Java--Mybatis万字长文经典面试题王者笔记《收藏版》
Posted java李阳勇
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java--Mybatis万字长文经典面试题王者笔记《收藏版》相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言:
前段时间一直和大家在分享java项目实战的内容、今天趁着周末给大家整理了Java工程师在面试中经常被问到持久层框架的面试题《Java--Mybatis》篇、希望大家喜欢、支持。后期也会继续整理其他的知识点、比如、ZooKeeper、Dubbo、Redis、MySQL、Spring、Spring Boot、Spring Cloud、等技术栈。下面就具体看看有哪些经典题目吧、喜欢的可以一键三连支持下哟
什么是 Mybatis框架?
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射,它内部封装了jdbc,不需要我们在写JDBC连接、使开发者只需要关注sql语句本身和业务,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement等繁杂的过程。直接通过配置文件或maven驱动包的方式加载导入就行。

Mybaits 的优点有哪些:
Mybatis基于SQL语句编程,很灵活,不会有任何影响现有应用程序或数据库的设计,SQL编写的XML,删除SQL和程序代码的耦合,便于统一管理,提供了XML标记,使您能够编写动态SQL语句和重用它们。
与JDBC相比,它减少了50%以上的代码量,消除了大量冗余的JDBC代码,不需要手动切换连接;
与各种数据库的良好兼容性(因为MyBatis使用JDBC连接数据库,所以只要JDBC支持数据库MyBatis就支持)。
与Spring和Spring MVCD框架的良好集成;
提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库ORM字段关系映射;提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组件的维护。
MyBatis 框架的缺点有哪些:
JDBC方式可以用用打断点的方式调试,但是Mybatis不能,需要通过log4j日志输出日志信息帮助调试,然后在配置文件中修改。
编写SQL语句是一项繁重的工作,特别是对于有许多字段和许多关联表的开发人员来说对于SQL语句的基础有一定的要求。
SQL语句依赖于数据库,导致数据库可移植性差。因此,不能随意更改数据库。
MyBatis 框架适用哪些场景:
因为MyBatis 专注于 SQL 本身,是一个足够灵活的 DAO 层解决方案。满足基本的单表的CRUD。
对性能的要求比较高,或者需求变化较多的项目,如互联网重的很多项目基本都是采用的MyBatis 作为持久层框架。
MyBatis 与 Hibernate 的区别?
MyBatis 支持通过 XML 或注解的方式来配置需要运行的 SQL 语句,并且,最终由框架本身将 Java 对象和 SQL 语句映射生成最终执行的 SQL ,执行后,再将结果映射成 Java 对象返回。相较于 Hibernate, Mybatis 因为可以编写原生的 SQL ,也就是说,能够严格控制 SQL 执行性能,灵活度高。但是灵活的前提是 MyBatis 无法做到数据库无关性,如果需要实现支持多种数据库的软件则需要自定义多套 SQL 映射文件,工作量大。
再来说说 Hibernate, 它对象/关系映射能力强,能做到数据库无关性。如果用 Hibernate 开发,无需关系 SQL 编写(不会写 SQL 的人都可以操作数据库),能节省很多代码,提高效率。但是 Hibernate 的缺点是学习门槛高,要精通门槛更高,而且怎么设计 O/R 映射,在性能和对象模型之间如何权衡,以及怎样用好 Hibernate 需要具有很强的经验和能力才行。
我觉得最后结合公司业务,选取最适合的框架,不要为了技术而技术,否则都是耍流氓。比如说,你所在的是相对来说较小的公司,数据量并不大,且公司开发人员的技术栈偏 Hibernate 多一些,推荐使用 JPA、Hibernate 这些无需手动编写 SQL 的持久层框架,提高开发效率、版本迭代速度。如果说,你所在的是一家互联网公司,用户数较大,对相关 SQL 执行性能要求较为严格,则推荐使用 Mybatis。总之,按照用户的需求在有限的资源环境下只要能做出维护性、扩展性良好的软件架构都是好架构,所以框架只有适合才是最好。
#{}和${}的区别是什么?
