传统A*算法的24邻域版本,附带完整代码实例注释以及算法改进
Posted slandarer
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了传统A*算法的24邻域版本,附带完整代码实例注释以及算法改进相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写了一个A星算法的24邻域版本,效果如下:
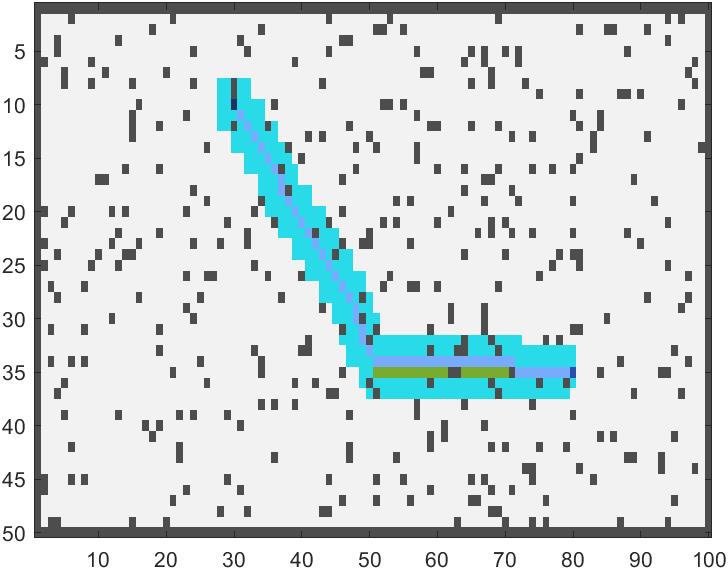
密集恐惧慎入:
1阻隔检测算法改进
首先就是解决邻域较大导致的穿墙问题,我们会在将节点加入open集合前,检测该点与父节点之间是否有阻拦,我们主要分为如下两种情况讨论
1.1阻隔情况一
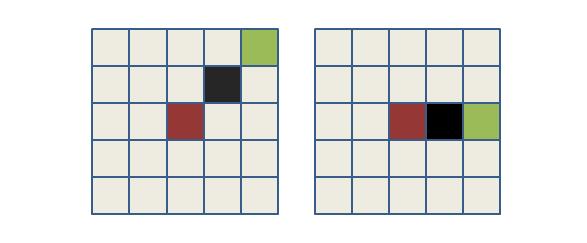
像是如下的情况红色代表父节点,绿色表示子节点 ,黑色表示障碍,我们如果取红色位置坐标和绿色位置坐标均值,就能够得到中间节点的位置,判断中间节点是否是阻隔,如果不是就将节点加入open集合。
但很多人又会说,我就不能绕路吗,就像下面一样:
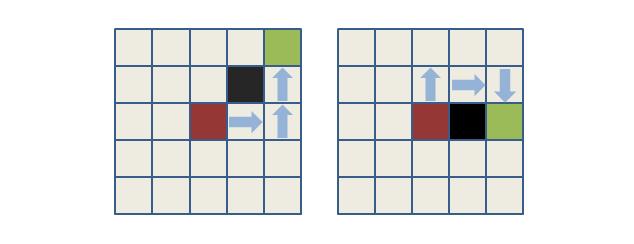
确实我们可以通过别的路径绕过去,但绕过去的同时我们已经是经过其他节点的状态,我们只要把其他节点正确的加入open集合,在后续的搜索中依旧能够搜索到被阻挡的节点,也就没有必要在本轮操作中就将其加入open集合。
1.2阻隔情况二
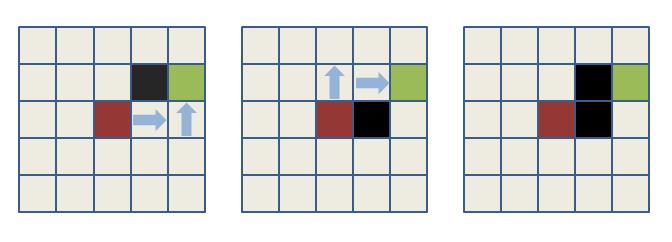
如下图所示,我们认为只有两个方块均为阻隔才不将绿色加入open集合(右图),这时候我们求取绿色和红色中点,会发现其坐标一个为整数值,而一个为小数,我们对其进行向上向下取证,获得两个坐标位置,检测这两个位置是否均为阻隔,若是则不将绿色加入open集合
1.3改进代码
% 如果它与父节点之间有障碍物,忽略它
midPnt=(newNode(1:2)+current(1:2))./2;
if any(midPnt-round(midPnt)==0)&&any(midPnt-round(midPnt)~=0)
tempPnt1=ceil(midPnt);
tempPnt2=floor(midPnt);
tempBool1=~isempty(intersect(tempPnt1,obstacle,'rows'));
tempBool2=~isempty(intersect(tempPnt2,obstacle,'rows'));
if tempBool1&&tempBool2
continue;
end
end
if ~isempty(intersect(midPnt,obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
2路径还原算法改进
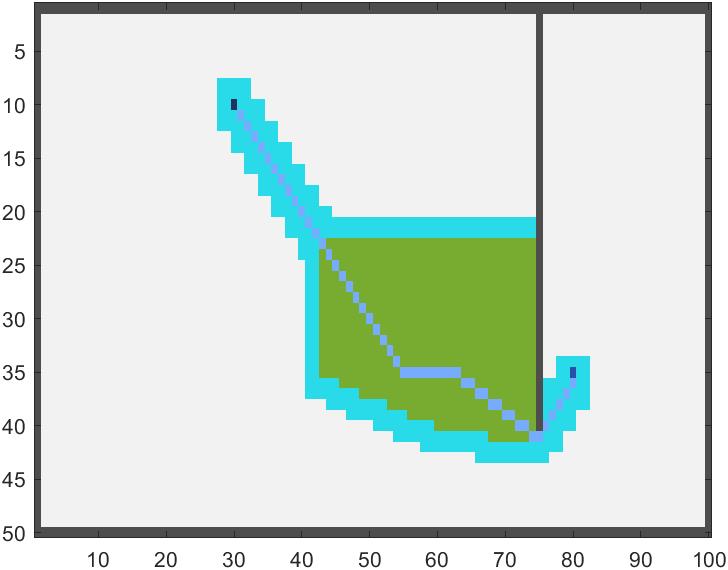
若是采用传统路径还原方法,我们的路径很大概率是隔一个取一个点,如图所示路径并不连续:
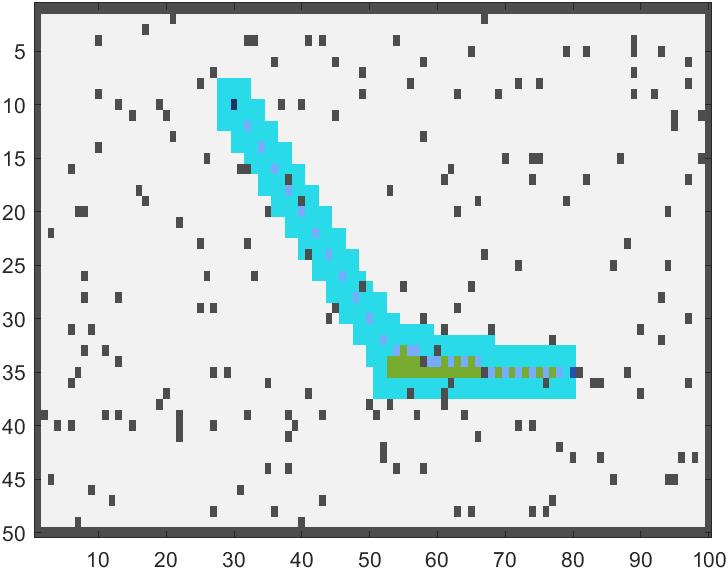
因此我们改进算法为:
初始化:将终点作为当前节点
- 将当前节点加入路径
- 若当前节点为起点终止循环
- 找寻当前节点父节点
- 将当前节点与父节点坐标取平均值
- 若平均坐标两数字均为小数值,舍去,将父节点作为当前节点并回到步骤 1
- 对平均值坐标向上向下取证得到两点坐标记为tempSet
