JUC并发编程 -- 线程常用方法之join()详解 & join同步应用 & join限时同步
Posted Z && Y
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC并发编程 -- 线程常用方法之join()详解 & join同步应用 & join限时同步相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. join()详解
1.1 引例:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test10")
public class Test10 {
// 1. 刚开始 r = 0;
static int r = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test1();
}
private static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("开始");
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("开始");
try {
// 线程休眠1s
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("结束");
// 2. 线程休眠1s后把r赋值为10
r = 10;
}, "t1");
t1.start();
// 3. 打印r的结果:
log.debug("结果为:{}", r);
log.debug("结束");
}
}
运行结果:

思考?为什么打印的r不是10呢?
分析:
- 因为主线程和线程 t1 是并行执行的,t1 线程需要 1 秒之后才能算出 r=10
- 而主线程一开始就要打印 r 的结果,所以只能打印出 r=0
解决方法:
- 用 sleep 行不行?为什么?: 可以这么做,但是这么做不太好,因为我们不知道t1线程休眠多久
- 用 join(join方法可以等待线程结束),加在 t1.start() 之后即可

现在的运行结果:
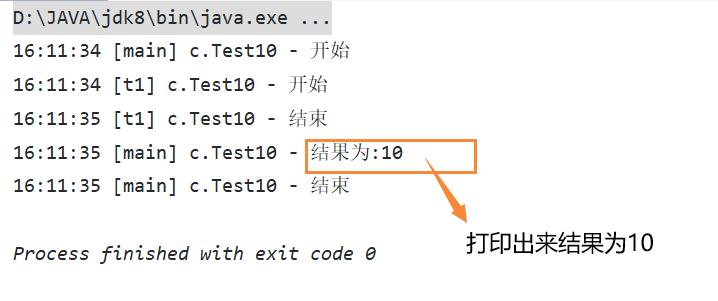
1.2 join方法的作用
等待某个线程运行结束
1.3 join同步应用
同步 & 异步:
以调用方角度来讲,如果:
- 需要等待结果返回,才能继续运行就是同步
- 不需要等待结果返回,就能继续运行就是异步
刚刚上面代码的运行流程:

等待多个结果:
1s后t1线程会把r1赋值为10,2s后t2线程会把r2赋值为20
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestJoin")
public class TestJoin {
static int r1 = 0;
static int r2 = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test();
}
private static void test() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
r1 = 10;
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
r2 = 20;
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("join begin");
t2.join();
log.debug("t2 join end");
t1.join();
log.debug("t1 join end");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("r1: {} r2: {} cost: {}", r1, r2, end - start);
}
}
运行结果:

程序流程:
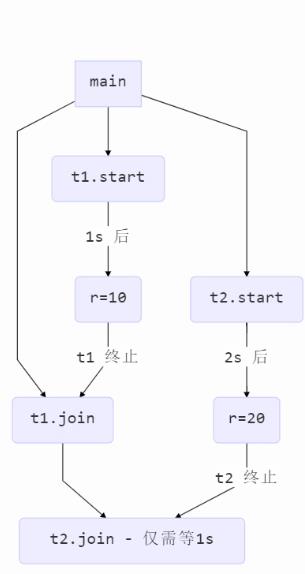
现在先调用t1的join方法,后调用t2的jion方法:

程序运行结果:

现在程序的运行流程:

1.4 join限时同步

代码:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestJoin")
public class TestJoin {
static int r1 = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
test3();
}
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
// t1线程睡眠2s后才会把r1赋值为10
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
r1 = 10;
});
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
t1.start();
// 线程执行结束会导致 join 结束
log.debug("join begin");
// join最多等待1.5s
t1.join(1500);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug("r1: {} cost: {}", r1, end - start);
}
}
运行结果:

延长join最大等待时间为3s

运行结果:

以上是关于JUC并发编程 -- 线程常用方法之join()详解 & join同步应用 & join限时同步的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章