基于MobileNet-v3和YOLOv5的餐饮有害虫鼠识别及防治系统的设计与实现
Posted 荣仔!最靓的仔!
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于MobileNet-v3和YOLOv5的餐饮有害虫鼠识别及防治系统的设计与实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在新时代的背景下, “清爽干净”和“卫生健康”成为老百姓对美好生活向往的两个重要因素,这也是当下餐饮行业管理者们不变的追求与目标。随着科技的发展与进步,人工智能成为了文明社会的重要产物,并逐渐应用于日常生活中的方方面面。基于此,设计并开发出一款可以有效预防虫鼠害的系统对于提升管理效率及卫生服务质量是非常有必要的……
本文阐述的内容主要包括:
- 基于 MobileNet-v3 的虫鼠识别功能的设计与实现
- 基于 YOLOv5 的鼠类检测功能的设计与实现
- 基于 PyQt5 的功能封装与人机交互界面的设计与实现
目录
2 基于 MobileNet-v3 的虫鼠识别功能的设计与实现
1 成品效果演示
1.1 图片成品效果演示

1.2 视频成品效果演示
2 基于 MobileNet-v3 的虫鼠识别功能的设计与实现
2.1 数据集的获取与整理
2.1.1 数据获取
众所周知,数据获取是深度学习领域一项必不可少的技能。数据获取方式多种多样,具体而言:①找与任务相关的公开数据集(如用来进行图像识别的 COCO 数据集、ImageNet 数据集等);②利用外包平台进行数据获取(如阿里众包、百度数据众包、京东微工等)③当然也可以根据需要自己抱着摄像头采集;④最后一种获取方式是利用网络爬虫技术获取。
在这里,用到的是第 4 种数据获取方式——网络爬虫。用到的是之前自己编写的一款百度图片爬虫APP。
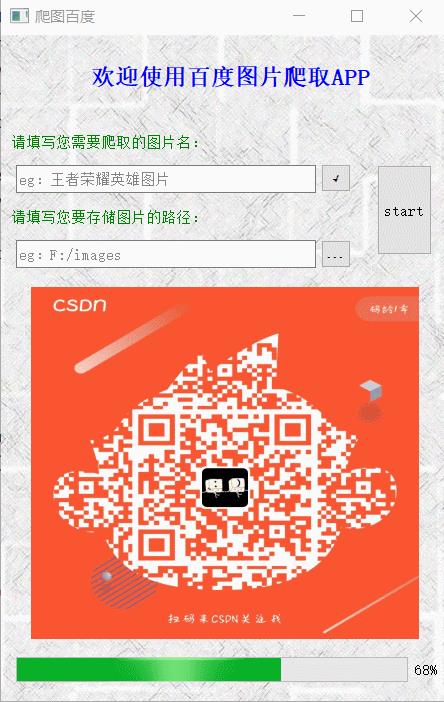
关于该百度图片爬虫 APP 有兴趣的读者请移步:
首发博文:当爬虫遇到PyQt5:GUI界面实现百度图片爬取
GitHub 源码获取:PyQt5/reptile at main · zhao302014/PyQt5 · GitHub
利用自己编写的爬虫工具,共获取了包括 ant、cockroach、fly、mouse、pillworm 在内的 5 种虫鼠类别的数据集,各 50 张,共 250 张。
2.1.2 数据整理
数据整理主要可以考虑三个层面的内容:数据检查与归一化、数据去重、数据集划分。
很显然,上一步获取的数据集不论是分量还是总量都太少,容易由于数据集量太小或模型过大产生过拟合现象。因此,这里采用最简单粗暴的方法防止过拟合:隐式的正则化方法——数据增强。具体而言,用到了包括 Scale、Horizontal、Rotate、Darker、Brighter、Translation、AddNoise 在内的数据增强方法(基于 OpenCV 的相关方法实现的)

# 数据增强之缩放操作
def Scale(image, scale):
return cv2.resize(image, None, fx=scale, fy=scale, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# 数据增强之水平翻转
def Flip_Horizontal(image):
return cv2.flip(image, 1, dst=None) # 水平镜像
# 数据增强之垂直翻转
def Flip_Vertical(image):
return cv2.flip(image, 0, dst=None) # 垂直镜像
# 数据增强之旋转
def Rotate(image, angle=15, scale=0.9):
w = image.shape[1]
h = image.shape[0]
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((w / 2, h / 2), angle, scale) # 旋转矩阵
image = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (w, h)) # 旋转
