React组件进阶
Posted webchang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了React组件进阶相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
react组件进阶
组件通讯介绍
组件是独立且封闭的单元,默认情况下,只能使用组件自己的数据。在组件化过程中,我们将一个完整的功能拆分成多个组件,以更好的完成整个应用的功能。而在这个过程中,多个组件之间不可避免的要共享某些数据。为了实现这些功能,就需要打破组件的独立封闭性,让其与外界沟通。这个过程就是组件通讯。
组件的props
- 组件是封闭的,接收外部数据应该通过props来实现
- props的作用:接收传递给组件的数据
- 接收数据:
- 函数组件通过参数props来接收数据,props是一个对象
- 类组件通过this.props接收数据
- 传递数据:在组件标签上添加属性
函数组件
const Hello = (props) =>
console.log(props);
return (
<div>props:props.name</div>
)
// 渲染
ReactDOM.render(<Hello name="jack" />, document.getElementById('root'))
批量传递数据:
function Hello(props)
const name, age, gender = props;
return (
<h2>name-age-gender</h2>
)
const data =
name: 'a',
age: 19,
gender: '女'
// 批量传递数据。这里的花括号表示内部是js表达式,正常情况下是不能直接写...data的,
// 如console.log(...data)就会报错。在react中允许这样做
ReactDom.render(<Hello ...data />, document.getElementById('root'));
类组件
class App extends React.Component
render()
console.log(this.props);
return (
<div>
props: this.props.name
</div>
)
// 渲染
ReactDOM.render(<App name="jack" />, document.getElementById('root'))
注意:使用类组件时,如果写了构造函数,应该将props作为参数传递给constructor和super,否则无法在构造函数中通过this获取到props。不过即使没有传递props参数给constructor,在其它地方,比如render方法中,还是可以正常使用this.props的。
技术点:在继承类的构造函数中必须调用super函数,super代表父类的构造函数。ES6 要求,子类的构造函数必须执行一次super函数,否则会报错。但是super函数内的this指向的是当前类的实例。
构造器是否接受 props,是否传递给 super,取决于是否希望在构造器中通过 this访问props。
- 当构造器中接收了props参数,super没有传递props,此时this.props是undefined,当然可以正常使用props(前边不加this)
- 当构造器中接收了props参数,super也传递props,可以通过this.props拿到对象
class App extends React.Component
constructor(props)
super(props);
render()
// constructor中有没有传递props,和这里没有关系
return (
<div>
props:this.props.name
</div>
)
数据类型
- 可以传递给组件任意类型的数据
- props是只读的对象,只能读取属性的值,无法修改对象
import React from 'react'
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
function Hello(props)
console.log(props);
props.fn();
return (
<div>
<h1>name:props.name</h1>
props.tag
</div>
)
ReactDom.render(
<Hello
name="小明"
age=18 // 如果要传递数字类型,需要使用包裹起来
age2='8'
colors=['red','green']
fn=() => console.log('啊啊啊') // 可以传递函数
tag=<p>这是一个p标签</p> // 可以传递tag标签
/>, document.getElementById('root'));
Props 默认值为 “True”
如果你没给 prop 赋值,它的默认值是 true。以下两个 JSX 表达式是等价的:
<MyTextBox autocomplete />
<MyTextBox autocomplete=true />
props深入
children属性
- children属性:表示组件标签的子节点。当组件标签有子节点时,props就会有该属性
- children属性与普通的props一样,值可以是任意值(文本、React元素、组件,甚至是函数)
class App extends React.Component
render()
console.log(this.props);
return (
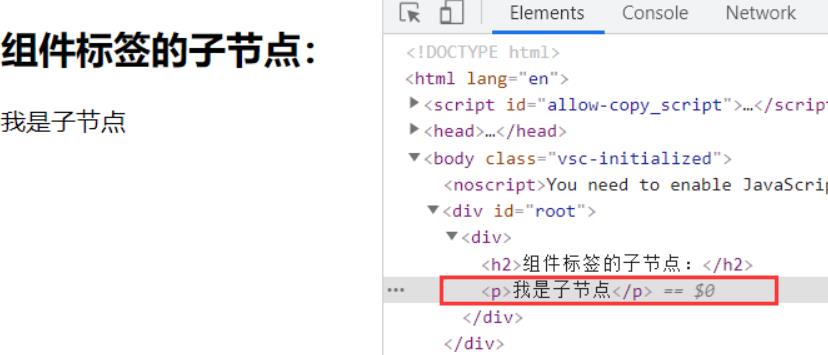
<div>
<h2>组件标签的子节点:</h2>
this.props.children // 我是子节点
</div>
)
ReactDom.render(
<App name="hello">
<p>我是子节点</p>
</App>, document.getElementById('root'));
属性展开
