codeforces 有意思的思维题 1 ~ 15
Posted 肆呀
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了codeforces 有意思的思维题 1 ~ 15相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
codeforces 思维题
- 1、给定数组,求满足i < j and ai * aj = i + j的数对数量
- 2、第 i 步向前跳 i 步或后退 1 步
- 3、给两个点,求正方形的另两个点
- 4、任选一些数,使得它们之和在w/2和w之间
- 5、使二进制串不含有010、101序列
- 6、判断x能否被11、111、1111……表示出来
- 7、若ai < ai+1,消掉其中一个,判断能否只剩一个数
- 8、已知 lcm(a,b) = x,求最小的max(a,b)
- 9、随意交换字符,问最多能有几个二进制回文
- 10、不超过20次猜出[2,100]中的一个未知数
- 11、查区间能凑几次10
- 12、能同时被2、3、5、7整除的最小n位数
- 13、斜矩阵求路径和不同的个数
- 14、只取叶节点,先取到x者胜
- 15、按照给定偏移量移动数轴,问是否会有点重叠
1、给定数组,求满足i < j and ai * aj = i + j的数对数量
codeforces 1541B. Pleasant Pairs
原题链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1541/B
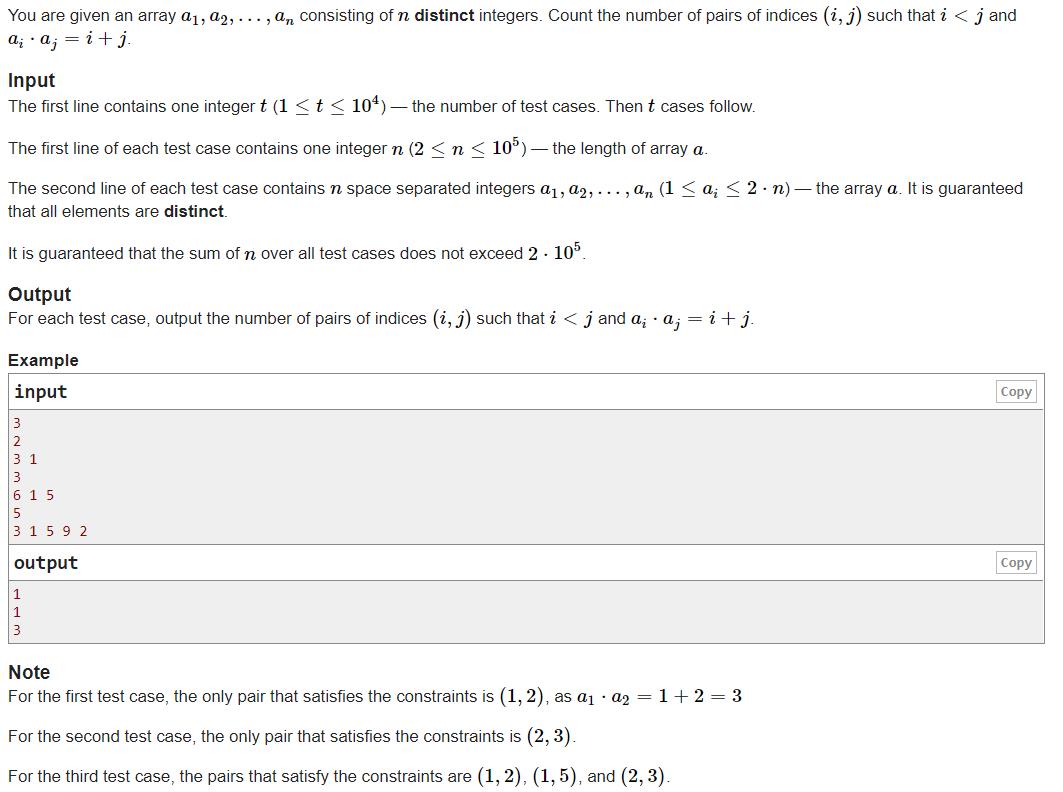
思路
因为3 <= i + j <= 2 * n - 1
那么 3 <= ai * aj <= 2 * n - 1
换句话说,可以枚举aiaj的乘积,若(ai 存在 && aj 存在 && ai下标 + aj下标 == aiaj)那么 ans ++。
值得注意的一点是,因为题目写明了a数组每一个值一定不会重复,所以不需要考虑组合数的问题,同时,并不需要考虑顺序,因为并不要求 ai < aj。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
#define getlen(array) {return (sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));}
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define PLL pair<ll, ll>
#define MEM(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define rin int n; scanf("%d", &n)
#define rln ll n; scanf("%lld", &n)
#define rim int m; scanf("%d", &m)
#define rit int t; scanf("%d", &t)
#define ria int a; scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 200010;
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}, dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
