js 高阶函数 发布订阅观察者模式 手撕promise
Posted lin-fighting
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了js 高阶函数 发布订阅观察者模式 手撕promise相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
promise
高阶函数
- 概念:1 一个函数返回一个函数。2 函数参数可以接受一个函数。
满足任意两点即可。
- 场景: 扩展方法
function core(...args)
// 核心代码
console.log('core');
要在core核心代码执行前后处理一些逻辑,但是不能修改Core的代码,怎么操作呢?
function core(...args)
// 核心代码
console.log("core", ...args);
Function.prototype.before = function (cb)
return (...args) =>
cb(); //cb就是要处理的逻辑
this(...args);
;
;
const newCode = core.before(() =>
console.log("我是先处理的");
);
//返回新的core函数,不需要知道里面做什么操作,只需要像调用core一样调用就行。
newCode(1, 2, 3);
通过高阶函数,使用回调函数,让需要处理的操作先执行,在执行core函数。结果如图:

函数柯里化
n参数的传入,把他转为n个函数。如
const fn = (a,b,c)=>return a+b+c
fn(1,2,3)
//柯里化,可以暂存变量。
const fn = (a,b) =>
//这里会利用闭包存放a,b的变量
return (c) =>
return a+b+c
fn(1,2)(3)
判断类型
function isType(type)
return (val) =>
return Object.prototype.toString.call(val) === `[object $type]`;
;
const utils = ;
[
"String",
"Number",
"Object",
"Gunction",
"Null",
"Nndefined",
"Boolean",
].forEach((item) =>
utils[`is$item`] = isType(item);
);
console.log(utils.isString(123)); //fase
console.log(utils.isString("123"));
采用柯里化保存每个类型。
并发问题
比如同时读取两个文件的内容,读取完后显示出来。
const fs = require("fs");
//多个请求并发,靠计数器实现
function after(times, callback)
//times控制数量
let arr = []; //记录结果
return (data, index) =>
arr[index] = data;
if (--times === 0)
callback(arr);
;
const out = after(2, (data) =>
console.log(data);
);
fs.readFile("./1.txt", "utf-8", (err, data) =>
out(data,1);
);
fs.readFile("./2.txt", "utf-8", (err, data) =>
out(data,0);
);
这里也是借助高阶函数的概念,拿到值之后存放起来。这种方法不是很好。
再次优化,发布订阅模式
//事件中心
