[Atcoder ABC222] F - Expensive Expense | 妙用树的直径 | Dijkstra
Posted PushyTao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[Atcoder ABC222] F - Expensive Expense | 妙用树的直径 | Dijkstra相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Time Limit: 4 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MB
Score : 500 points
Problem Statement
The Kingdom of AtCoder is composed of
N
N
N towns and
N
−
1
N−1
N−1 roads.
The towns are labeled as Town 1, Town 2, …, Town N. Similarly, the roads are labeled as Road 1, Road 2, …, Road N−1. Road i connects Towns
A
i
A_i
Ai and
B
i
B_i
Bi bidirectionally, and you have to pay the toll of
C
i
C_i
Ci to go through it. For every pair of different towns
(
i
,
j
)
(i,j)
(i,j), it is possible to go from Town
A
i
A_i
Ai to Town
B
j
B_j
Bj via the roads.
You are given a sequence
D
=
(
D
1
,
D
2
,
…
,
D
N
)
D=(D_1,D_2,…,D_N)
D=(D1,D2,…,DN), where
D
i
D_i
Di is the cost to do sightseeing in Town i. Let us define the travel cost
E
i
,
j
E_{i,j}
Ei,j from Town
i
i
i to Town
j
j
j as the total toll incurred when going from Town
i
i
i to Town
j
j
j, plus
D
j
D_j
Dj. More formally,
E
i
,
j
E_{i,j}
Ei,j is defined as 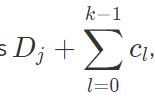
, where the shortest path between
i
i
i and
j
j
j is
i
=
p
0
,
p
1
,
…
,
p
k
−
1
,
p
k
=
j
i=p_0,p_1,…,p_{k−1},p_k=j
i=p0,p1,…,pk−1,pk=j and the toll for the road connecting Towns
p
l
p_l
pl and
p
l
+
1
p_{l+1}
pl+1 is
c
l
c_l
cl.
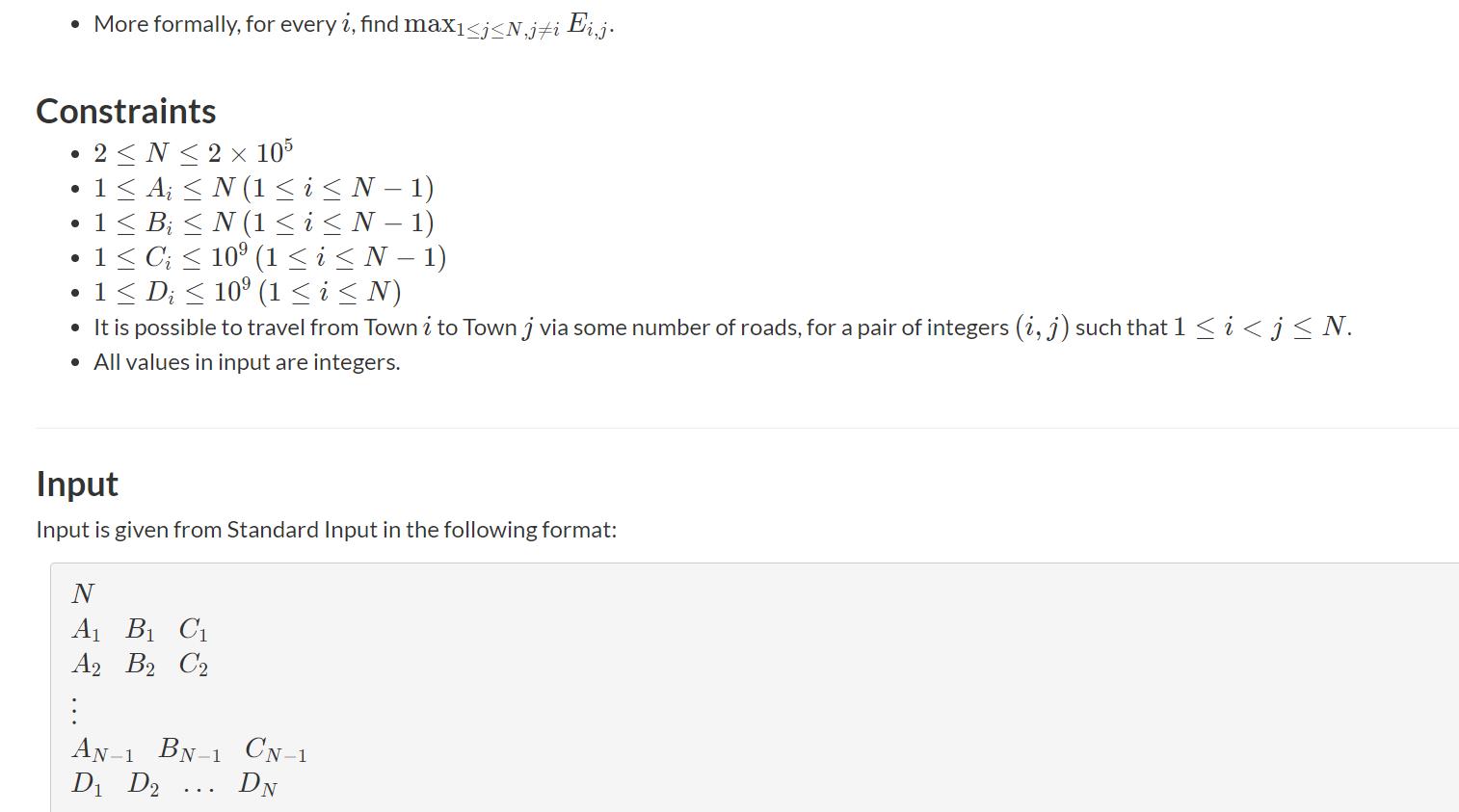
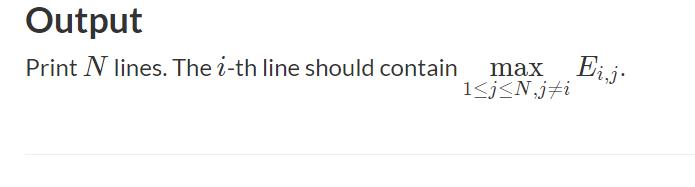
For every i, find the maximum possible travel cost when traveling from Town i to another town.