- 删除tempSet中与父节点和当前节点重合的节点
- 删除tempSet中为障碍物的节点
- 将tempSet集合中不在open或close集合中的节点删掉
- 若此时tempSet不为空集,则选择tempSet中F较小的坐标作为中间节点,将中间节点加入路径,将父节点作为当前节点并回到步骤 1
代码实现:
%追溯路径
Index=1;
while 1
path=[path;close(Index,1:2)];
if isequal(close(Index,1:2),map.start)
break;
end
[~,IndexInClose,~]=intersect(close(:,1:2),close(Index,5:6),'rows');
% 以下为找到中间点的过程
midPnt=(close(Index,1:2)+close(Index,5:6))./2;
if ~all(midPnt~=round(midPnt))% 若中点两个数值均不是整数,则说明两节点间中间点
% 若有一个数字不是整数,或两个数字均为整数
% 下向上向下取整
tempPnt1=floor(midPnt);
tempPnt2=ceil(midPnt);
tempPntSet=[tempPnt1;tempPnt2];
% 判断取整后节点是否和原节点重合
[~,tempIndex1,~]=intersect(tempPntSet,close(Index,1:2),'rows');
tempPntSet(tempIndex1,:)=[];
[~,tempIndex2,~]=intersect(tempPntSet,close(Index,5:6),'rows');
tempPntSet(tempIndex2,:)=[];
% 判断中间点是否为障碍物,并选择F值最小的中间点
openAndCloseSet=[open;close];
[~,~,tempIndex]=intersect(tempPntSet,openAndCloseSet(:,1:2),'rows');
tempF=openAndCloseSet(tempIndex,3);
if ~isempty(tempF)
tempIndex3=find(tempF==min(tempF));
tempIndex3=tempIndex3(1);
midPnt=openAndCloseSet(tempIndex(tempIndex3),:);
path=[path;midPnt(1:2)];
end
end
Index=IndexInClose;
end
3完整代码
3.1demo入口:AStar_demo_24.m
% 24邻域A*算法demo运行入口
% author @slandarer
% 地图初始化
mapMat=zeros(50,100);
% 设置起点终点
map.start=[10,30];
map.goal=[35,80];
% 障碍物初始化
mapMat(1,:)=1;mapMat(end,:)=1;
mapMat(:,1)=1;mapMat(:,end)=1;
mapMat(randi([1,5000],[200,1]))=1;
mapMat(map.start(1),map.start(2))=0;
mapMat(map.goal(1),map.goal(2))=0;
% 获取障碍物坐标
[obX,obY]=find(mapMat==1);
obstacle=[obX,obY];
% 使用改进A*算法计算open集合与close集合