return image
# 数据增强之变暗
def Darker(image, percetage=0.9):
image_copy = image.copy()
w = image.shape[1]
h = image.shape[0]
for xi in range(0, w):
for xj in range(0, h):
image_copy[xj, xi, 0] = int(image[xj, xi, 0] * percetage)
image_copy[xj, xi, 1] = int(image[xj, xi, 1] * percetage)
image_copy[xj, xi, 2] = int(image[xj, xi, 2] * percetage)
return image_copy
# 数据增强之变亮
def Brighter(image, percetage=1.1):
image_copy = image.copy()
w = image.shape[1]
h = image.shape[0]
for xi in range(0, w):
for xj in range(0, h):
image_copy[xj, xi, 0] = np.clip(int(image[xj, xi, 0] * percetage), a_max=255, a_min=0)
image_copy[xj, xi, 1] = np.clip(int(image[xj, xi, 1] * percetage), a_max=255, a_min=0)
image_copy[xj, xi, 2] = np.clip(int(image[xj, xi, 2] * percetage), a_max=255, a_min=0)
return image_copy
# 数据增强之平移
def Translation(img, x, y):
img_info = img.shape
height = img_info[0]
width = img_info[1]
mat_translation = np.float32([[1, 0, x], [0, 1, y]]) # 变换矩阵:设置平移变换所需的计算矩阵:2行3列(平移变换:其中x表示水平方向上的平移距离,y表示竖直方向上的平移距离)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img, mat_translation, (width, height)) # 变换函数
return dst
# 数据增强之增加椒盐噪声
def SaltAndPepper(src, percetage):
SP_NoiseImg = src.copy()
SP_NoiseNum = int(percetage * src.shape[0] * src.shape[1])
for i in range(SP_NoiseNum):
randR = np.random.randint(0, src.shape[0] - 1)
randG = np.random.randint(0, src.shape[1] - 1)
randB = np.random.randint(0, 3)
if np.random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
SP_NoiseImg[randR, randG, randB] = 0
else:
SP_NoiseImg[randR, randG, randB] = 255
return SP_NoiseImg
# 数据增强之增加高斯噪声
def GaussianNoise(image, percetage):
G_Noiseimg = image.copy()
w = image.shape[1]
h = image.shape[0]
G_NoiseNum = int(percetage * image.shape[0] * image.shape[1])
for i in range(G_NoiseNum):
temp_x = np.random.randint(0, h)
temp_y = np.random.randint(0, w)