const fs = require("fs");
// 解耦合,将每个逻辑写到了各自的类里面
const events =
arr: [],
on(cb)
events.arr.push(cb);
,
emit(data)
events.arr.forEach((item) => item(data));
,
;
events.on(() =>
console.log("每次发布就打印一次");
);
const arr = [];
events.on((data) =>
arr.push(data);
);
events.on(() =>
if (arr.length === 2)
console.log(arr);
);
fs.readFile("./1.txt", "utf-8", (err, data) =>
events.emit(data)
);
fs.readFile("./2.txt", "utf-8", (err, data) =>
events.emit(data)
);
观察者模式vue2 基于发布订阅
发布订阅之间是没有依赖关系的,而观察者模式是有关系的。
vue2中的Updater类,在每个数据调用get方法的时候,会订阅watcher,将wathcer放入updater中。然后set方法的时候通知updater,Updater类就会调用每个watcher的updater方法通知数据改变了。
class Subsject
//被观察者,需要将观察者收集起来。改变的时候通知观察者。
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
this.observers = [];
this.state = "正常";
attach(o)
this.observers.push(o);
setState(state)
this.state = state;
//通知观察者
this.observers.forEach((item) => item.update(this.state));
class Observer
//观察者
constructor(name)
this.name = name;
update(state)
console.log(`我是$this.name,宝宝现在$state`);
// vue数据改变了, 需要通知依赖的视图
//被观察者
let s = new Subsject("小宝宝");
//观察者
let o1 = new Observer("爸爸");
let o2 = new Observer("妈妈");
//模范get方法时手机依赖
s.attach(o1);
s.attach(o2);
//宝宝状态改变,模仿set方法
s.setState("不开心了");
使用宝宝模拟被观察者,使用父母模拟观察者。当被观察者状态改变的时候,就会通知,调用观察者的update方法。
promise
使用promise的时候会传入一个执行器,会立即执行。
promise有三个状态,pending,fullied,reject。默认是pending。
const PENDING = "PENDING";
const FULFILLED = "FULFILLED";
const REJECTED = "REJECTED";
class Promise
constructor(executor)
this.status = PENDING; //状态
this.value = undefined; //成功
this.reason = undefined; //失败原因
const resolve = (value) =>
//成功resolve函数
if (this.status !== PENDING)