如果你已经有了一个 props 对象,你可以使用展开运算符 ... 来在 JSX 中传递整个 props 对象。以下两个组件是等价的:
function App1()
return <Greeting firstName="Ben" lastName="Hector" />;
function App2()
const props = firstName: 'Ben', lastName: 'Hector';
return <Greeting ...props />;
你还可以选择只保留当前组件需要接收的 props,并使用展开运算符将其他 props 传递下去。
const Button = props =>
const kind, ...other = props;
const className = kind === "primary" ? "PrimaryButton" : "SecondaryButton";
return <button className=className ...other />;
;
const App = () =>
return (
<div>
<Button kind="primary" onClick=() => console.log("clicked!")>
Hello World!
</Button>
</div>
);
;
在上述例子中,kind 的 prop 会被安全的保留,它将_不会_被传递给 DOM 中的 元素。 所有其他的 props 会通过 ...other 对象传递,使得这个组件的应用可以非常灵活。你可以看到它传递了一个 onClick 和 children 属性。
props校验
- props校验:允许在创建组件的时候,就指定props的类型、格式等
- 作用:捕获使用组件时因为props导致的错误,给出明确的错误提示,增加组件的健壮性
使用步骤
- 安装包prop-types
npm i prop-types - 导入prop-types包
- 使用**组件名.propTypes =**来给组件的props添加校验规则
- 校验规则通过PropTypes 对象来指定
约束规则:
- 常见类型: array、bool、func、number、object、string
- React元素类型: element
- 必填项:isRequired
- 自定义特定结构: shape( )
类组件中props校验的写法
import React from 'react'
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class App extends React.Component
render()
console.log(this.props);
let arr = this.props.colors;
let list = arr.map((item, index) => <li key=index>index-item</li>)
return (
<ul>
list
</ul>
)
// 添加props校验
App.propTypes =
colors: PropTypes.array,
a: PropTypes.number, // 数值类型
fn: PropTypes.func.isRequired, // 函数func并且必填,注意这里是func
tag: PropTypes.element, // react元素
filter: PropTypes.shape( // 自定义类型
area: PropTypes.string,
price: PropTypes.number
)
// 当没有传递对应的prop时的默认值
App.defaultProps =
gender: '保密',
age: 18
上边代码的写法是在类的外部给类加上自定义的属性,如何在类的内部就进行这些操作呢?类的静态属性 指的是 Class 本身的属性,即Class.propName,而不是定义在实例对象(this)上的属性。类的静态属性,写法是在实例属性的前面,加上static关键字。
class App extends React.Component
// 添加props校验
static propTypes =
colors: PropTypes.array
// 当没有传递对应的prop时的默认值
static defaultProps =
gender: '保密',
age: 18
render()
console.log(this.props);
let arr = this.props.colors;
let list = arr.map((item, index) => <li key=index>index-item</li>)
return (
<ul>
list
</ul>
)
函数组件中props校验的写法
由于函数中不能使用static关键字,所以定义props校验的部分只能写在函数组件的外部。
function Hello(props)
const name, age, gender = props;
return (
<h2>name-age-gender</h2>
)
// 提供类型限制
Hello.propTypes =
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired
// 当没有传递对应的prop时的默认值
Hello.defaultProps =
gender: '保密',
age: 18
const data =
name: 'a',
age: 19
ReactDom.render(<Hello ...data />, document.getElementById('root'));
refs
过时 API:String 类型的 Refs
react之前的 API 中的 ref 属性是string 类型的,例如 “textInput”。可以通过 this.refs.textInput 来访问 DOM 节点。官方不建议使用它,因为 string 类型的 refs 存在 一些问题,效率不高。
class App extends React.Component
showData = () =>
