LeetCode 99. 恢复二叉搜索树
Posted ZSYL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode 99. 恢复二叉搜索树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目描述
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的两个节点被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树。
进阶:使用 O(n) 空间复杂度的解法很容易实现。你能想出一个只使用常数空间的解决方案吗?
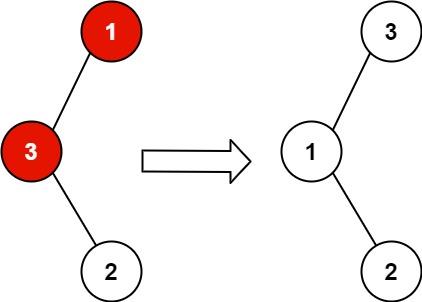
输入:root = [1,3,null,null,2]
输出:[3,1,null,null,2]
解释:3 不能是 1 左孩子,因为 3 > 1 。交换 1 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。

输入:root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
输出:[2,1,4,null,null,3]
解释:2 不能在 3 的右子树中,因为 2 < 3 。交换 2 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
显式中序遍历
思路与算法:
二叉搜索树:左节点.val<根节点.val<右节点.val
我们需要考虑两个节点被错误地交换后对原二叉搜索树造成了什么影响。对于二叉搜索树,我们知道如果对其进行中序遍历,得到的值序列是递增有序的,而如果我们错误地交换了两个节点,等价于在这个值序列中交换了两个值,破坏了值序列的递增性。
我们来看下如果在一个递增的序列中交换两个值会造成什么影响。假设有一个递增序列 a=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]。如果我们交换两个不相邻的数字,例如 2 和 6,原序列变成了 a=[1,6,3,4,5,2,7],那么显然序列中有两个位置不满足 a i < a i + 1 a_i<a_i+1 ai<ai+1,在这个序列中体现为 6>3,5>2,因此只要我们找到这两个位置,即可找到被错误交换的两个节点。如果我们交换两个相邻的数字,例如 2 和 3,此时交换后的序列只有一个位置不满足 a i < a i + 1 a_i<a_i+1 ai<ai+1。因此整个值序列中不满足条件的位置或者有两个,或者有一个。
至此,解题方法已经呼之欲出了:

实现部分,本方法开辟一个新数组 nums 来记录中序遍历得到的值序列,然后线性遍历找到两个位置 i 和 j,并重新遍历原二叉搜索树修改对应节点的值完成修复,具体实现可以看下面的代码。
class Solution
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, nums);
int[] swapped = findTwoSwapped(nums);
recover(root, 2, swapped[0], swapped[1]);
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums)
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, nums);
public int[] findTwoSwapped(List<Integer> nums)
int n = nums.size();
int index1 = -1, index2 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
if (nums.get(i + 1) < nums.get(i))
index2 = i + 1;
if (index1 == -1)
index1 = i;
else
break;
int x = nums.get(index1), y = nums.get(index2);
return new int[]x, y;
public void recover(TreeNode root, int count, int x, int y)
if (root != null)
if (root.val == x || root.val == y)
root.val = root.val == x ? y : x;
if (--count == 0)
return;
recover(root.right, count, x, y);
recover(root.left, count, x, y);
class Solution
public:
void inorder(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums)
if (root == nullptr)
return;
inorder(root->left, nums);
nums.push_back(root->val);
inorder(root->right, nums);
pair<int,int> findTwoSwapped(vector<int>& nums)
int n = nums.size();
int index1 = -1, index2 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
if (nums[i + 1] < nums[i])
index2 = i + 1;
if (index1 == -1)
index1 = i;
else
break;
int x = nums[index1], y = nums[index2];
return x, y;
void recover(TreeNode* r, int count, int x, int y)
if (r != nullptr)
if (r->val == x || r->val == y)
r->val = r->val == x ? y : x;
if (--count == 0)
return;
recover(r->left, count, x, y);
recover(r->right, count, x, y);
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root)
vector<int> nums;
inorder(root, nums);
pair<int,int> swapped= findTwoSwapped(nums);
recover(root, 2, swapped.first, swapped.second);
;
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 为二叉搜索树的节点数。中序遍历需要 O(N) 的时间,判断两个交换节点在最好的情况下是 O(1),在最坏的情况下是 O(N),因此总时间复杂度为 O(N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N)。我们需要用 nums 数组存储树的中序遍历列表。
隐式中序遍历
思路与算法
方法一是显式地将中序遍历的值序列保存在一个 nums 数组中,然后再去寻找被错误交换的节点,但我们也可以隐式地在中序遍历的过程就找到被错误交换的节点 x 和 y。
具体来说,由于我们只关心中序遍历的值序列中每个相邻的位置的大小关系是否满足条件,且错误交换后最多两个位置不满足条件,因此在中序遍历的过程我们只需要维护当前中序遍历到的最后一个节点 pred,然后在遍历到下一个节点的时候,看两个节点的值是否满足前者小于后者即可,如果不满足说明找到了一个交换的节点,且在找到两次以后就可以终止遍历。
这样我们就可以在中序遍历中直接找到被错误交换的两个节点 x 和 y,不用显式建立 nums 数组。
中序遍历的实现有迭代和递归两种等价的写法,在本方法中提供迭代实现的写法。使用迭代实现中序遍历需要手动维护栈。
class Solution
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root)
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
TreeNode x = null, y = null, pred = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null)
while (root != null)
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
root = stack.pop();
if (pred != null && root.val < pred.val)
y = root;
if (x == null)
x = pred;
else
break;
pred = root;
root = root.right;
swap(x, y);
public void swap(TreeNode x, TreeNode y)
int tmp = x.val;
x.val = y.val;
y.val = tmp;
class Solution
public:
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root)
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
TreeNode* x = nullptr;
TreeNode* y = nullptr;
TreeNode* pred = nullptr;
while (!stk.empty() || root != nullptr)
while (root != nullptr)
stk.push(root);
root = root->left;
root = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if (pred != nullptr && root->val < pred->val)
y = root;
if (x == nullptr)
x = pred;
else break;
pred = root;
root = root->right;
swap(x->val, y->val);
;
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:最坏情况下(即待交换节点为二叉搜索树最右侧的叶子节点)我们需要遍历整棵树,时间复杂度为 O(N),其中 N 为二叉搜索树的节点个数。
- 空间复杂度:O(H),其中 H 为二叉搜索树的高度。中序遍历的时候栈的深度取决于二叉搜索树的高度。
加油!
感谢!
努力!
以上是关于LeetCode 99. 恢复二叉搜索树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
⭐算法入门⭐《二叉树 - 二叉搜索树》中等09 —— LeetCode 99. 恢复二叉搜索树