自己动手编写stylelint规则
Posted Jtag特工
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了自己动手编写stylelint规则相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
自己动手编写stylelint规则
之前我们介绍了如何编写eslint规则,现在我们开始挑战更偏前端的新领域 - stylelint.
从运行测试用例入手
按照惯例,我们还是从测试用例入手。测试用例是将css代码和规则快速运行起来的最有效手段。
首先我们把stylelint的代码拉下来:
git clone https://github.com/stylelint/stylelint
好,我们下面找个例子看看stylelint的测试用例是什么样的。我们以对于颜色的检查的规则为例,这个规则是检查颜色的16进制值是不是正确的,比如#000,#000000都是正确的,#0000就是错误的,这个大家都清楚哈:
const messages, ruleName = require('..');
testRule(
ruleName,
config: [true],
accept: [
code: 'a color: pink; ',
,
code: 'a color: #000; ',
,
code: 'a something: #000, #fff, #ababab; ',
,
...
],
reject: [
code: 'a color: #ababa; ',
message: messages.rejected('#ababa'),
line: 1,
column: 12,
,
code: 'a something: #00, #fff, #ababab; ',
message: messages.rejected('#00'),
line: 1,
column: 16,
,
code: 'a something: #000, #fff1az, #ababab; ',
message: messages.rejected('#fff1az'),
line: 1,
column: 22,
,
code: 'a something:#000,#fff,#12345aa; ',
message: messages.rejected('#12345aa'),
line: 1,
column: 25,
,
],
);
accept数组是可以通过的case,reject是失败的用例,还要给出理由和错误位置。
stylelint的测试用例是用jest测试框架写的,运行使用jest:
./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js lib/rules/color-no-invalid-hex/__tests__/index.js
运行结果如下:
PASS lib/rules/color-no-invalid-hex/__tests__/index.js
color-no-invalid-hex
accept
[ true ]
'a color: pink; '
✓ no description (26 ms)
'a color: #000; '
✓ no description (1 ms)
'a something: #000, #fff, #ababab; '
✓ no description (1 ms)
'a color: #0000ffcc; '
✓ eight digits (2 ms)
'a color:#00fc; '
✓ four digits (2 ms)
'a padding: 000; '
✓ no description (1 ms)
'a::before content: "#ababa"; '
✓ no description (1 ms)
"a background-image: svg-load('x.svg', fill=url(#a)); "
✓ svg-load url with fill (2 ms)
'a background-image: url(#a); '
✓ url standalone hash (2 ms)
'a background-image: url(x.svg#a); '
✓ url with hash (1 ms)
'@font-face \\n' +
'font-family: dashicons;\\n' +
'src: url(data:application/font-woff;charset=utf-8;base64, ABCDEF==) format("woff"),\\n' +
'url(../fonts/dashicons.ttf) format("truetype"),\\n' +
'url(../fonts/dashicons.svg#dashicons) format("svg");\\n' +
'font-weight: normal;\\n' +
'font-style: normal;\\n' +
''
✓ no description (3 ms)
'a color: #colors[somecolor]; '
✓ Less map usage (11 ms)
'a border-#$side: 0; '
✓ ignore sass-like interpolation (7 ms)
'a box-sizing: #$type-box; '
✓ ignore sass-like interpolation (1 ms)
'export default <h1 style= color: "#ffff" >Test</h1>;'
○ skipped no description
reject
[ true ]
'a color: #ababa; '
✓ no description (2 ms)
'a something: #00, #fff, #ababab; '
✓ no description (2 ms)
'a something: #000, #fff1az, #ababab; '
✓ no description (2 ms)
'a something:#000,#fff,#12345aa; '
✓ no description (1 ms)
'export default <h1 style= color: "#fffff" >Test</h1>;'
○ skipped no description
Test Suites: 1 passed, 1 total
Tests: 2 skipped, 18 passed, 20 total
Snapshots: 0 total
Time: 0.635 s, estimated 1 s
Ran all test suites matching /lib\\/rules\\/color-no-invalid-hex\\/__tests__\\/index.js/i.