这个问题比较基础也比较经典、但是在面试中是基本必问的、
#{}是预编译处理,${}是字符串替换。
Mybatis 在处理#{}时,会将 sql 中的#{}替换为?号,调用 PreparedStatement 的 set 方法来赋值;
Mybatis 在处理${}时,就是把${}替换成变量的值。
使用#{}可以有效的防止 SQL 注入,提高系统安全性。
下面通过一个例子来说明明吧
大家都知道Mybatis 的Mapper.xml语句中parameterType向SQL语句传参有两种方式:#{}和${}
我们经常使用的是#{},一般解说是因为这种方式可以防止SQL注入,简单的说#{}这种方式SQL语句是经过预编译的,它是把#{}中间的参数转义成字符串,举个例子:
select * from student where student_name = #{name} 预编译后,会动态解析成一个参数标记符?
select * from student where student_name = #{name} 而使用${}在动态解析时候,会传入参数字符串
select * from student where student_name = #{name}
当实体类中的属性名和表中的字段名不一样 ,怎么办?
举例说明:一种是在Mapper映射文件中使用resultMap来自定义映射规则
<!-- 自定义高级映射 -->
<!-- namespace属性:必须是接口的全类名 -->
<mapper namespace="com.tt.mybatis.mapper.EmployeeMapper">
<!--
id属性:必须是接口中方法的方法名
resultType属性:必须是方法的返回值的全类名
-->
<select id="getEmployeeById" resultMap="myMap">
select * from employees where id = #{id}
</select>
<!-- 自定义高级映射 -->
<resultMap type="com.tt.mybatis.entities.Employee" id="myMap">
<!-- 映射主键 -->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!-- 映射其他列 -->
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="salary" property="salary"/>
<result column="dept_id" property="deptId"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
还有就是sql语句时起别名
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- 开启驼峰命名规则 ,可以将数据库中的下划线映射为驼峰命名
例如:last_name可以映射为lastName
-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 注册映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
模糊查询 like 语句该怎么写?
举例说明:在 Java 代码中添加 sql 通配符。
string wildcardname = “%smi%”;
list<name> names = mapper.selectlike(wildcardname);<select id=”selectlike”>
select * from foo where bar like #{value}
</select>另一种方式就是在 sql 语句中拼接通配符,但是可能会引起 sql 注入
string wildcardname = “smi”;
list<name> names = mapper.selectlike(wildcardname);<select id=”selectlike”>
select * from foo where bar like "%"#{value}"%"
</select>Mybatis Dao层 接口的工作原理是什么?Dao 接口里的方法,参数不同时,方法能重载吗?
举例说明: Dao接口就是Mapper接口,---可以基于注解的方式创建接口,接口内定义抽象方法;
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from users where id=#{id}")
public User getUserById(int id);
}接口的全限名,就是映射文件中的namespace的值:
<mapper namespace="com.mybatis.test3.orderMapper">
<select id="selectUser" parameterType="int" resultType="Order">
select * from users where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>接口的全名是映射文件中命名空间的值:
<mapper namespace="com.mybatis.test3.orderMapper">
<select id="selectUser" parameterType="int" resultType="Order">
select * from users where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>接口方法名(getUserById)是映射文件中MappedStatement中的id值(selectUser),接口方法中的参数是传递给SQL的参数(#{id} >>> #{id})。
Mapper接口没有实现类。当调用接口方法时,将接口名称+方法名称与字符串连接作为键值,以唯一定位MappedStatement。例如:Com。Mybatis。Test2。usermap。只能找到com的名称空间。Mybatis。Test2。UserMapper id = insertUser MappedStatement如下。
在Mybatis中,每个<select>, < INSERT >, <update>, and <delete>标记都被解析为一个MappedStatement对象。
关于重载和工作原理解释
Dao接口中的2个方法不能被覆盖,因为它是一个全名+方法名的保存和查找策略。
Dao接口的工作原理是JDK动态代理。Mybatis运行时,将使用JDK动态代理为Dao接口生成代理代理对象。
Mybatis 是如何进行分页的?分页插件的原理是什么?
