JUC并发编程 -- 经典实例之卖票 & 转账
Posted Z && Y
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC并发编程 -- 经典实例之卖票 & 转账相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 卖票
代码:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ExerciseSell")
public class ExerciseSell {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟多人买票
TicketWindow window = new TicketWindow(10000);
// 所有线程的集合
List<Thread> threadList = new ArrayList<>();
// 卖出的票数统计
List<Integer> amountList = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 买票
int amount = window.sell(random(5));
// 统计买票数
amountList.add(amount);
});
threadList.add(thread);
thread.start();
}
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
thread.join();
}
// 统计卖出的票数和剩余票数
log.debug("余票:{}", window.getCount());
log.debug("卖出的票数:{}", amountList.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).sum());
}
// Random 为线程安全
static Random random = new Random();
// 产生随机数
public static int random(int amount) {
return random.nextInt(amount) + 1;
}
}
// 售票窗口
class TicketWindow {
private int count;
public TicketWindow(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
// 获取余票数量
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 售票
public int sell(int amount) {
if (this.count >= amount) {
this.count -= amount;
return amount;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
运行结果:

原因:
因为在TicketWindow 中有一个成员变量count,sell方法多count进行了读写操作,所以在多线程的情况下会发生互斥的情况
改进方法:

现在的运行结果:

2. 转账
代码:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Random;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ExerciseTransfer")
public class ExerciseTransfer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Account a = new Account(1000);
Account b = new Account(1000);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
a.transfer(b, randomAmount());
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
b.transfer(a, randomAmount());
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
// 查看转账2000次后的总金额
log.debug("total:{}", (a.getMoney() + b.getMoney()));
}
// Random 为线程安全
static Random random = new Random();
// 随机 1~100
public static int randomAmount() {
return random.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
}
// 账户
class Account {
private int money;
public Account(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
// 转账
public void transfer(Account target, int amount) {
if (this.money >= amount) {
this.setMoney(this.getMoney() - amount);
target.setMoney(target.getMoney() + amount);
}
}
}
运行结果:

原因分析:
money是成员变量,后面又对它进行了读写操作,在多个线程操作的情况下,会发生互斥
错误的解决方法:
我们仿照卖票的思路,给transfer方法加上synchronized关键字,锁住this

原因: 这样只锁住了this,没有锁住穿过的参数target,还是会发生互斥的现象
正确的解决方法:
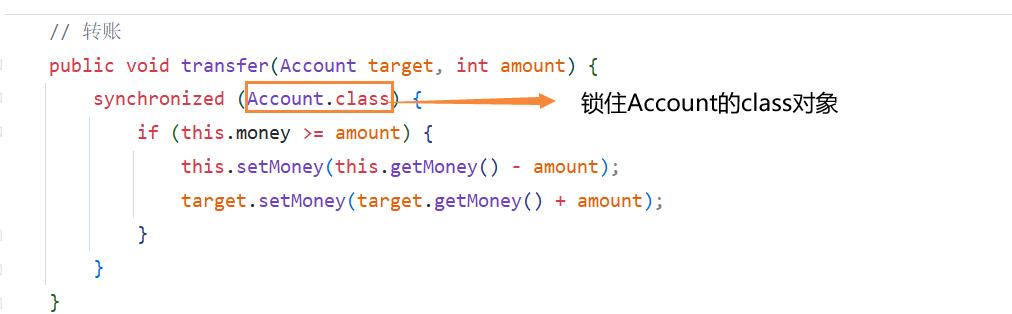
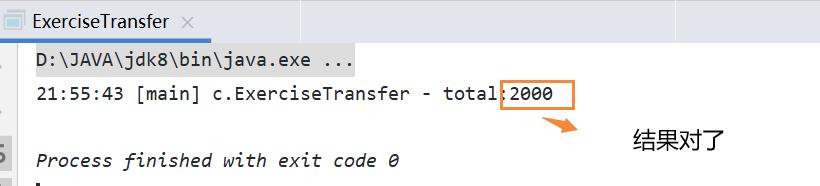
原因: 因为每个类只有一个class对象,所以锁住class对象,就不会发生互斥
思考:我们们可不可以同时锁住this和target呢?

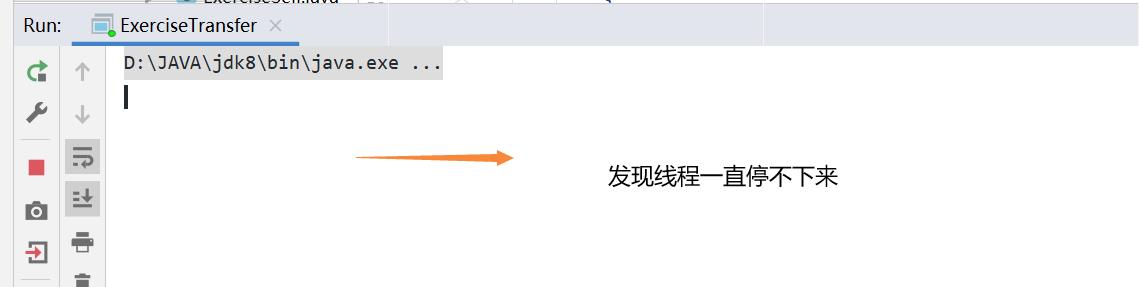
不要这样去用,容易发生死锁的现象
以上是关于JUC并发编程 -- 经典实例之卖票 & 转账的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章