G_Noiseimg[temp_x][temp_y][np.random.randint(3)] = np.random.randn(1)[0]
return G_Noiseimg
# 数据增强之增加高斯滤波
def Blur(img):
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (7, 7), 1.5) # cv2.GaussianBlur(图像,卷积核,标准差)
return blur2.2 为什么选择 MobileNet-v3
2.2.1 同样数据集下与其他模型比较
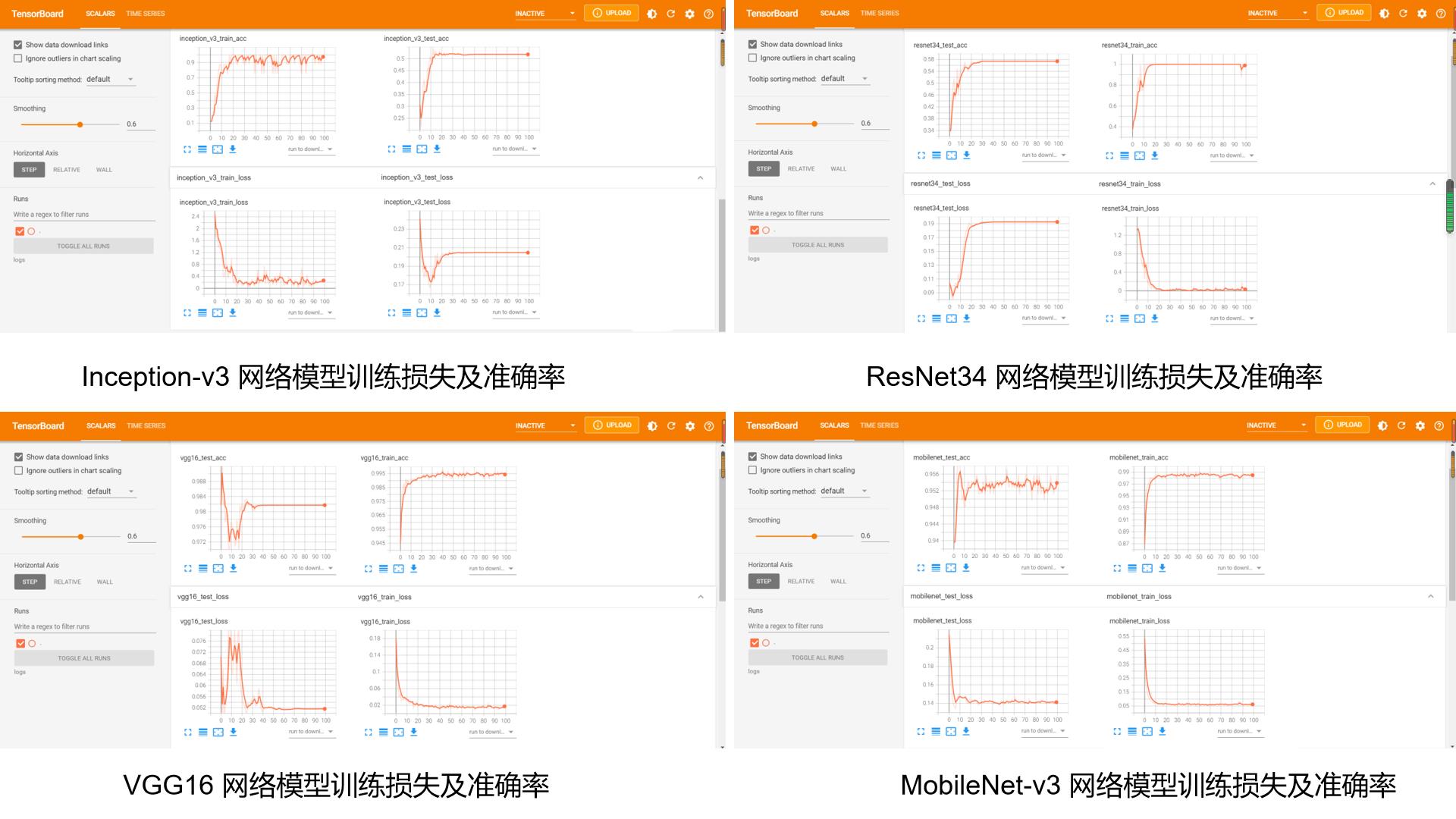
2.2.2 MobileNet-v3 简介
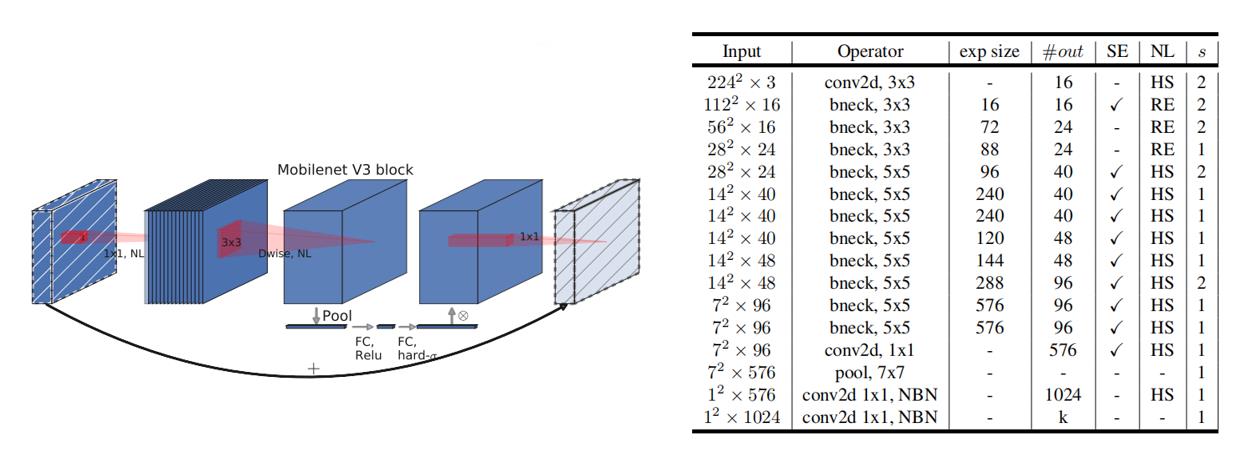
MobileNet-v3 综合了 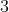 种模型的思想:
种模型的思想:
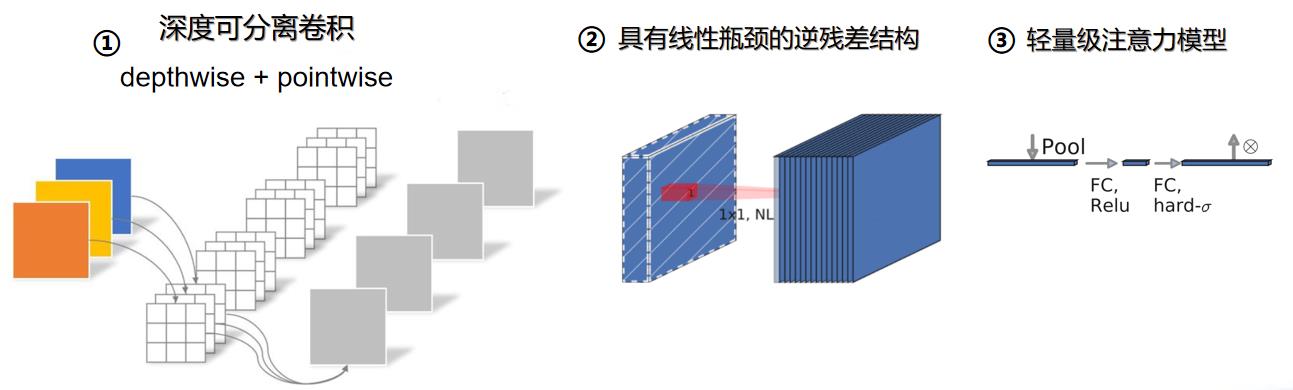
2.3 种类提示及灭除策略实现
这两个功能实际上运用两种方式实现:“种类提示”功能实现运用的是爬虫技术,数据来源是百度百科词条概述部分内容;“灭除策略”功能实现运用的是传统的字符串返回方式。
基于爬虫技术实现的核心代码:
def class_value(content):
# 请求地址
url = 'https://baike.baidu.com/item/' + urllib.parse.quote(content)
# 请求头部
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (Khtml, like Gecko) Chrome/67.0.3396.99 Safari/537.36'
}
# 利用请求地址和请求头部构造请求对象
req = urllib.request.Request(url=url, headers=headers, method='GET')
# 发送请求,获得响应
response = urllib.request.urlopen(req)
# 读取响应,获得文本
text = response.read().decode('utf-8')
# 构造 _Element 对象
html = etree.HTML(text)
# 使用 xpath 匹配数据,得到匹配字符串列表
sen_list = html.xpath('//div[contains(@class,"lemma-summary") or contains(@class,"lemmaWgt-lemmaSummary")]//text()')
# 过滤数据,去掉空白
sen_list_after_filter = [item.strip('\\n') for item in sen_list]
# 将字符串列表连成字符串并返回
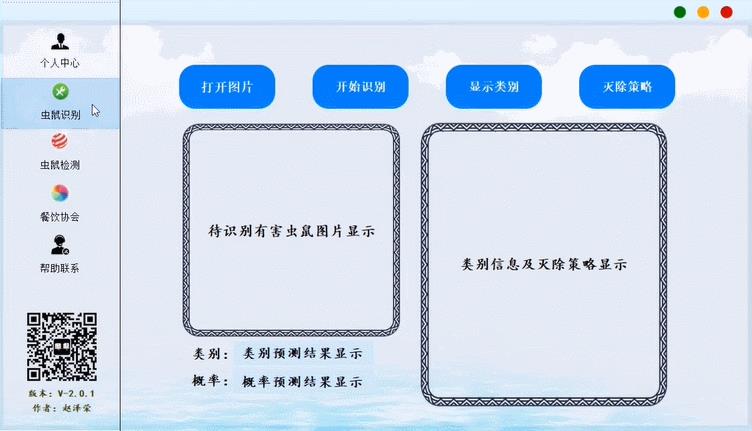
return ''.join(sen_list_after_filter)2.4 demo实现效果
| 模型大小 | 速度 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1-score |
| 5.96 MB | 169ms/img | 91.20% | 83.71% | 0.8729 |
2.5 未来展望
当然,这只是一个实验性的  ,如果要实际落地当然相差甚远。最大的原因是数据集种类太少,这也是未来的需要改进的点……
,如果要实际落地当然相差甚远。最大的原因是数据集种类太少,这也是未来的需要改进的点……
3 基于 YOLOv5 的鼠类检测功能的设计与实现
3.1 数据集的整理与获取
同样,数据集获取的是 500 张日常生活中常见的鼠类图片,用到的爬虫工具是前面提到的自己写的百度图片爬虫 APP,由于该功能的本质是目标检测,要用到 Make Sense 线上标注工具。
3.2 YOLOv5 简介
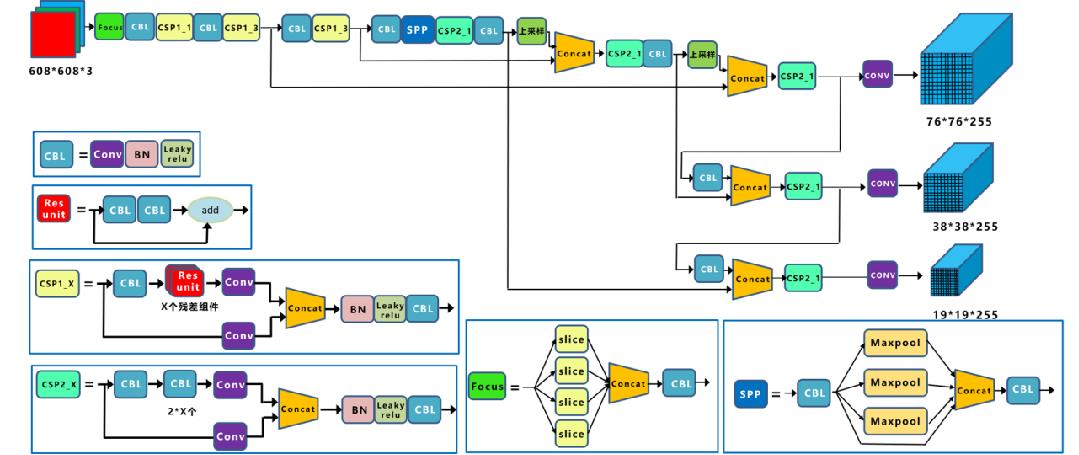
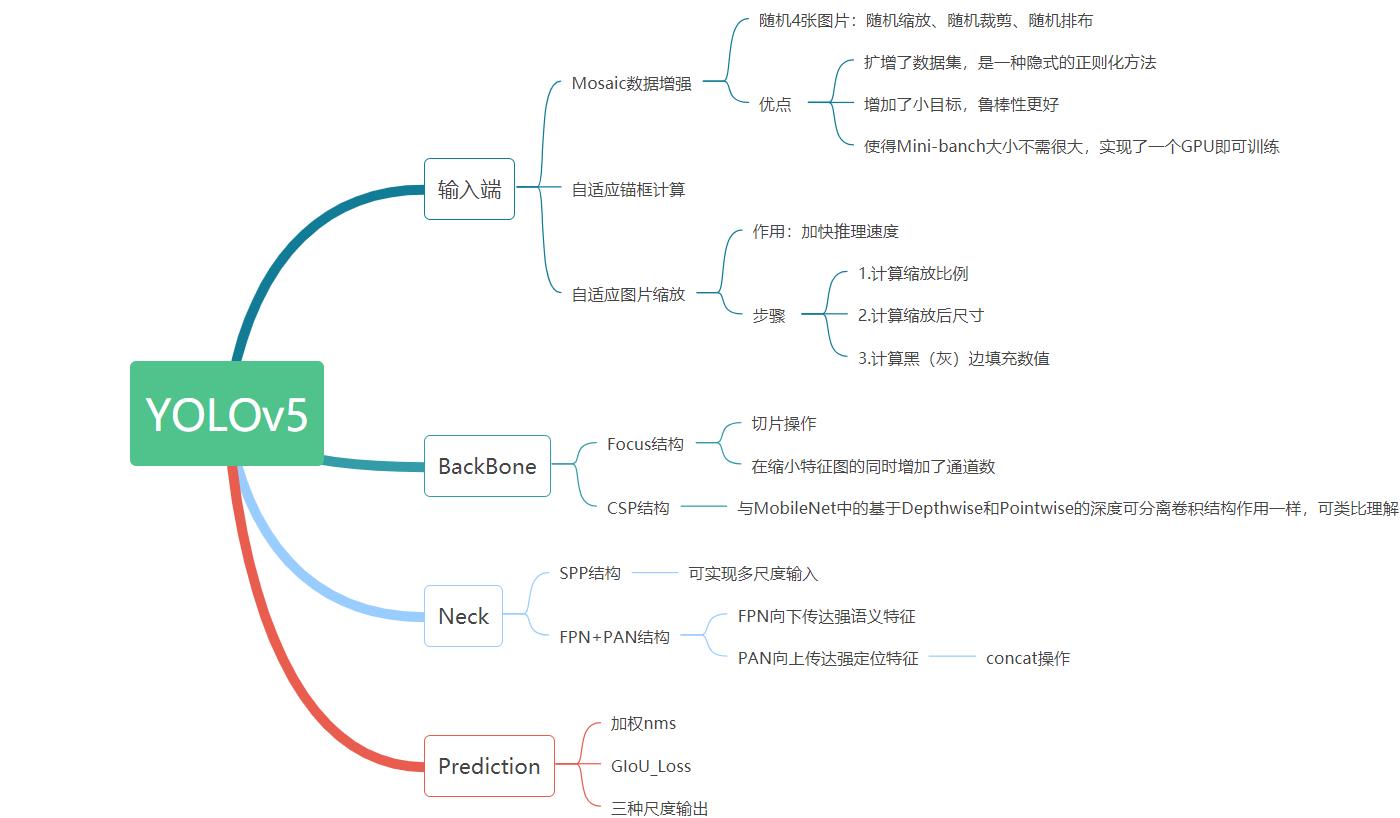