Mybatis 使用 RowBounds 对象进行分页,它是针对 ResultSet 结果集执行的内存分页,而非物理分页。可以在 sql 内直接书写带有物理分页的参数来完成物理分页功能,也可以使用分页插件来完成物理分页。下面看看Mybatis的如何进行分页
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping)
throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext resultContext = new DefaultResultContext();
// 跳到offset位置,准备读取
skipRows(rsw.getResultSet(), rowBounds);
// 读取limit条数据
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && rsw.getResultSet().next()) {
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rsw.getResultSet(), resultMap, null);
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap);
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
private void skipRows(ResultSet rs, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
if (rs.getType() != ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY) {
if (rowBounds.getOffset() != RowBounds.NO_ROW_OFFSET) {
// 直接定位
rs.absolute(rowBounds.getOffset());
}
} else {
// 只能逐条滚动到指定位置
for (int i = 0; i < rowBounds.getOffset(); i++) {
rs.next();
}
}
}
原理的话大家参考这篇文章MyBatis之分页插件(PageHelper)工作原理
Mybatis 是如何将 sql 执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
第一种方法是使用<resultMap>标记逐个定义数据库列名和对象属性名之间的映射。
第二种方法是使用SQL列的别名函数将列的别名作为对象属性名写入。
使用列名和属性名之间的映射,Mybatis通过反射创建对象并使用反射对象的属性逐个赋值并返回,如果找不到映射关系,则无法完成赋值。
Mybatis 如何执行批量插入?
-
首先,创建一个简单的INSERT语句:
<insert id=”insertname”>
insert into names (name) values (#{value})
</insert>然后在Java代码中执行批量插入操作:
list < string > names = new arraylist();
names.add(“fred”);
names.add(“barney”);
names.add(“betty”);
names.add(“wilma”);
// 注意 executortype.batch
sqlsession sqlsession =sqlsessionfactory.opensession(executortype.batch);
try {
namemapper mapper = sqlsession.getmapper(namemapper.class);
for (string name: names) {
mapper.insertname(name);
}
sqlsession.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e;
} finally {
sqlsession.close();
}Mybatis 如何获取自动生成的(主)键值?
Mapper文件insert语句设置
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"Mybatis 在 mapper 中如何传递多个参数?
第一种方案 DAO层的函数方法
Public User selectUser(String name,String area); 对应的Mapper.xml配置文件
<select id="selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.String">
select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{0} and user_area=#{1}
</select>其中,#{0}代表接收的是dao层中的第一个参数,#{1}代表dao层中第二参数,更多参数一致往后加即可。
第二种Dao层的函数方法
Public User selectUser(@param(“userName”)Stringname,@param(“userArea”)String area); 对应的Mapper.xml配置文件
<select id=" selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR} and user_area=#{userArea,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</select> 个人觉得这种方法比较好,能让开发者看到dao层方法就知道该传什么样的参数,比较直观,个人推荐用此种方案。
Mybatis 动态 sql 有什么用?执行原理?有哪些动态 sql?