return;
this.value = value
this.status = FULFILLED;
;
const reject = (reason) =>
//失败函数
if (this.status !== PENDING)
return;
this.reason = reason
this.status = REJECTEDD;
;
//执行器有可能会跑错。
try
executor(resolve, reject);
catch (e)
reject(e)
then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
if (this.status === PENDING)
else if (this.status === FULFILLED)
onFulfilled(this.value);
else
onRejected(this.reason);
catch(onRejected)
onRejected(this.reason)
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
console.log("promise");
resolve(1);
reject(2);
);
promise.then(
(data) =>
console.log(data);
,
(err) =>
console.log(123123);
console.log(err);
);
简单的promise的实现,主要实现三个状态的改变以及执行器执行的时候也可能会抛出错误,所以需要try catch一下。这样简单的同步promise就实现了。
接着继续实现异步的。
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
console.log("promise");
setTimeout(() =>
resolve(2);
, 2000);
);
实现思路:
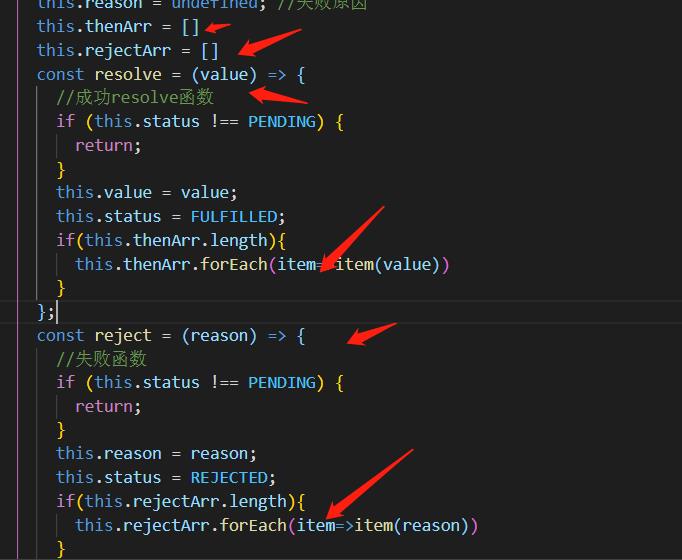
当我们调用then的时候resolve还没执行,此时status还是Pending,所以我们需要把当前的回调函数暂存起来,当resolve执行的时候需要取出来去执行。
const PENDING = "PENDING";
const FULFILLED = "FULFILLED";
const REJECTED = "REJECTED";
class Promise
constructor(executor)
this.status = PENDING; //状态
this.value = undefined; //成功
this.reason = undefined; //失败原因
this.thenArr = []
this.rejectArr = []
const resolve = (value) =>
//成功resolve函数
if (this.status !== PENDING)
return;
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
if(this.thenArr.length)
this.thenArr.forEach(item=>item(value))
;
const reject = (reason) =>
//失败函数
if (this.status !== PENDING)
return;
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
if(this.rejectArr.length)