3.3 鼠类检测的设计与实现
该项目基于 YOLOv5 的设计与实现运用的是 GitHub 上 Yolov 5 v5.0 版本的开源项目源码。
关于从安装到实例运用全方位系列讲解 GitHub YOLOv5 开源代码专栏感兴趣的读者请移步:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_11244228.html
最终实现的效果演示:

| 模型大小 | 速度 | 精确率 | 召回率 | mAP_0.5 |
| 54.4 MB | 69.7s/100img (NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti) | 93.17% | 91.65% | 0.9240 |
3.4 未来展望
- 在远距离检测方面改进
- 在个体检测方面改进
4 基于 PyQt5 的功能封装与人机交互界面的设计与实现
4.1 PyQt5 环境安装
首先安装 PyQt:
pip install pyQt5 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
或
pip install -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple pyQt5
或
pip install pyQt5 -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
或
混合使用接下来安装 QtDesigner:
pip install pyqt5-tools -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
或
pip install -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple pyqt5-tools
或
pip install pyqt5-tools-i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
或
混合使用注:关于 Python GUI 安装细则感兴趣的读者请移步:Python GUI 快速入门_荣仔的博客-CSDN博客
4.2 关键语句摘录
去边框
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.FramelessWindowHint)设定背景图
window_pale = QtGui.QPalette()
window_pale.setBrush(self.backgroundRole(), QtGui.QBrush(QtGui.QPixmap("background.jpg")))
self.setPalette(window_pale)设置弹窗
QMessageBox.information(self, "抱歉", "该功能正在抢修中...")重写鼠标事件
# 重写鼠标移动事件
def mouseMoveEvent(self, e: QMouseEvent):
if self._tracking:
self._endPos = e.pos() - self._startPos
self.move(self.pos() + self._endPos)
self.setCursor(QCursor(Qt.SizeAllCursor))
# 重写鼠标“按”事件
def mousePressEvent(self, e: QMouseEvent):
if e.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
self._startPos = QPoint(e.x(), e.y())
self._tracking = True
# 重写鼠标“抬”事件
def mouseReleaseEvent(self, e: QMouseEvent):
if e.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
self._tracking = False
self._startPos = None
self._endPos = None