[path,close,open]=AStar_24(obstacle,map);
% 地图数据更新
open=open(:,1:2);
mapMat(open(:,1)+(open(:,2)-1)*size(mapMat,1))=4;
close=close(:,1:2);
mapMat(close(:,1)+(close(:,2)-1)*size(mapMat,1))=5;
mapMat(path(:,1)+(path(:,2)-1)*size(mapMat,1))=6;
mapMat(map.start(1),map.start(2))=2;
mapMat(map.goal(1),map.goal(2))=3;
% 绘制结果
drawMap(mapMat);
3.2A星算法主要部分:AStar_24.m
function [path,close,open]=AStar_24(obstacle,map)
% obstacle :障碍物坐标,mx2大小数组
% map :包含以下元素的结构体
% map.start [x1,y1] 起点
% map.goal [x2,y2] 终点
% 用于存储路径
path=[];
close=[];
% open集合初始化
% [节点X坐标 ,节点Y坐标 ,代价值F=G+H ,代价值G,父节点X ,父节点Y ]
open=[map.start(1),map.start(2),0+10*sum(abs(map.start-map.goal)),0 ,map.start(1), map.start(2)];
% 邻域集合
xyMat=ones(5,5);
xyMat(3,3)=0;
[x,y]=find(xyMat);
next=[x,y]-3;
next=[next,sqrt(next(:,1).^2+next(:,2).^2).*10];
while true
% 若open集合被取完,则无路径
if isempty(open(:,1))
disp('No path to goal!!');
return;
end
% 判断目标点是否出现在open列表中
[~,~,IndexGoal]=intersect(map.goal,open(:,1:2),'rows');
if ~isempty(IndexGoal)
disp('Find Goal!!');
close=[open(IndexGoal,:);close];
break;
end
[~,IndexSort] = sort(open(:,3)); % 获取OpenList中第三列大小顺序
open=open(IndexSort,:); % 将open集合按照Index排序
% 将最小open移至close集合并作为当前点
close=[open(1,:);close];
current=open(1,:);
open(1,:)=[];
for i=1:size(next,1)
newNode=[current(1)+next(i,1),current(2)+next(i,2),0,0,0,0];
newNode(4)=current(4)+next(i,3); % 相邻节点G值
newNode(3)=10*sum(abs(newNode(1:2)-map.goal))+newNode(4); % 相邻节点F值
% 如果它不可达,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它与父节点之间有障碍物,忽略它
midPnt=(newNode(1:2)+current(1:2))./2;
