使用Java和OpenCV调用YOLOv3完成实施目标检测
Posted 报错中.....
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用Java和OpenCV调用YOLOv3完成实施目标检测相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
使用Java和OpenCV调用YOLOv3完成实施目标检测,识别到目标就将包含目标的图片保存下来,没有目标就不保存。详细代码以及步骤。
第一步:在IDEA中完成对OpenCV包的导入
从官网上下载OpenCV:Releases - OpenCV。选择window版本下载,解压之后
把 opencv\\build\\目录下的java文件整个复制到项目文件下,名字随意。
File>Project Structure>Libraries ,选择+号,选择java,之后选择jar包位置。导入即可。
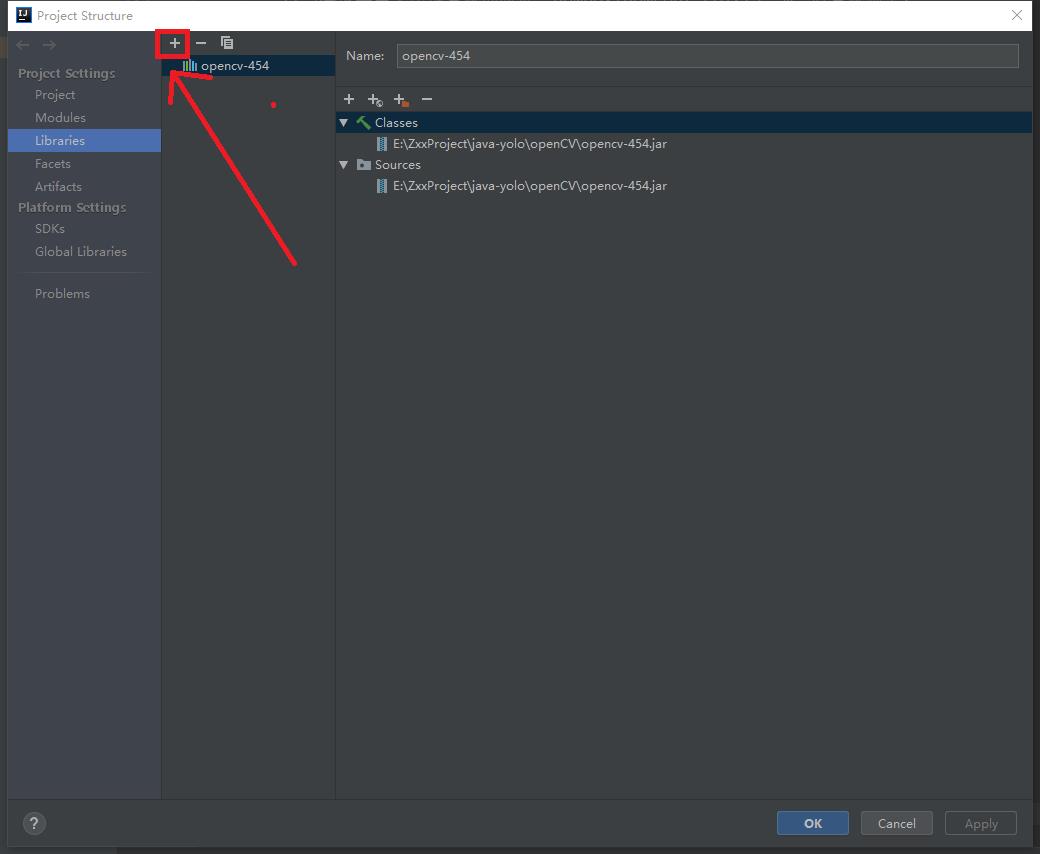
这里我已经导入过了。最后再配置dll
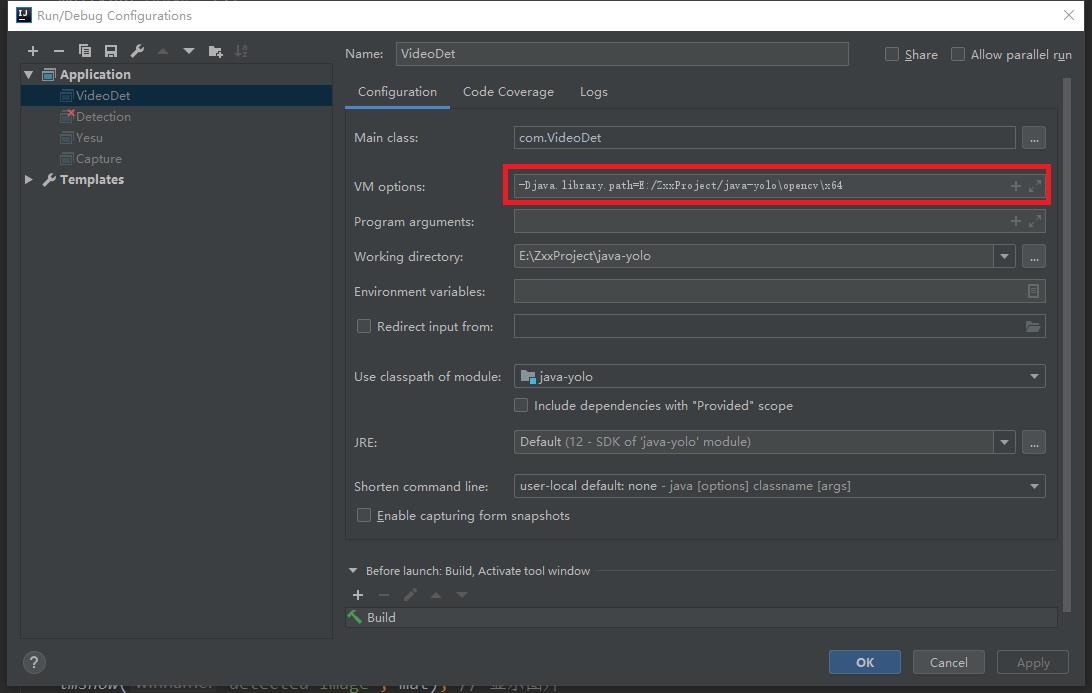
Run>Edit Configurations ,选中你所要配置的java文件,填入以下内容:
-Djava.library.path=$PROJECT_DIR$\\opencv\\x64 (64位选x64,32位选x86)
第二步:完成目标检测
首先下载darknet:GitHub - pjreddie/darknet: Convolutional Neural Networks
为了方便操作,这里只需要将darknet的路径以及保存的图片路径修改为自己的即可。下边直接上代码。当然你也可以训练自己的YOLOv3模型来完成相关的操作。
主程序
import org.opencv.core.*;
import org.opencv.core.Point;
import org.opencv.dnn.Dnn;
import org.opencv.dnn.Net;
import org.opencv.imgcodecs.Imgcodecs;
import org.opencv.videoio.VideoCapture;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static org.opencv.dnn.Dnn.NMSBoxes;
import static org.opencv.highgui.HighGui.*;
import static org.opencv.highgui.HighGui.waitKey;
import static org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc.*;
import static org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX;
public class VideoDet{
final static String ROOTDIR = "E:\\\\ZxxProject\\\\darknet-master"; // 根路径
final static float CONTHRES = 0.8f; // 置信度阈值
final static float NMSTHRES = 0.8f; // iou阈值
final static List<String> CLASSES = new ArrayList<>(); // 存放类别的列表集合(这里直接用的原模型,所以是80类)
public static int count=0;//标记,用来间隔多少次来保存图片
public static boolean judge=true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.loadLibrary(Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME);//必须要加,不然程序不可执行
//配置 权重 图片路径 类别文件
String modelConfiguration = ROOTDIR + "\\\\cfg\\\\yolov3.cfg"; // 模型配置文件
String modelWeights = ROOTDIR + "\\\\yolov3.weights"; // 模型权重文件
String classesFile = ROOTDIR + "\\\\data\\\\coco.names"; // 模型可识别类别的标签文件
// 进入识别图片的方法
try {
detect_image(modelWeights, modelConfiguration, classesFile);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