self.setCursor(QCursor(Qt.ArrowCursor))显示图片
self.classlabel = QLabel(self)
self.classlabel.setFixedSize(100, 100)
self.classlabel.move(100, 100)
self.classlabel.setPixmap(QPixmap("image.png"))
self.classlabel.setScaledContents(True)显示文字
self.classlabel = QLabel(self)
self.classlabel.setText("文本内容……")
self.classlabel.move(100, 100)
self.classlabel.setStyleSheet(
"QLabel{color:black;font-size:15px;font-weight:bold;font-family:KaiTi;}"
)模拟  系统重写“最小化”、“缩小界面”、“关闭”按钮
系统重写“最小化”、“缩小界面”、“关闭”按钮
# 红色按钮:重写“关闭”事件
self.button_red = QPushButton(self)
self.button_red.move(900, 11)
self.button_red.setFixedSize(18, 18)
self.button_red.setStyleSheet("QPushButton{background:#CE0000;color:white;box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px;border-radius: 9px}"
"QPushButton:hover{background:red;}"
"QPushButton:pressed{border: 1px solid #3C3C3C!important;background:black}")
self.button_red.clicked.connect(self.quit_button)
# 黄色按钮:重写“缩小”事件
self.button_orange = QPushButton(self)
self.button_orange.move(865, 11)
self.button_orange.setFixedSize(18, 18)
self.button_orange.setStyleSheet("QPushButton{background:orange;color:white;box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px;border-radius: 9px}"
"QPushButton:hover{background:#FFD306}"
"QPushButton:pressed{border: 1px solid #3C3C3C!important;background:black}")
# 绿色按钮:重写“最小化”事件
self.button_green = QPushButton(self)
self.button_green.move(830, 11)
self.button_green.setFixedSize(18, 18)
self.button_green.setStyleSheet("QPushButton{background:green;color:white;box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px;border-radius: 9px}"
"QPushButton:hover{background:#08BF14}"
"QPushButton:pressed{border: 1px solid #3C3C3C!important;background:black}")
def quit_button(self):
quit()实现图片轮播
self.classlabel = QLabel(self)
self.classlabel.setFixedSize(777, 333)