规则的内容我稍删节一点细节,大致是下面这样:
...
const valueParser = require('postcss-value-parser');
const ruleName = 'color-no-invalid-hex';
const messages = ruleMessages(ruleName,
rejected: (hex) => `Unexpected invalid hex color "$hex"`,
);
...
const rule = (primary) =>
return (root, result) =>
...
root.walkDecls((decl) =>
if (!isStandardSyntaxHexColor(decl.value))
return;
valueParser(decl.value).walk(( value, type, sourceIndex ) =>
if (type === 'function' && value.endsWith('url')) return false;
if (type !== 'word') return;
const hexMatch = /^#[0-9A-Za-z]+/.exec(value);
if (!hexMatch) return;
const hexValue = hexMatch[0];
if (isValidHex(hexValue)) return;
report(
message: messages.rejected(hexValue),
node: decl,
index: declarationValueIndex(decl) + sourceIndex,
result,
ruleName,
);
);
);
;
;
...
如何遍历声明
css基本上都是一些声明,我们都过root.walkDecls去遍历它们。
比如对于
a color: pink;
来说,decl.value的值就是pink.
对于有多个值的,例如:
a something: #000, #fff, #ababab;
Decl.value值就是"#000, #fff, #ababab"
这时候的value就需要进一步拆分,就是valueParser(decl.value).walk的作用。
valueParser.walk的参数是值、类型、源代码索引的列表。
比如"pink"的类型是word, "#000"也是word, ","是div, "svg-load"是function, "x.svg"是string等。
类型一共有7种: word, string, div, space, comment, function和unicode-range.
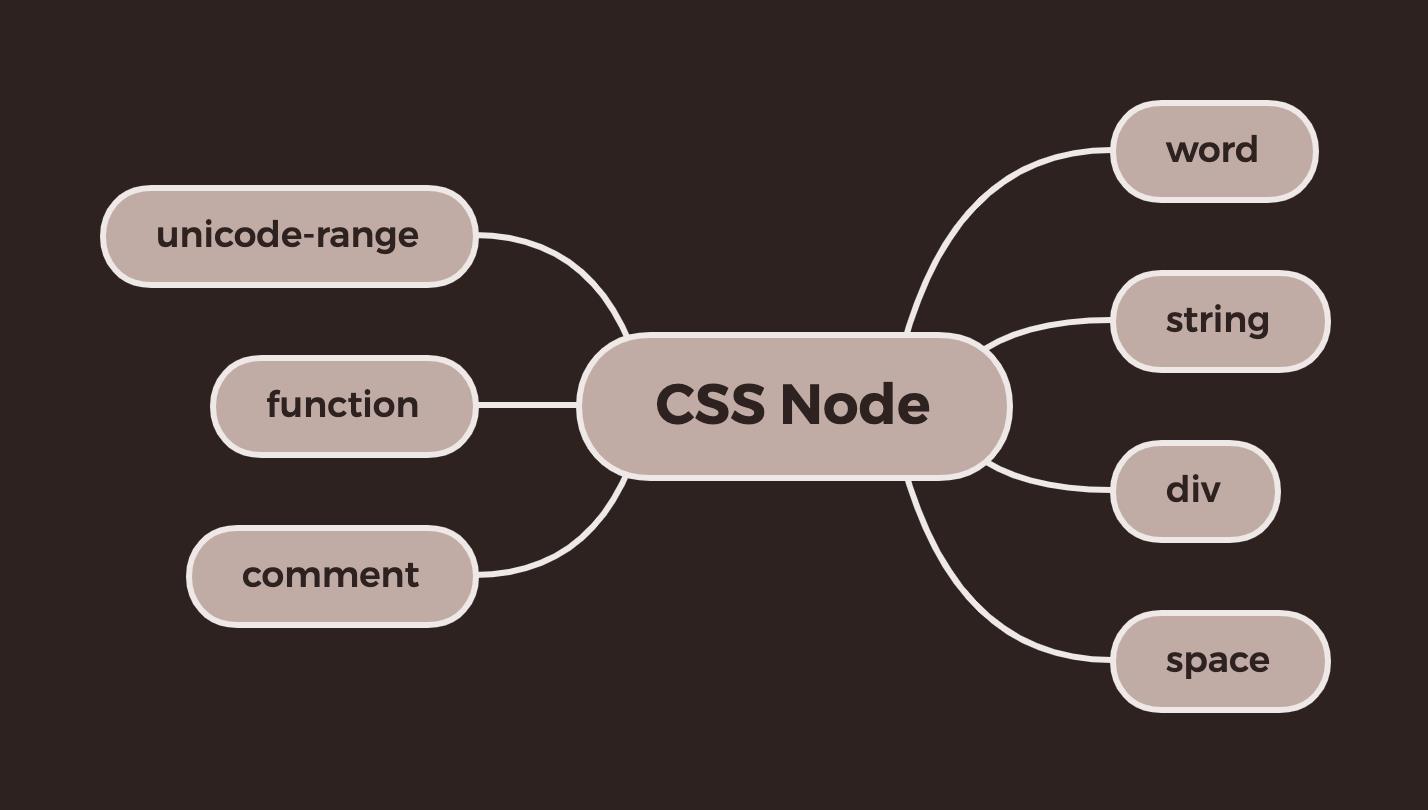
报错信息仍然和eslint一样,是通过report接口来实现的。
再看一个完整例子
我们再看一个简单例子,禁止使用"!important"属性。
const report = require('../../utils/report');
const ruleMessages = require('../../utils/ruleMessages');
const validateOptions = require('../../utils/validateOptions');
const ruleName = 'declaration-no-important';
const messages = ruleMessages(ruleName,
rejected: 'Unexpected !important',
);
const rule = (primary) =>
return (root, result) =>
const validOptions = validateOptions(result, ruleName, actual: primary );
if (!validOptions)
return;
root.walkDecls((decl) =>
if (!decl.important)
return;
report(
message: messages.rejected,
node: decl,
word: 'important',
result,
ruleName,
);
);
;
;
rule.ruleName = ruleName;
rule.messages = messages;
module.exports = rule;
因为important是decl的属性,解析器已经替我们搞好了,我们只要判断这一个属性即可。
Postcss-value-parser解析器
上面我们使用的valueParser是postcss-value-parser解析器。
我们来看看如何单独使用postcss-value-parser去解析css代码,其实非常简单,只要一个valueParser就可以了:
const valueParser = require('postcss-value-parser');