Mybatis 动态 sql 可以在 Xml 映射文件内,以标签的形式编写动态 sql,
执行原理是根据表达式的值 完成逻辑判断并动态拼接 sql 的功能。
动态 sql有九种、具体是:trim | where | set | foreach | if | choose| when | otherwise | bind。
具体九种动态SQL举例:
if标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名 -->
<select id=" getStudentListLikeName " parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
<if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
WHERE ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
</if>
</select> where标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名,=性别 -->
<select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
<where>
<if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
</if>
<if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
set标签
<!-- 更新学生信息 -->
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
<set>
<if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #{studentName},
</if>
<if test="studentSex!=null and studentSex!='' ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex},
</if>
<if test="studentBirthday!=null ">
STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday},
</if>
<if test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID!=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">
STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
</if>
</set>
WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID};
</update>
trim标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名,=性别 -->
<select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR">
<if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
</if>
<if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
choose when otherwise标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名、或=性别、或=生日、或=班级,使用choose -->
<select id="getStudentListChooseEntity" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
<where>
<choose>
<when test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
</when>
<when test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
</when>
<when test="studentBirthday!=null">
AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday}
</when>
<when test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID !=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">
AND ST.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
</when>
<otherwise>
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
foreach
<select id="getStudentListByClassIDs" resultMap="studentResultMap">
SELECT * FROM STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.CLASS_ID IN
<foreach collection="list" item="classList" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{classList}
</foreach>
</select>
Mybatis 的 Xml 映射 文件 中,不同 的 Xml 映射 文件 , id 是否 可以 重复 ?
不同的Xml映射文件 ,如果配置了namespace,那么id可以重复;
如果没有配置namespace,那么id不能重复;原因就是namespace+id是作为Map<String, MapperStatement>的key使用的,如果没有namespace,就剩下id,那么,id重复会导致数据互相覆盖。
有了namespace,自然id就可以重复 ,namespace不同 ,namespace+id自然也就不同 。
Xml 映射文件中,除了常见的 select|insert|updae|delete 标签之外,还有哪些标签?
<resultMap>、<parameterMap>、<sql>、<include>、<selectKey> ,加上动态 sql 的 9 个标签,其中 <sql> 为 sql 片段标签,通过<include> 标签引入 sql 片段, <selectKey> 为不支持自增的主键生成策略标签。
为什么说 Mybatis 是半自动 ORM 映射工具?它与全自动的区别在哪里?
Hibernate属于全自动ORM映射工具 ,使用Hibernate查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取 ,所以它是全自动的。而Mybatis在查询关联对象或关联集合对象时,需要手动编写sql来完成,所以 ,称之为半自动ORM映射工具。
Mybatis 的一对一、一对多的关联查询 ?
一对一关联查询
<mapper namespace="com.lcb.mapping.userMapper">
<!--association 一对一关联查询 -->
<select id="getClass" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassesResultMap">
select * from class c,teacher t where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.lcb.user.Classes" id="ClassesResultMap">
<!-- 实体类的字段名和数据表的字段名映射 -->
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="com.lcb.user.Teacher">
<id property="id" column="t_id"/>
<result property="name" column="t_name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
</mapper> 一对多关联查询
<!--collection 一对多关联查询 -->
<select id="getClass2" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassesResultMap2">
select * from class c,teacher t,student s where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=s.class_id and c.c_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.lcb.user.Classes" id="ClassesResultMap2">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="com.lcb.user.Teacher">
<id property="id" column="t_id"/>
<result property="name" column="t_name"/>
</association>
<collection property="student" ofType="com.lcb.user.Student">
<id property="id" column="s_id"/>
<result property="name" column="s_name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
MyBatis 实现一对一有几种方式?具体怎么操作的?
有联合查询和嵌套查询,
联合查询是几个表联合查询,只查询一次,通过在resultMap里面配置association节点配置一对一的类就可以完成;
嵌套查询是先查一个表,根据这个表里面的结果的外键id,去再另外一个表里面查询数据,也是通过association配置,但另外一个表的查询通过select属性配置
MyBatis 实现一对多有几种方式,怎么操作的?
有联合查询和嵌套查询。
联合查询是几个表联合查询,只查询一次,通过在resultMap里面的collection节点配置一对多的类就可以完成;嵌套查询是先查一个表,根据这个表里面的结果的外键id,去再另外一个表里面查询数据,也是通过配置collection,但另外一个表的查询通过select节点配置。
Mybatis 是否支持延迟加载?如果支持,它的实现原理是什么?