self.classlabel.move(100, 222)
self.classlabel.setPixmap(QPixmap("image.jpg"))
self.classlabel.setScaledContents(True)
global lu
self.n = 1
self.lu = "./images/" + str(self.n) + ".jpg"
self.pm = QPixmap(self.lu)
self.lbpic = myLabel(self)
self.lbpic.setPixmap(self.pm)
self.lbpic.resize(777, 333)
self.lbpic.move(100, 222)
self.lbpic.setScaledContents(True)
self.lbpic._signal.connect(self.callbacklog) # 连接信号
self.timer1 = QTimer(self)
self.timer1.timeout.connect(self.timer_TimeOut)
self.timer1.start(2000)
self.show()
def timer_TimeOut(self):
self.n += 1
if self.n > 3:
self.n = 1
self.lu = "./images/" + str(self.n) + ".jpg"
self.pm = QPixmap(self.lu)
self.lbpic.setPixmap(self.pm)
def callbacklog(self, msg):
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = Image.open(self.lu)
plt.figure("image")
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
实现按钮选择
self.radioButton_1 = QtWidgets.QRadioButton(self)
self.radioButton_1.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(100, 100, 100, 100))
self.radioButton_1.setStyleSheet("color:black;font-size:18px;font-weight:bold;font-family:KaiTi;")
self.radioButton_1.setObjectName("radioButton_1")
self.radioButton_2 = QtWidgets.QRadioButton(self)
self.radioButton_2.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(100, 100, 100, 100))
self.radioButton_2.setStyleSheet("color:black;font-size:18px;font-weight:bold;font-family:KaiTi;")
self.radioButton_2.setObjectName("radioButton_2")
translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
self.radioButton_1.setText(translate("Form", "选项一"))
self.radioButton_1.setChecked(True)
self.radioButton_2.setText(translate("Form", "选项二"))
实现下拉列表选择
self.cb1 = QComboBox(self)
self.cb1.move(503, 181)
self.cb1.addItems(['选项 1'])
self.cb2 = QComboBox(self)
self.cb2.move(606, 181)
self.cb2.addItems(['选项 2.1', '选项 2.2', '选项 2.3'])