this.rejectArr.forEach(item=>item(reason))
;
//执行器有可能会跑错。
try
executor(resolve, reject);
catch (e)
reject(e);
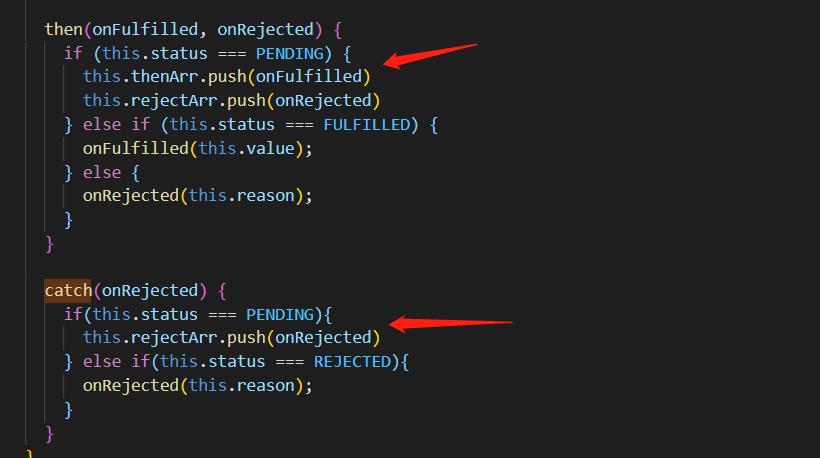
then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
if (this.status === PENDING)
this.thenArr.push(onFulfilled)
this.rejectArr.push(onRejected)
else if (this.status === FULFILLED)
onFulfilled(this.value);
else
onRejected(this.reason);
catch(onRejected)
if(this.status === PENDING)
this.rejectArr.push(onRejected)
else if(this.status === REJECTED)
onRejected(this.reason);
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
console.log("promise");
setTimeout(()=>
resolve(2)
,2000)
);
promise.then(
(data) =>
console.log('data1', data);
,
(err) =>
console.log("err", err);
);
promise.catch(err=>
console.log('catch',err);
)
promise.then(
(data) =>
console.log('data2', data);
,
(err) =>
console.log("err", err);
);
promise.then(
(data) =>
console.log('data2', data);
,
(err) =>
console.log("err", err);
);
通过发布订阅的模式就可以实现。
promise的特点
解决了 链式调用解决回调地狱 和 同步并发 的问题。
- 链式调用
情况1: then中返回一个普通值(不是promise)的情况,会作为外层下一次then的成功结果。每次then返回的是新的promise。
promise.then(
(data) =>
console.log("data1", data);
throw new Error(333)
,
(err) =>
console.log("err", err);
).then(data2=>
console.log('data2', data2);
, err2=>
console.log('err2', err2);
);
第一次then中的返回值会作为第二次then的结果,抛错会被第二层catch捕获。
情况2: then中方法抛错,会作为下一次then的失败结果。(如果下一次then没有捕获,会继续往下走)
无论上一次then走的是成功还是失败,只要返回普通值,都会执行下一次then的成功。
情况3: then中返回新的promise,成功则走成功,失败或者报错就被捕获。
实现:
- 思路:就是then方法和catch方法每次返回一个新的promise,然后因为我们的.then是微任务,所以我们使用setTimeout将then要执行的函数挂起来,让同步任务先走。这里不是queueMicrotask模拟微任务是因为它本来就是Promise实现的。