Mybatis仅支持association关联对象和collection关联集合对象的延迟加载,association指的就是一对一,collection指的就是一对多查询。在Mybatis配置文件中,可以配置是否启用延迟加载lazyLoadingEnabled=true|false。
它的原理是,使用CGLIB创建目标对象的代理对象,当调用目标方法时,进入拦截器方法,比如调用a.getB().getName(),拦截器invoke()方法发现a.getB()是null值,那么就会单独发送事先保存好的查询关联B对象的sql,把B查询上来,然后调用a.setB(b),于是a的对象b属性就有值了,接着完成a.getB().getName()方法的调用。这就是延迟加载的基本原理。
当然了,不光是Mybatis,几乎所有的包括Hibernate,支持延迟加载的原理都是一样的。
Mybatis 的一级、二级缓存
一级缓存:
Mybatis支持缓存,但在没有配置的情况下,默认情况下它只启用一级缓存。级别1缓存只对相同的SqlSession启用。因此,如果SQL参数一模一样,我们使用相同的SqlSession对象调用映射方法,通常只执行SQL一次,因为第一个查询使用SelSession MyBatis将把它放在缓存中,和将来查询,如果没有声明需要刷新,如果缓存中没有,SqlSession将获取当前缓存的数据,并且不会再次向数据库发送SQL

二级缓存:
MyBatis的二级缓存是Application级别的缓存,它可以提高对数据库查询的效率,以提高应用的性能。二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用PerpetualCache,HashMap存储,不同在于其存储作用域为Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如Ehcache。默认不打开二级缓存,要开启二级缓存,使用二级缓存属性类需要实现Serializable序列化接口(可用来保存对象的状态),可在它的映射文件中配置<cache/>;
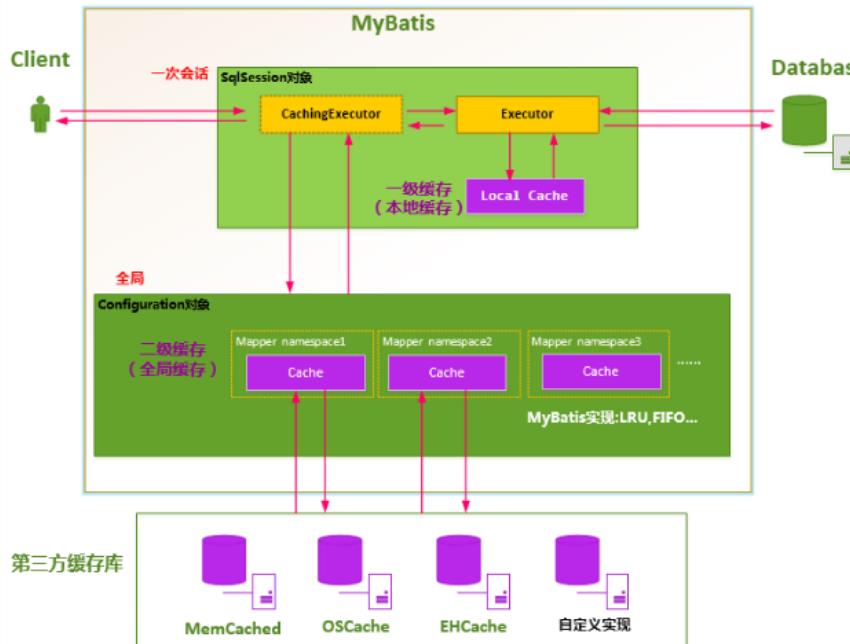
对于缓存数据更新机制,当某一个作用域(一级缓存Session/二级缓存Namespaces)的进行了C/U/D操作后,默认该作用域下所有select中的缓存将被clear。
什么是 MyBatis 的接口绑定?有哪些实现方式?
接口绑定,就是在MyBatis中任意定义接口,然后把接口里面的方法和SQL语句绑定,我们直接调用接口方法就可以,这样比起原来了SqlSession提供的方法我们可以有更加灵活的选择和设置。
接口绑定有两种实现方式,一种是通过注解绑定,就是在接口的方法上面加上@Select、@Update等注解,里面包含Sql语句来绑定;
另外一种就是通过xml里面写SQL来绑定,在这种情况下,要指定xml映射文件里面的namespace必须为接口的全路径名。
当Sql语句比较简单时候,用注解绑定,当SQL语句比较复杂时候,用xml绑定,一般用xml绑定的比较多。
使用 MyBatis 的 mapper 接口调用时有哪些要求?