self.cb3 = QComboBox(self)
self.cb3.move(693, 181)
self.cb3.addItems(['选项 3.1', '选项 3.2', '选项 3.3', '选项 3.4', '选项 3.5'])
实现选择本地文件夹导出图片
def openimage(self):
self.imgName, self.imgType = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, '选择图片', '.', '图像文件(*.jpg)')
jpg_img = QtGui.QPixmap(self.imgName).scaled(self.imglabel.width(), self.imglabel.height())
self.imglabel.setPixmap(jpg_img)
实现选择本地文件夹导出视频
def button_video_open(self):
video_name, _ = QtWidgets.QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "打开视频", "", "*.mp4;;*.avi;;All Files(*)")
flag = self.cap.open(video_name)
if flag == False:
QtWidgets.QMessageBox.warning(self, u"Warning", u"打开视频失败", buttons=QtWidgets.QMessageBox.Ok,
defaultButton=QtWidgets.QMessageBox.Ok)
else:
self.out = cv2.VideoWriter('prediction.avi', cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'MJPG'), 20,
(int(self.cap.get(3)), int(self.cap.get(4))))
self.timer_video.start(30)
self.pushButton_video.setDisabled(True)
self.pushButton_img.setDisabled(True)
self.pushButton_camera.setDisabled(True)
实现摄像头显示效果
def button_camera_open(self):
if not self.timer_video.isActive():
# 默认使用第一个本地camera
flag = self.cap.open(0)
if flag == False:
QtWidgets.QMessageBox.warning(self, u"Warning", u"打开摄像头失败", buttons=QtWidgets.QMessageBox.Ok,
defaultButton=QtWidgets.QMessageBox.Ok)
else:
self.out = cv2.VideoWriter('prediction.avi', cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'MJPG'), 20,
(int(self.cap.get(3)), int(self.cap.get(4))))
self.timer_video.start(30)
self.pushButton_video.setDisabled(True)
self.pushButton_img.setDisabled(True)
self.pushButton_camera.setText(u"关闭摄像头")
else:
self.timer_video.stop()
self.cap.release()
self.out.release()
self.label.clear()
self.init_logo()
self.pushButton_video.setDisabled(False)
self.pushButton_img.setDisabled(False)
self.pushButton_camera.setText(u"摄像头检测")