ll a[N];
ll book[N]; // book[i] 表示值为 i 的下标是 book[i]
int main() {
//freopen("D:\\\\in.txt", "r", stdin);
rit;
while (t --) {
rin;
MEM(book, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> a[i];
book[a[i]] = i;
}
ll ans = 0;
//枚举有可能的乘积
for (int i = 3; i <= 2 * n - 1; ++ i) {
int len = sqrt(i);
for (int j = 1; j <= len; ++ j) {
// if(ai 存在 && aj 存在 && ai下标 + aj下标 == ai*aj)
if (i % j == 0 && j * j != i) {
if (book[j] > 0 && book[i / j] > 0
&& book[j] + book[i / j] == i) {
++ ans;
}
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、第 i 步向前跳 i 步或后退 1 步
codeforces 1455B Jumps
原题链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1455/B
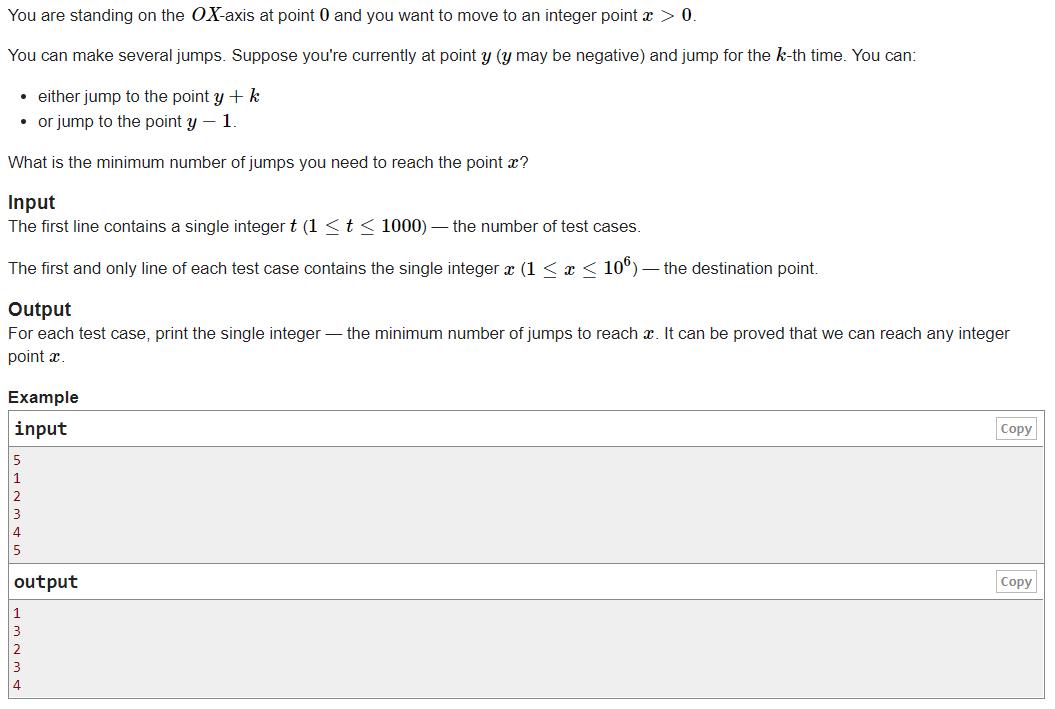

大体题意
对于每一个数 x,可以确保在操作 x 次以内到达点 x,求最小操作数。
操作:①对于第 i 次操作,可以+i步
②对于第 i 次操作,可以往后退一步
思路
假如一直都是采取操作①,那么对于 x = 7,我们可以有以下讨论:
走第一步到达 1
走第二步到达 3
走第三步到达 6
走第四步到达 10
此时是第一次操过 x,我们可以发现我们一定可以通过把已经走过的其中一步变成后退就能到达7。
因为我们需要减掉10 - 7 = 3步,但本身包含了后退的那一步,所以我们需要把第二步变成后退即可。
结论:二分找到第一个走完后总步数会大于等于 x 的那一步的位置 p,假如总步数 == x,那么ans == p;假如总步数 == x + 1, 那么ans == p + 1; 假如总步数 >= x + 2,那么 ans == p。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
#define getlen(array) {return (sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));}
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define PLL pair<ll, ll>
#define MEM(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define rin int n; scanf("%d", &n)
#define rln ll n; scanf("%lld", &n)
#define rim int m; scanf("%d", &m)
#define rit int t; scanf("%d", &t)