启动摄像头
public static void detect_image(String modelWeights, String modelConfiguration, String classesFile) throws Exception {
// 使用字节输入流读取classesFile路径的文件(从硬盘读取数据到内存)
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(classesFile);
int allByte = inputStream.available();
byte[] bytes = new byte[allByte]; //通过调节allByte的值来完成每次读取多少字节,这里直接读完
inputStream.read(bytes);
String allContent = new String(bytes); // 文件中的所有内容
String[] tempContent = allContent.trim().split("\\n"); // allContent去除首尾空格,再按换行符分割。
// 遍历tempContent,添加到保存类别名的列表classes里。
for(int i=0; i<tempContent.length; i++){
CLASSES.add(tempContent[i]);
}
System.out.println(CLASSES.size());
Net net = Dnn.readNetFromDarknet(modelConfiguration, modelWeights);
//打开摄像头
VideoCapture cameraCapture = new VideoCapture(0);
namedWindow("实时检测");
int frame_width = (int) cameraCapture.get(3);
int frame_height = (int) cameraCapture.get(4);
Mat frame = new Mat();
Size sz1 = new Size(frame_width, frame_height);
while (judge) {
cameraCapture.read(frame);
count=count+1;
System.out.println("-----------第"+count+"轮----------------");
Mat blobImg = Dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1.0F / 255.0F, sz1);
net.setInput(blobImg);
// 获取网络输出层信息(所有输出层的名字),设定并前向传播
List<String> ln = net.getLayerNames(); // 获得YOLO各层的名字
List<String> x = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> out = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = net.getUnconnectedOutLayers().toList(); // 获得未连接的输出层的索引列表
out.add(temp);
// out中存放的是一个List ,get(0)得到的就是list i 索引列表
List<Integer> i = out.get(0);
System.out.println(i.size()); // 3
for (int a = 0; a < i.size(); a++) {
String n = ln.get(i.get(a) - 1); // 输出层的名字
x.add(n); // 找到所有的输出层
}
ln = x; // 给ln重新赋值
// 矩阵列表 [Mat[...], Mat[...], Mat[...]]
List<Mat> outs = new ArrayList<Mat>();
net.forward(outs, ln); // ln此时为输出层的名字列表,向前传播,将得到的检测结果传入outs
// 检测识别
detection(frame, outs);
}
}
检测摄像头中的目标
public static void detection(Mat frame, List<Mat> outs) {
System.out.println("检测过程开始");
List<Rect2d> boxes = new ArrayList<>(); // 矩形框列表
List<Integer> classIds = new ArrayList<>(); // 类的序号列表