if any(midPnt-round(midPnt)==0)&&any(midPnt-round(midPnt)~=0)
tempPnt1=ceil(midPnt);
tempPnt2=floor(midPnt);
tempBool1=~isempty(intersect(tempPnt1,obstacle,'rows'));
tempBool2=~isempty(intersect(tempPnt2,obstacle,'rows'));
if tempBool1&&tempBool2
continue;
end
end
if ~isempty(intersect(midPnt,obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它在close集合中,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),close(:,1:2),'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它不在open集合中
if isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),open(:,1:2),'rows'))
newNode(5:6)=current(1:2); % 将当前节点作为其父节点
open=[open;newNode]; % 将此相邻节点加放OpenList中
else % 若在
[~,~,IndexInOpen]=intersect(newNode(1:2),open(:,1:2),'rows');
if newNode(3)<open(IndexInOpen,3)
% 若F更小,则将此相邻节点的父节点设置为当前节点,否则不作处理
newNode(5:6)=current(1:2); % 将当前节点作为其父节点
open(IndexInOpen,:)=newNode; % 将此相邻节点在OpenList中的数据更新
end
end
end
end
%追溯路径
Index=1;
while 1
path=[path;close(Index,1:2)];
if isequal(close(Index,1:2),map.start)
break;
end
[~,IndexInClose,~]=intersect(close(:,1:2),close(Index,5:6),'rows');
% 以下为找到中间点的过程
midPnt=(close(Index,1:2)+close(Index,5:6))./2;
if ~all(midPnt~=round(midPnt))% 若中点两个数值均不是整数,则说明两节点间中间点
% 若有一个数字不是整数,或两个数字均为整数
% 下向上向下取整
tempPnt1=floor(midPnt);
tempPnt2=ceil(midPnt);
tempPntSet=[tempPnt1;tempPnt2];
% 判断取整后节点是否和原节点重合
[~,tempIndex1,~]依据象限搜索及混合预计耗费的A*改进算法,包含8邻域及24邻域的改进
依据象限搜索及混合预计耗费的A*改进算法,包含8邻域及24邻域的改进
智能算法变邻域搜索算法(Variable Neighborhood Search,VNS)超详细解析和TSP代码实例以及01背包代码实例
MATLAB 如何将视频和音频写入同一个文件?以视频上下颠倒为例,附带详细注释