#define ria int a; scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1000010;
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}, dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
ll a[N];
//二分找位置
int find(int n) {
int l = 1, r = n;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (a[mid] < n) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
while (l >= 1 && a[l] > n) -- l;
while (l <= n && a[l] < n) ++ l;
//分类讨论
if (a[l] == n) return l;
else if (a[l] == n + 1) return l + 1;
else return l;
}
int main() {
freopen("D:\\\\in.txt", "r", stdin);
rit;
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++ i) {
a[i] = a[i - 1] + i; //求步数前缀和
}
while (t --) {
rin;
cout << find(n) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3、给两个点,求正方形的另两个点
原题链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/459/A

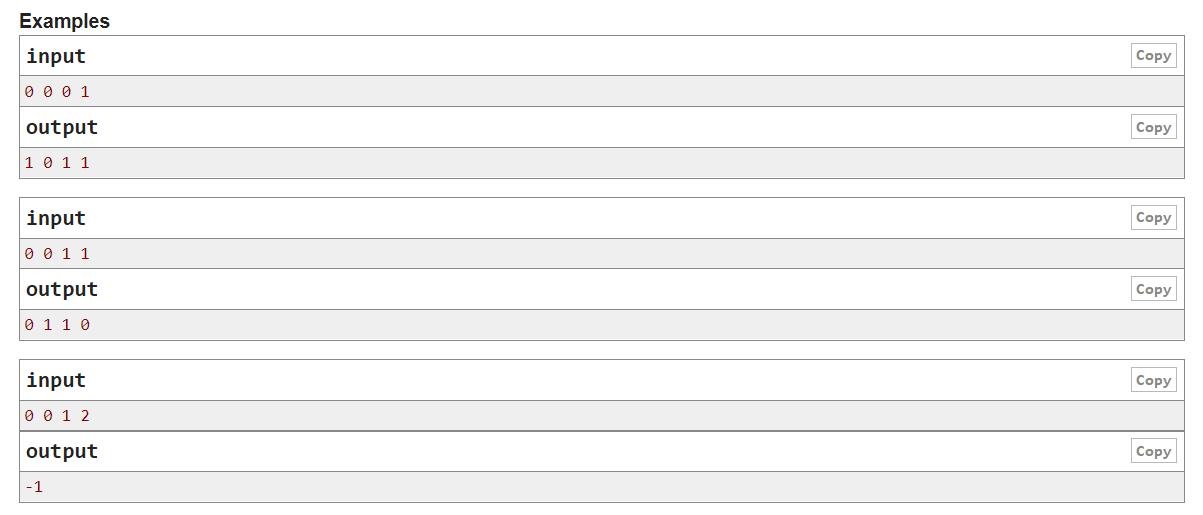
思路
题意要求正方形的边长必须与xy轴平行。
一开始以为平平无奇分类讨论同x、同y、对角线,但是数据范围包含负数,wa了一发,后面先把所有xy都加上110平移到第一象限,输出答案的时候再-110即可。
不平移的:

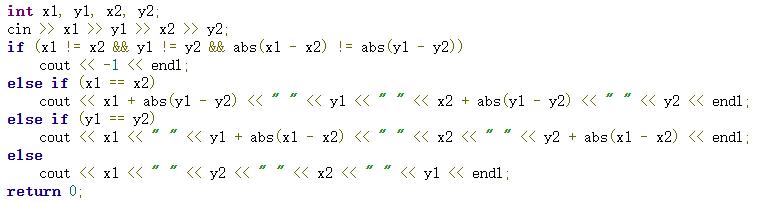
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
#define getlen(array) {return (sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));}
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define PLL pair<ll, ll>
#define MEM(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof x)
#define rin int n; scanf("%d", &n)
#define rln ll n; scanf("%lld", &n)
#define rim int m; scanf("%d", &m)
#define rit int t; scanf("%d", &t)
#define ria int a; scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 10000;