- 接着,我们需要判断返回的值x是什么类型,如果是普通类型直接调用resolve即可,如果是Promise就会判断promise的状态的。
- 异步执行也是一样的道理,将setTiemout包裹起来放进去数组里面,等待resolve执行去调用,才会继续走下去。
const PENDING = "PENDING";
const FULFILLED = "FULFILLED";
const REJECTED = "REJECTED";
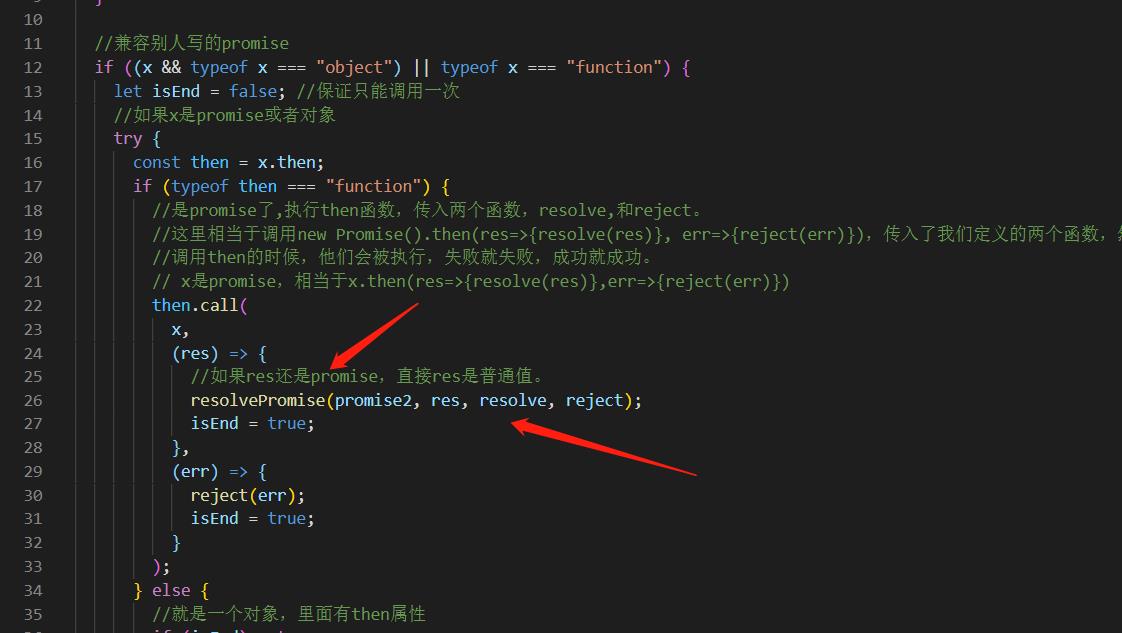
function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)
if (promise2 === x)
//如果函数执行返回的是自己的promise2,那么就死循环
throw new TypeError("不能引用自己的promise");
//兼容别人写的promise
if ((x && typeof x === "object") || typeof x === "function")
//如果x是promise或者对象
try
const then = x.then;
if (typeof then === "function")
//是promise了,执行then函数,传入两个函数,resolve,和reject。
//这里相当于调用new Promise().then(res=>resolve(res), err=>reject(err)),传入了我们定义的两个函数,然后
//调用then的时候,他们会被执行,失败就失败,成功就成功。
// x是promise,相当于x.then(res=>resolve(res),err=>reject(err))
then.call(
x,
(res) =>
resolve(res);
,
(err) =>
reject(err);
);
else
//就是一个对象,里面有then属性
resolve(x);
catch (e)
reject(e);
else
//返回的x是普通纸,直接resolve即可
resolve(x);
class Promise
constructor(executor)
this.status = PENDING; //状态
this.value = undefined; //成功
this.reason = undefined; //失败原因
this.thenArr = [];
this.rejectArr = [];
const resolve = (value) =>
//成功resolve函数
if (this.status !== PENDING)
return;
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
if (this.thenArr.length)
this.thenArr.forEach((item) =>
item(value);
);
this.thenArr = [];
;
const reject = (reason) =>
//失败函数
if (this.status !== PENDING)
return;
this.reason = reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
if (this.rejectArr.length)
this.rejectArr.forEach((item) =>
item(reason);
);
this.rejectArr = [];
;
//执行器有可能会跑错。
try
executor(resolve, reject);
catch (e)
reject(e);