const hellocss1 = `
#hellocss
background-color: blue;
`
const parsedCss = valueParser(hellocss1);
console.log(parsedCss);
解析出来的结果如下:
ValueParser
nodes: [
type: 'space', sourceIndex: 0, sourceEndIndex: 1, value: '\\n' ,
type: 'word',
sourceIndex: 1,
sourceEndIndex: 10,
value: '#hellocss'
,
type: 'space', sourceIndex: 10, sourceEndIndex: 11, value: ' ' ,
type: 'word', sourceIndex: 11, sourceEndIndex: 12, value: '' ,
type: 'space',
sourceIndex: 12,
sourceEndIndex: 17,
value: '\\n '
,
type: 'word',
sourceIndex: 17,
sourceEndIndex: 33,
value: 'background-color'
,
type: 'div',
sourceIndex: 33,
sourceEndIndex: 35,
value: ':',
before: '',
after: ' '
,
type: 'word',
sourceIndex: 35,
sourceEndIndex: 40,
value: 'blue;'
,
type: 'space', sourceIndex: 40, sourceEndIndex: 41, value: '\\n' ,
type: 'word', sourceIndex: 41, sourceEndIndex: 42, value: '' ,
type: 'space', sourceIndex: 42, sourceEndIndex: 43, value: '\\n'
]
要去进一步处理ValueParser解析出来的数据,可以通过walk函数来进一步处理:
const valueParser = require('postcss-value-parser');
const hellocss1 = `
#hellocss
width: 20px;
`
const parsedCss = valueParser(hellocss1);
parsedCss.walk((node) =>
console.log(node.type, node.value, node.sourceIndex);
);
输出的结果如下:
space
0
word #hellocss 1
space 10
word 11
space
12
word width 17
div : 22
word 20px; 24
space
29
word 30
space
31
解析单位
css中比起javascript来,有一个特有的问题,就是很多属性是带单位的,比如px, rpx, em, rem等。将值解析成数字和单位是非常通用的需求。valueParser为我们提供了unit函数来实现这个功能:
const s1 = '20px';
const value1 = valueParser.unit(s1);
console.log(value1);
选择器宇宙
这部分看起来有点复杂,因为涉及到的层次比较多。请大家稍耐心一点点,要不然解析的时候就找不到对象了。
单项选择器
普通属性处理完之后,我们需要专门设一节来说选择器,postcss有一个专门的库postcss-selector-parser来处理选择器。
选择器的特点就是属性多,有各种复杂组合。
我们从最基础的看起。
const parser = require('postcss-selector-parser');
const transform = selectors =>
selectors.walk(selector =>
console.log(selector.type)
);
;
parser(transform).processSync('p');
输出为:
selector
tag
说明p是tag selector。
我们可以打印完整的selector对象的结构来看下:
const parser = require('postcss-selector-parser');
const transform = selectors =>
selectors.walk(selector =>
console.log(selector)
);
;
parser(transform).processSync('p');
输出如下:
<ref *1> Selector
source: start: line: 1, column: 1 , end: line: 1, column: 1 ,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