Mapper接口方法名和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的id相同;
Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的parameterType的类型相同;
Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同;
Mapper.xml文件中的namespace即是mapper接口的类路径。
Mapper 编写的几种实现方式?
第一、接口实现类继承 SqlSessionDaoSupport:使用此种方法需要编写mapper 接口,mapper 接口实现类、mapper.xml 文件。
1、在 sqlMapConfig.xml 中配置 mapper.xml 的位置
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" />
<mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" />
</mappers>2、定义 mapper 接口.
3、实现类集成 SqlSessionDaoSupportmapper 方法中可以this.getSqlSession()进行数据增删改查。
4、spring 配置
<bean id=" " class="mapper 接口的实现">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>第二、使用 org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean:
1、在 sqlMapConfig.xml 中配置 mapper.xml 的位置,如果 mapper.xml 和mappre 接口的名称相同且在同一个目录,这里可以不用配置
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" />
<mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" />
</mappers>2、定义 mapper 接口:
2.1、mapper.xml 中的 namespace 为 mapper 接口的地址
2.2、mapper 接口中的方法名和 mapper.xml 中的定义的 statement 的 id 保持一致
2.3、Spring 中定义
<bean id="" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="mapper 接口地址" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>第三、使用 mapper 扫描器:
1、mapper.xml 文件编写:mapper.xml 中的 namespace 为 mapper 接口的地址;mapper 接口中的方法名和 mapper.xml 中的定义的 statement 的 id 保持一致;如果将 mapper.xml 和 mapper 接口的名称保持一致则不用在 sqlMapConfig.xml中进行配置。
2、定义 mapper 接口:注意 mapper.xml 的文件名和 mapper 的接口名称保持一致,且放在同一个目录
3、配置 mapper 扫描器:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="mapper 接口包地址"></property>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName"value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>4、使用扫描器后从 spring 容器中获取 mapper 的实现对象
简述 Mybatis 的插件运行原理,以及如何编写一个插件?
Mybatis只能为ParameterHandler, ResultSetHandler,StatementHandler和Executor接口。Mybatis使用JDK的动态生成为需要被拦截的接口生成代理对象,以便在执行这4种类型时实现接口方法拦截Invoke (), Invoke (), Invoke ()、当然,方法只会拦截那些您指定需要拦截的方法。
编写插件:实现Mybatis的Interceptor接口
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}复制intercept()方法插件会编写注解来指定要拦截接口的哪些方法。记住不要忘记配置文本配置你编写的插件哈。
public class Invocation {
private final Object target;
private final Method method;
private final Object[] args;
public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
public Object getTarget() {
return target;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public Object[] getArgs() {
return args;
}
public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
}方法说明:这个东西包含了四个概念:
- target 拦截的对象
- method 拦截target中的具体方法,也就是说Mybatis插件的粒度是精确到方法级别的。
- args 拦截到的参数。
- proceed 执行被拦截到的方法,你可以在执行的前后做一些事情。
精彩推送:
Springboot项目毕设实战100套
JavaWeb项目毕设实战100套
JavaSwing项目实战100套
总结:
好了,今天就分享到这里啦、这篇文章总体来说对于学习或面试来说都是比较不错的、文章中涉及的知识点都比较关键。
另外需要白嫖java学习资料包括《JVM、Netty、Mysql、Mybatis、Redis、Dubbo、nginx、设计模式》等10G资料礼包、可以看我主页或私信博主都行。
打卡Java更新 15 / 100天
大家可以点赞、收藏、关注、评论我啦 、下面的投票也可以积极互动起来哟
以上是关于Java--Mybatis万字长文经典面试题王者笔记《收藏版》的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章