Component
render()
return (
// 这样就不用写一个div了。
<Fragment>
<input type="text"/>
</Fragment>
);
export default Index;
空标签的用法:
import React, Component,Fragment from 'react';
class Index extends Component
render()
return (
// fixme 也可以使用一个空标签
<>
<input type="text"/>
</>
);
export default Index;
Fragment 与 空标签 区别:
- 作用相同,但是Fragment可以有一个key属性,作为唯一标识使用(只有key属性)。
八、React 的 Context
context是 一种组件间通信方式, 常用于【祖组件】与【后代组件】间通信。
考虑两种情况:
- 对象式组件 和 函数式组件,不过一般项目中使用了redux就不会使用该方式了。
1) 创建Context容器对象:
const XxxContext = React.createContext()
2) 渲染子组时,外面包裹xxxContext.Provider, 通过value属性给后代组件传递数据:
<xxxContext.Provider value=数据>
子组件
</xxxContext.Provider>
3) 后代组件读取数据:
// fixme 第一种方式:仅适用于类组件
static contextType = xxxContext // 声明接收context
this.context // 读取context中的value数据
// fixme 第二种方式: 函数组件与类组件都可以
<xxxContext.Consumer>
value => ( // value就是context中的value数据
要显示的内容
)
</xxxContext.Consumer>
九、React 的 PureComponent
1. Component组件的两个问题
1. 只要执行setState(),即使不改变状态数据, 组件也会重新render() ==> 效率低。
2. 只当前组件重新render(), 就会自动重新render子组件,
纵使子组件没有用到父组件的任何数据。==> 效率低。
上面就会导致效率降低的情况。
导致上面情况的发生,因为,Component中的shouldComponentUpdate()钩子函数总是返回true。

2. PureComponent 纯组件
使用PureComponent
PureComponent重写了shouldComponentUpdate(), 只有state或props数据有变化才返回true
注意:
只是进行state和props数据的浅比较, 如果只是数据对象内部数据变了, 返回false
不要直接修改state数据, 而是要产生新数据
项目中一般使用PureComponent来优化
注意:不要直接修改state数据,直接修改state虽然属性变了,但自身对象地址未发生变化(也就是个浅赋值),而是要产生新数据,不然PureComponent无法检测到。
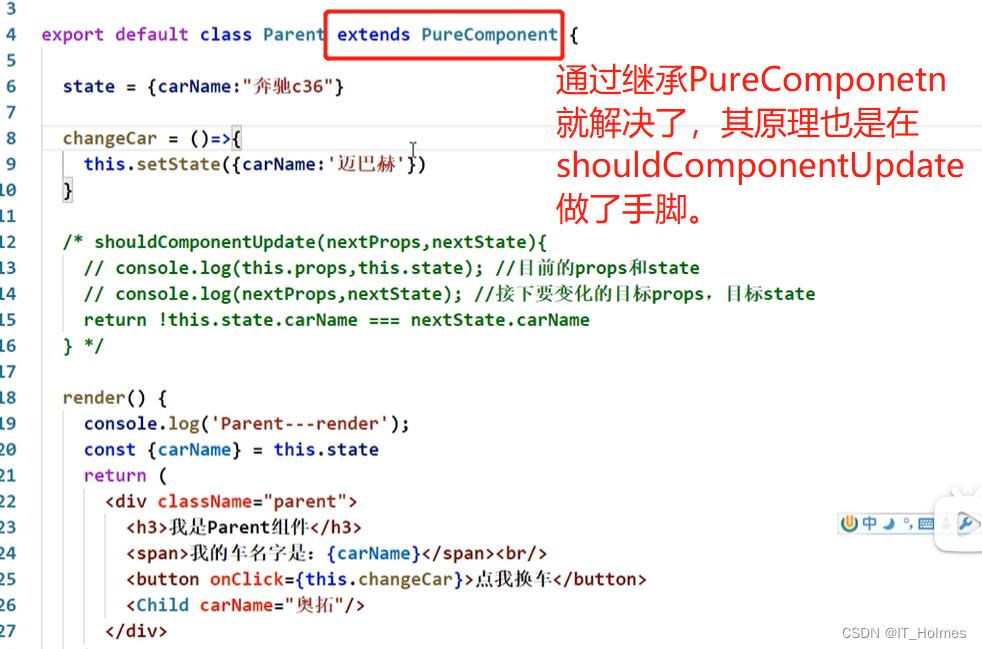
还是要注意纯组件失效不更新的情况。
十、React 的 render props
1. 组成父子组件的 两种方式
第一种方式:

第二种方式:
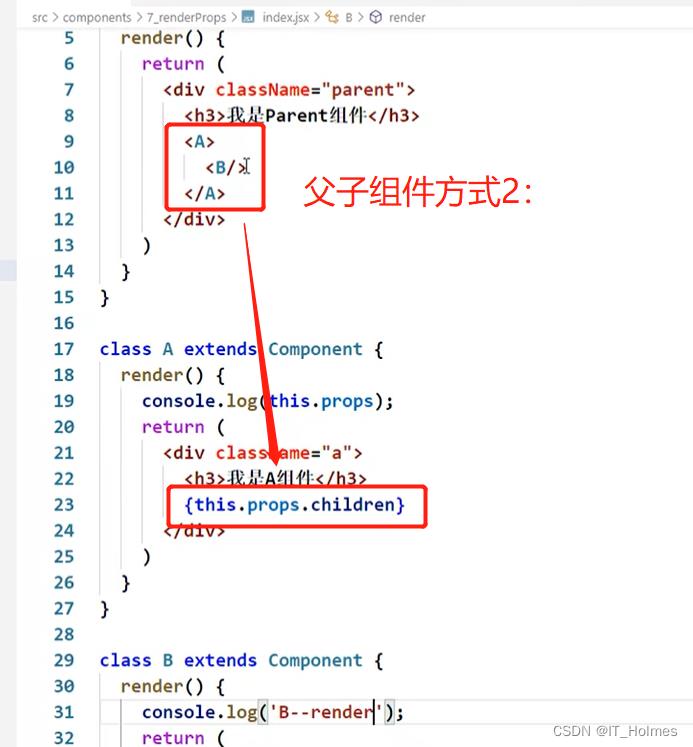
注意:第二种方式有瑕疵,那么\\<B name=this.state/\\>的this指向的是谁?此处便是缺点。
2. render props 的 使用
// 比较Vue 和 React:
Vue中:
使用slot技术, 也就是通过组件标签体传入结构 <A><B/></A>
React中:
使用children props: 通过组件标签体传入结构
使用render props: 通过组件标签属性传入结构,而且可以携带数据,一般用render函数属性

// 其实render prop就是为了解决如下情况:
<A>
<B>xxxx</B>
</A>
this.props.children
问题: 如果B组件需要A组件内的数据, ==> 做不到
十一、React 的 ErrorBoundary
错误边界(Error boundary):用来捕获后代组件错误,渲染出备用页面,实际上就是有一个出错后能显示的页面。
只能捕获后代组件生命周期产生的错误,不能捕获自己组件产生的错误和其他组件在合成事件、定时器中产生的错误。
通过getDerivedStateFromError配合componentDidCatch来实现:
class Index extends Component
state =
hashError:'' // 用于标识子组件是否产生错误
// 生命周期函数,一旦后台组件报错,就会触发
static getDerivedStateFromError(error)
console.log(error);
// 在render之前触发
// 返回新的state
return
hasError: true,
;
// 将错误信息返回后台(需要的话。)
componentDidCatch(error, info)
// 统计页面的错误。发送请求发送到后台去
console.log(error, info);
render()
return (
<div>
<h3>组件</h3>
this.state.hashError ? <h2>当前不稳定,请稍后重试!</h2> : <Child/>
</div>
);
十二、React 组件通信方式总结

以上是关于React 学习笔记总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章