then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
//返回全新的Promise
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
if (this.status === PENDING)
//改造onFuil
this.thenArr.push(() =>
setTimeout(() =>
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
);
);
this.rejectArr.push(() =>
setTimeout(() =>
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
, 0);
);
else if (this.status === FULFILLED)
//必须通过setTimoeut才能拿到promise2。不然同步的话promise还没执行完无法传给resolvePromise
setTimeout(() =>
const x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
, 0);
else
setTimeout(() =>
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
, 0);
);
return promise2;
catch(onRejected)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
if (this.status === PENDING)
this.rejectArr.push(onRejected);
else if (this.status === REJECTED)
setTimeout(() =>
const x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
, 0);
);
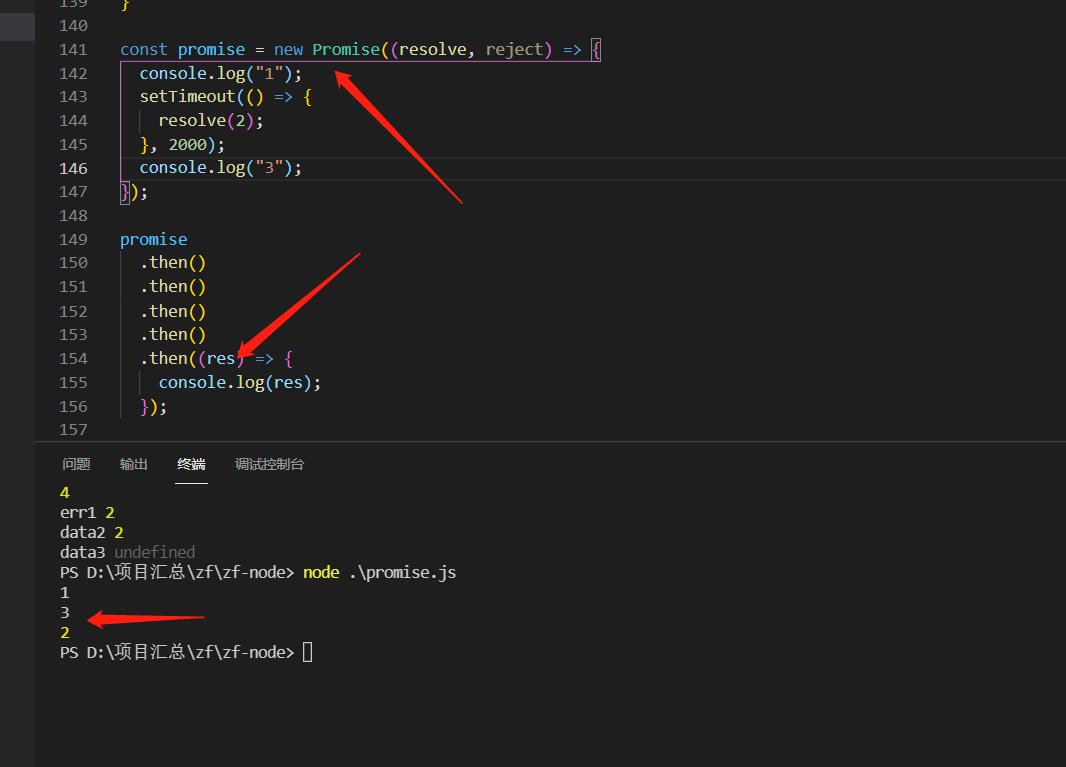
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
console.log("1");
setTimeout(() =>
reject(2);
, 2000);
console.log("3");
);
promise
.then(
(data) =>
console.log("data1", data);
,
(err) =>
console.log("err1", err);
return new Promise((re, rj) =>
re(2);
);
)
.then(
(data2) =>
console.log("data2", data2);
,
(err2) =>
console.log("err2", err2);
)
.then((data3) =>
console.log("data3", data3);
);
console.log(4);
关键就是:

这里的then返回新的promise,对于异步的,需要将其包裹成一个函数存放起来,当resolve执行的时候再去拿出来执行,再去执行真正的then函数。
而同步的话就是直接放入setTimeout,模拟微任务。获取then函数返回的值x。调用resolvePromise函数。
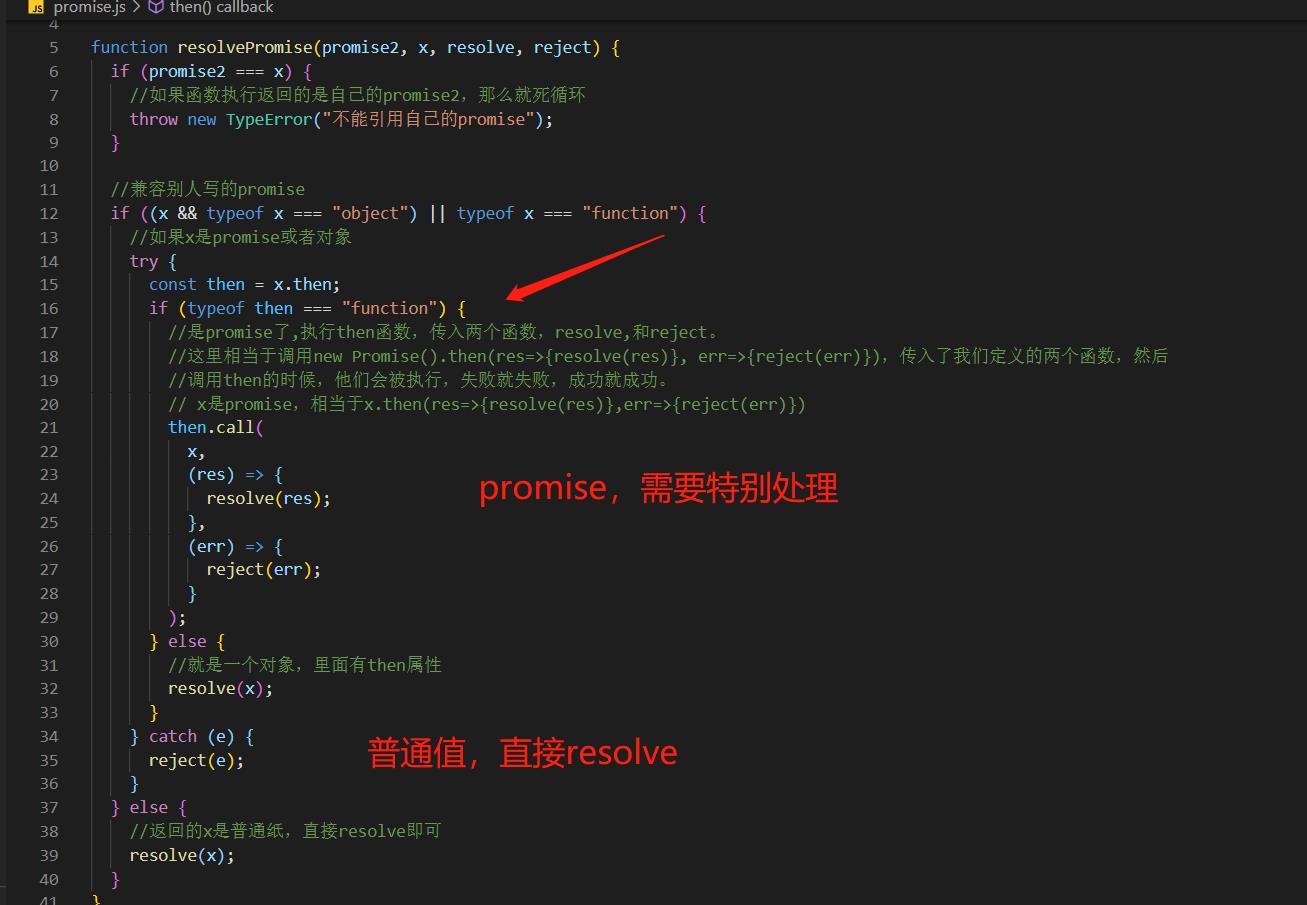
这里对返回的x做判断,如果是prmise就做对应的处理。
这样我们的promise就完成了。
但是,如果返回的promise的resolve又是promise呢?