Sample Input 1
Copy
3
1 2 2
2 3 3
1 2 3
Sample Output 1
Copy
8
6
6

Sample Input 2
Copy
6
1 2 3
1 3 1
1 4 4
1 5 1
1 6 5
9 2 6 5 3 100
Sample Output 2
Copy
105
108
106
109
106
14
Sample Input 3
Copy
6
1 2 1000000000
2 3 1000000000
3 4 1000000000
4 5 1000000000
5 6 1000000000
1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output 3
Copy
5000000006
4000000006
3000000006
3000000001
4000000001
5000000001
不得不说题解给的很妙
- 树的直径
- 换根dp
树的直径:
树中任意两点之间的最短距离的最大值,即为树的直径,树的直径是树上两点之间的距离的最大值,对于题目中给定的代表节点游览花费 D D D数组,对于某一个节点 u u u的值 D [ u ] D[u] D[u]我们可以当最是有另外的一个节点 u ′ u' u′与u连了一条值为 D [ u ] D[u] D[u],然后在找直径的时候顺便把 D D D考虑进去,然后找到树的直径的两个端点之后,在进行两次最短路,分别将得到的距离 d i s [ ] dis[] dis[]存放起来
下面在算贡献的时候,直接找该点到端点(记得是两个)的距离的最大值即可
方法1:
#define Clear(x, val) memset(x, val, sizeof x)
typedef pair<ll, int> PII;
int cnt, head[maxn];
struct node {
int u, v, nex;
ll w;
} e[maxn << 1];
void init() {
Clear(head, -1);
cnt = 0;
}
void add(int u, int v, ll w) {
e[cnt].u = u;
e[cnt].v = v;
e[cnt].w = w;
e[cnt].nex = head[u];
head[u] = cnt++;
}
ll dis[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void Dijkstra(int x) {
memset(dis, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof dis);
Clear(vis, 0);
dis[x] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> que;
que.push({dis[x], x});
while (que.size()) {
PII top = que.top();
que.pop();
ll w = top.first;
int u = top.second;
if (vis[u]) continue;
vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nex) {
int to = e[i].v;
if (dis[to] > w + e[i].w) {
dis[to] = dis[u] + e[i].w;
if (!vis[to]) {
que.push({dis[to], to});
}
}
}
}
}
ll cost[maxn];
ll dis2[maxn];
int n;
int main() {
n = read;
init();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u = read, v = read;
ll w = read;
add(u, v, w);
add(v, u, w);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cost[i] = read;
Dijkstra(1);
ll mx = -1;
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == 1) continue;
if (cost[i] + dis[i] > mx) {
mx = cost[i] + dis[i];
pos = i;
}
}
Dijkstra(pos);
int pos2 = 0;
mx = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == pos) continue;
if (cost[i] + dis[i] > mx) {
mx = cost[i] + dis[i];
pos2 = i;
}
}
/// the long_est one is from pos to pos2
Dijkstra(pos);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) dis2[i] = dis[i];
Dijkstra(pos2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ll out = 0;
if (i != pos) out = max(out, dis2[i] + cost[pos]);
if (i != pos2) out = max(out, dis[i] + cost[pos2]);
cout << out << endl;
}
return 0;
}
以上是关于[Atcoder ABC222] F - Expensive Expense | 妙用树的直径 | Dijkstra的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
AtCoder Beginner Contest 222 F - Expensive Expense(换根dp)
AtCoder ABC 127F Absolute Minima