nodes: [
Tag
value: 'p',
source: [Object],
sourceIndex: 0,
spaces: [Object],
type: 'tag',
parent: [Circular *1]
],
type: 'selector',
parent: Root
source: start: [Object], end: [Object] ,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
nodes: [ [Circular *1] ],
type: 'root',
_error: [Function (anonymous)],
lastEach: 1,
indexes: '1': 0
<ref *1> Tag
value: 'p',
source: start: line: 1, column: 1 , end: line: 1, column: 1 ,
sourceIndex: 0,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
type: 'tag',
parent: Selector
source: start: [Object], end: [Object] ,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
nodes: [ [Circular *1] ],
type: 'selector',
parent: Root
source: [Object],
spaces: [Object],
nodes: [Array],
type: 'root',
_error: [Function (anonymous)],
lastEach: 1,
indexes: [Object]
,
lastEach: 1,
indexes: '1': 0
我们再看下类选择器、ID选择器和*:
parser(transform).processSync('.class1');
parser(transform).processSync('#id1');
parser(transform).processSync('*');
类选择器的类型是ClassName:
...
<ref *1> ClassName
_value: 'class1',
source: start: line: 1, column: 1 , end: line: 1, column: 7 ,
sourceIndex: 0,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
type: 'class',
_constructed: true,
parent: Selector
source: start: [Object], end: [Object] ,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
nodes: [ [Circular *1] ],
type: 'selector',
parent: Root
...
,
lastEach: 1,
indexes: '1': 0
ID选择器的类型是ID:
...
<ref *1> ID
value: 'id1',
source: start: line: 1, column: 1 , end: line: 1, column: 4 ,
sourceIndex: 0,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
type: 'id',
parent: Selector
source: start: [Object], end: [Object] ,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
nodes: [ [Circular *1] ],
type: 'selector',
parent: Root
...
,
lastEach: 1,
indexes: '1': 0
*选择器的类型是Universal:
...
<ref *1> Universal
value: '*',
source: start: line: 1, column: 1 , end: line: 1, column: 1 ,
sourceIndex: 0,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
type: 'universal',
parent: Selector
source: start: [Object], end: [Object] ,
spaces: before: '', after: '' ,
nodes: [ [Circular *1] ],
type: 'selector',
parent以上是关于自己动手编写stylelint规则的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章