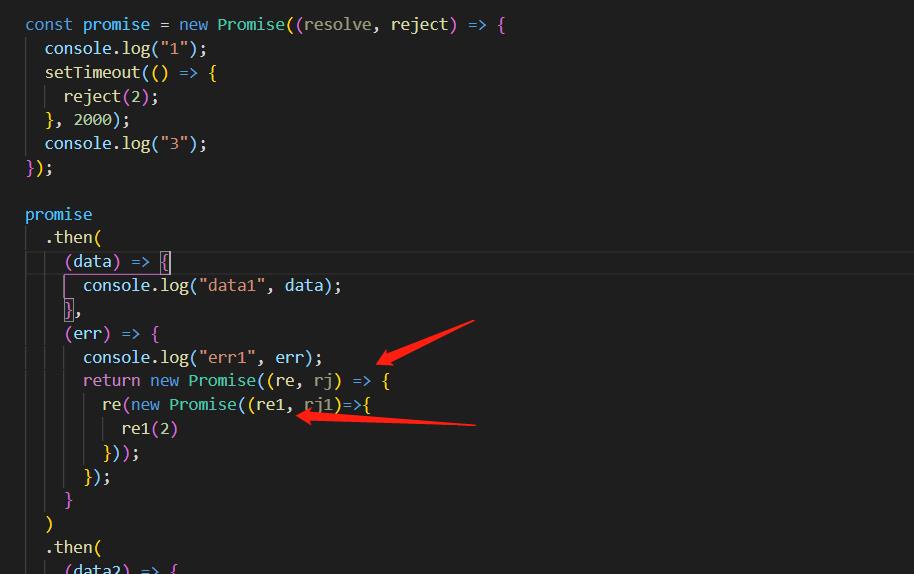
这里对res的处理还必须包一层。
而且then的两个参数是可选的,也要做处理。
原生的实现,如果没有被处理,会一直往外传。
原生promise的then,如果onFuillied或者onReject如果不是函数,会被忽略。
思路:处理很简单,如果不是函数,我们就自己写一个函数,将值传递下去就行了,只需要注意reject是需要抛出错误的,而不是传递,传递的话会被下一个resolve捕获。抛出错误才会被try catch捕获交给reject。

改写即可。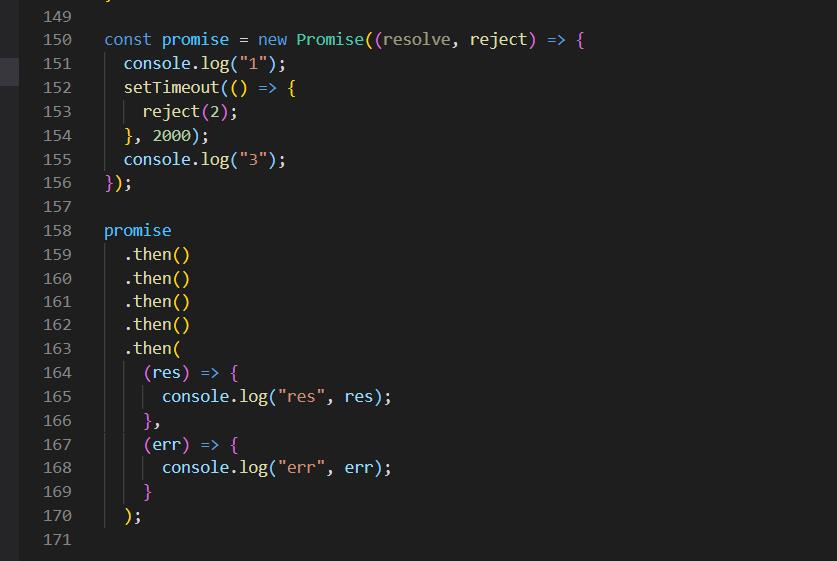

会一层一层跑下来。
总结
promise可以是一个函数,或者一个类,他接受一个执行器。传入对应的参数。有三个状态,执行resolve的时候会将状态改为fuilled,执行reject的时候会将状态改为reject。顺便将值存起来。当同步的时候,调用.then或者.catch的时候,再将值作为入参传给函数。
异步的时候,调用.then的时候状态还未改变,需要将then的参数存放起来,等异步执行完毕调用resolve或者reject的时候再执行。
因为promise可以链式调用。所以.then必须返沪一个新的promise。为了模拟微任务,需要将then函数的内容放入setTimeout去执行。不会阻塞同步代码。
这样我们的promise就基本实现了。接着需要实现他的静态方法。
以上是关于js 高阶函数 发布订阅观察者模式 手撕promise的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章