let input = this.refs.input1;
alert(input.value)
showData2 = (e) =>
alert(e.target.value);
render()
return (
<div>
<input ref="input1" type="text" />
<button onClick=this.showData>提示</button>
<input onBlur=this.showData2 type="text" />
</div>
)
回调refs
class App extends React.Component
state =
count: 0
showData = () =>
let input = this.input1;
alert(input.value)
updateCount = () =>
this.setState(
count: this.state.count + 1
)
render()
return (
<div>
/* 注意这里的ref是箭头函数,currentNode是当前节点,
react内部会自动调用,然后将当前节点赋值给this的input1 */
<input ref=currentNode => this.input1 = currentNode; console.log('--', currentNode) type="text" />
<button onClick=this.showData>提示</button>
<h1>this.state.count</h1>
<button onClick=this.updateCount>更新</button>
</div>
)
如果 ref 回调函数是以内联函数的方式定义的,在更新过程中它会被执行两次,第一次传入参数 null,然后第二次会传入参数 DOM 元素。这是因为在每次渲染时会创建一个新的函数实例,所以 React 清空旧的 ref 并且设置新的。通过将 ref 的回调函数定义成 class 的绑定函数的方式可以避免上述问题,但是大多数情况下它是无关紧要的。
如图,每次更新时,ref的回调函数会被调用两次
将回调函数改为class的函数方式是这样的:
class App extends React.Component
showData = () =>
let input = this.input1;
alert(input.value)
setInputRef = (c) =>
console.log(c)
this.input1 = c;
render()
return (
<div>
<input ref=this.setInputRef type="text" />
<button onClick=this.showData>提示</button>
</div>
)
React.createRef
React.createRef调用后可以返回一个容器,该容器可以存储被ref所标识的节点,该容器是“专人专用”的
class App extends React.Component
inputRef = React.createRef();
inputRef2 = React.createRef();
showData = () =>
let input = this.inputRef.current;
console.log(input.value)
showData2 = () =>
console.log(this.inputRef2.current.value)
render()
return (
<div>
/* react内部会将当前节点存储到this.inputRef中 */
<input ref=this.inputRef type="text" />
<button onClick=this.showData>提示</button>
<input onBlur=this.showData2 ref=this.inputRef2 type="text" />
</div>
)
组件通讯总结
组件间的关系
- 父子组件:props
- 兄弟组件(非嵌套组件):消息订阅-发布、集中式管理、状态提升
- 祖孙组件(跨级组件):消息订阅-发布、集中式管理、context
- props:
- children props
- render props
- 消息订阅-发布:pubs-sub、event等等
- 集中式管理:redux、dva等等
- context:生产者-消费者模式
父组件传递数据给子组件
- 父组件提供要传递的state数据
- 给子组件标签添加属性,值为state中的数据
- 子组件中通过props接收父组件中传递的数据
本质上和前边讲到的props的使用方式是一样的,只不过换了一种应用方式
class App extends React.Component
state =
lastName: '老王'
render()
return (
<div className="parent">
父组件
<Child name=this.state.lastName />
</div>
)
function Child(props)
return (
<div className="child">
<h1>子组件:props.name</h1>
</div>
)
ReactDom.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
子组件传递数据给父组件
思路:利用回调函数,父组件提供回调,子组件调用,将要传递的数据作为回调函数的参数。
- 父组件提供一个回调函数(用于接收数据)
- 将该函数作为属性的值,传递给子组件
- 子组件通过props调用回调函数,将子组件的数据作为参数传递给回调函数
class App extends React.Component
state =
lastName: '老王',
childData: ''
// 1.父组件提供接收子组件数据的回调函数,参数就是子子组件传递过来以上是关于React组件进阶的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章