List<Float> confidences = new ArrayList<>(); // 置信度列表
List<Integer> indices = new ArrayList<>(); //数量标记
MatOfRect2d newbox = new MatOfRect2d();
MatOfFloat newconf = new MatOfFloat();
MatOfInt ind = new MatOfInt();
ind.fromList(indices);
//TODO
for (int i = 0; i < outs.size(); i++) {
Mat mat = outs.get(i);
// 循环每一个mat对象
for (int j = 0; j < mat.rows(); j++) {
int probaility_index = 5; // [x,y,h,w,c,class1,class2] 所以是标号5
int size = (mat.cols() * mat.channels());
float[] data = new float[size];
mat.get(j, 0, data);
float confidence = -1;//初始值设为-1,
int classId = -1;
// 按列循环
for (int k = 0; k < mat.cols(); k++) {
if (k >= probaility_index && confidence < data[k]) {
confidence = data[k]; // 最大值付给confidence
classId = k - probaility_index; // 得到检测的类别索引
}
}
// 过滤掉置信度较小的检测结果
if (confidence > 0.6) {
System.out.println("Result Object:" + j);
for (int k = 0; k < mat.cols(); k++) {
if (data[k] > 0) {
System.out.println(" " + k + ":" + data[k]);
}
}
float x = data[0]; // centerX 矩形中心点的X坐标
float y = data[1]; // centerY 矩形中心点的Y坐标
float width = data[2]; // 矩形框的宽
float height = data[3]; //矩形框的高
float xLeftBottom = (x - width / 2) * frame.cols(); // 矩形左下角点的X坐标
float yLeftBottom = (y - height / 2) * frame.rows(); // 矩形左下角点的Y坐标
float xRightTop = (x + width / 2) * frame.cols(); // 矩形右上角点的X坐标
float yRightTop = (y + height / 2) * frame.rows(); // 矩形右上角点的Y坐标
// boxes主要包括左下角坐标与右上角坐标
boxes.add(new Rect2d(new Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom), new Point(xRightTop, yRightTop)));
newbox.fromList(boxes);
confidences.add(confidence);
newconf.fromList(confidences);
classIds.add(classId);
}
}
}
//使用OpenCV的非极大抑制
NMSBoxes(newbox, newconf, CONTHRES, NMSTHRES, ind);
//当摄像头中无出现目标的时候,newbox/newconf.cols()==0,有目标则是1。
if (newbox.cols() == 0 && newconf.cols() == 0) {
imshow("实时检测", frame);
waitKey(-1);
return;
}
List<Integer> indices1 = ind.toList();
List<Rect2d> bboxs1 = newbox.toList();
List<Float> conf1 = newconf.toList();
List<Mat> cutImages = new ArrayList<>();
int a = 0;
if (indices1.size() > 0) {
for (int b = 0; b < indices1.size(); b++) {
a = a + 1;
Rect2d box = bboxs1.get(indices1.get(b));