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}, dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int main() {
//freopen("D:\\\\in.txt", "r", stdin);
int a, b, c, d;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
//平移到第一象限
a += 110;
b += 110;
c += 110;
d += 110;
int x, y, z, p;
//同x
if (a == c) {
x = a + abs(b - d);
y = min(b, d);
z = a + abs(b - d);
p = max(b, d);
}
//同y
else if (b == d) {
x = min(a, c);
y = b + abs(a - c);
z = max(a, c);
p = b + abs(a - c);
}
//对角线
else if (abs(a - c) == abs(b - d)) {
if ((a < c && b < d) || (c < a && d < b)) {
x = min(a, c);
y = max(b, d);
z = max(a, c);
p = min(b, d);
}
else {
x = min(a, c);
y = min(b, d);
z = max(a, c);
p = max(b, d);
}
}
//不合法
else {
cout << "-1";
return 0;
}
x -= 110;
y -= 110;
z -= 110;
p -= 110;
cout << x << " " << y << " " << z << " " << p;
return 0;
}
4、任选一些数,使得它们之和在w/2和w之间
codeforces A. Knapsack
原题链接:https://editor.csdn.net/md?articleId=120272340

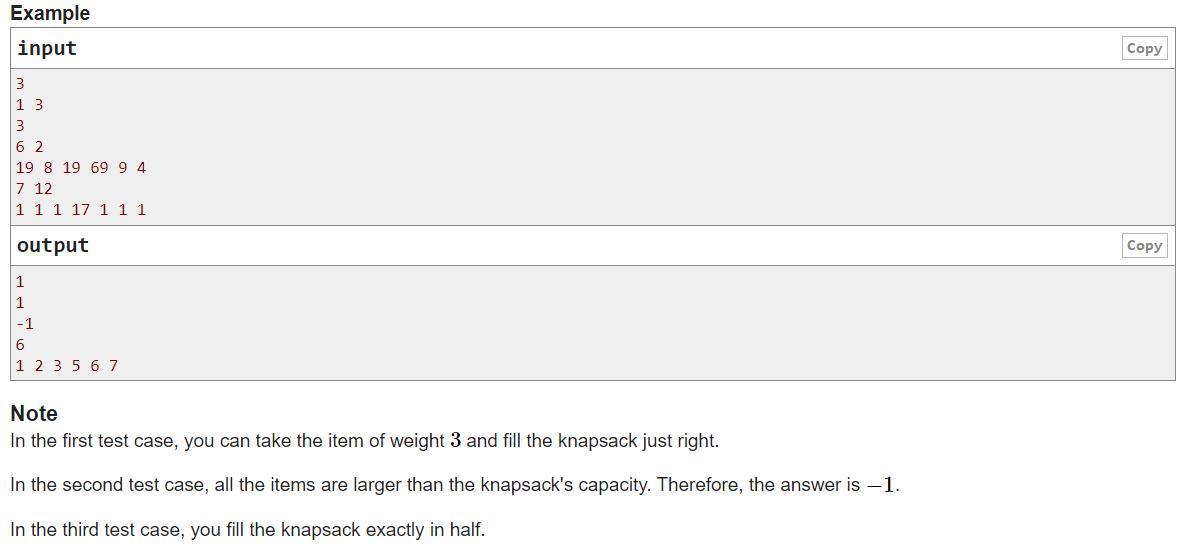
这道题目很有意思
思路
首先剔除掉所有比w大的数,再将剩下的数从大到小排序获得a0、a1、a2……。
如果a0大于等于w / 2,那么直接输出结果;
否则sum去累加a0、a1、……直到sum >= w / 2.
如果sum把所有ai都加完还没到达 w / 2,说明不存在方案,输出-1。
这样贪心合理的原因是,如果需要用sum去累加ai,那么第一个数a0都不满 w/2了,那么后面的数每一次加起来是不会有超过 w 的现象,除非sum超过w/2之后还继续加。这就是w/2~w这个区间设计的妙的地方。
(同时需要注意是向上取整 (w + 1) / 2 ~ w )
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include 以上是关于codeforces 有意思的思维题 1 ~ 15的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
CodeForces 719A Vitya in the Countryside 思维题
Codeforces Global Round 15 CF1552 A~G 题解