实现界面中插入网页
# 新建一个QWebEngineView()对象
self.qwebengine = QWebEngineView(self)
# 设置网页在窗口中显示的位置和大小
self.qwebengine.setGeometry(100, 100, 100, 100)
# 在QWebEngineView中加载网址
self.qwebengine.load(QUrl("http://www.baidu.com"))4.3 未来展望
- 与数据库相连,实现用户注册功能,使得该项目更加接近实际落地预期。
5 主要参考文献
[1] J. Redmon, S. Divvala, R. Girshick, and A. Farhadi. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.02640, 2015.
[2] Joseph Redmon, Ali Farhadi. YOLO9000:Better, Faster, Stronger. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.08242v1, 2015.
[3] J. Redmon and A. Farhadi. Yolov3: An incremental improve_x0002_ment. arXiv, 2018.
[4] Alexey Bochkovskiy, Chien-Yao Wang and Hong-Yuan Mark Liao. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv, 2020.
[5] Andrew Howard, Mark Sandler, Grace Chu, Liang-Chieh Chen, Bo Chen, Mingxing Tan, Weijun Wang, Yukun Zhu, Ruoming Pang, Vijay Vasudevan, Quoc V. Le, Hartwig Adam.Searching for MobileNetV3. arXiv, 2019.
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「荣仔!最靓的仔!」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议。
转载请在醒目位置附上原文出处链接及本声明。CSDN博主「荣仔!最靓的仔!」的其他原创专栏链接:
《机器学习》学习笔记专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_9920949.html
《数字图像处理》学习笔记专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_9899861.html
《Python网络数据爬取及分析》专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_10097766.html
《GitHub YOLOv5 开源代码项目系列讲解》专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_11244228.html
《「深度学习一遍过」必修篇》专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_11251478.html
《23种设计模式在王者荣耀中的应用》专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/it_charge/category_9842143.html
感谢阅读 ! 感谢支持 ! 感谢关注 !
欢迎大家交流评论,一起学习!
 年
年  月
月  日于中国大陆 • 重庆
日于中国大陆 • 重庆
END
以上是关于基于MobileNet-v3和YOLOv5的餐饮有害虫鼠识别及防治系统的设计与实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
基于MobileNet-v3和YOLOv5的餐饮有害虫鼠识别及防治系统的设计与实现