Point p1 = box.tl(); // 获得左 上角点
Point p2 = box.br(); // 获得右下角点
int classId = classIds.get(a - 1); // 得到类别序号
float confidence = conf1.get(a - 1); // 得到置信度值
// 在原图上绘制目标边框
drawPic(classId, confidence, frame, p1, p2);
cutImages.add(frame);
}
}
System.out.println("cutImages" + cutImages);
// 将含有目标的图片存入本地路径,无目标不保存
String outputFilePath = "E:\\\\ZxxProject\\\\darknet-master\\\\imgRes";
for (int i = 0; i < cutImages.size(); i++) {
Mat mat = cutImages.get(i);
//显示图片
imshow("实时检测", mat); // 显示图片
waitKey(-1);
if (count % 10 == 0) {
MatOfByte mob = new MatOfByte();
Imgcodecs.imencode(".jpg", mat, mob);
byte[] byteArray = mob.toArray();
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArray);
try {
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(in);
OutputStream bOut = new FileOutputStream(outputFilePath + "/" + count + ".jpg");
ImageIO.write(image, "jpg", bOut);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}绘制边框程序
public static void drawPic(int classId, float confidence, Mat im, Point p1, Point p2){
String text;
double x = p1.x; // p1 的 x 坐标
double y = p1.y; // p1 的 y 坐标
if(classId == 0){
System.out.println("1");
rectangle(im, p1, p2, new Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
text = CLASSES.get(classId) + ":" + confidence;
putText(im, text, new Point(x, y-5), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.3, new Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
}else {
System.out.println("2");
rectangle(im, p1, p2, new Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1); // 画框
text = String.format("%s %f", CLASSES.get(classId), confidence); // 标签内容
System.out.println(text);
putText(im, text, new Point(x, y-5), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, new Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
}
}
}第三步:结果
结果中可能出现的绘制的框过多的现象,代码还有许多优化的地方,可以在评论中留言。
参考文章
以上是关于使用Java和OpenCV调用YOLOv3完成实施目标检测的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
使用OpenCV自带的预训练模型YOLOv3调用摄像头进行目标检测超少代码!懒人必备!
[OpenCV实战]7 使用YOLOv3和OpenCV进行基于深度学习的目标检测
深度学习和目标检测系列教程 15-300:在 Python 中使用 OpenCV 执行 YOLOv3 对象检测
深度学习和目标检测系列教程 15-300:在 Python 中使用 OpenCV 执行 YOLOv3 对象检测