数据结构--栈(Stack)
Posted 小鹿可可乐
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构--栈(Stack)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.栈的定义
- 定义:
栈:一种先进后出,后进先出的数据结构
(如箱子存放东西)
栈和队列都是受到限制的顺序表
- 栈分为顺序栈和链式栈
- 栈只能在一端进行插入和删除,插入和删除的这一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底
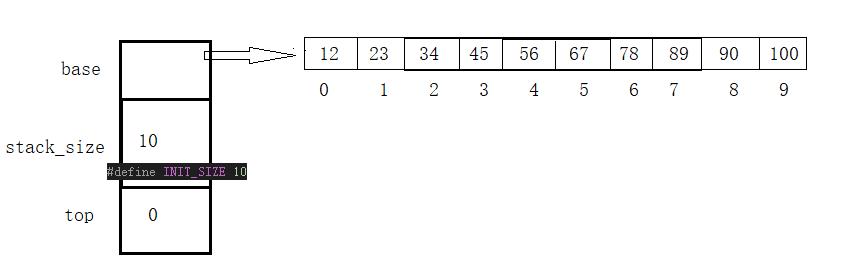
2.顺序栈
- 结构体的设计:
2.1代码设计解析
- 获取栈顶元素的值,但不删除
//返回类型和存放的值类型一致,当我们断言失败时候,返回的值有可能就是我们要存放的值,会起冲突
bool Get_top(PStack ps);
//reval 是我们的输出参数
bool Get_top(PStack ps,int *rtval);
错误示范:
int get_top(pstack)
{
assert(ps!=null);
if(ps = null)
return ??; //-1 \\0
//\\0只有字符串认识他,别人不理 ‘#’也不行 '#'==35
if(isempty(ps))
{
return ??;
}
}
- 清空
ps->top = 0;//让0下标为可插入的位置,不关注里边的值
//栈顶指针直接指向0
2.2源代码
头文件(stack.h)
#pragma once //防止头文件重复
//顺序栈的栈顶在尾部,因为入栈和出栈的时间复杂度为O(1)
#define INIT_SIZE 10
typedef int ELEMTYPE;
typedef struct PStack
{
int *base;//用来malloc申请动态内存
int stack_Size;//栈总体个数
int top;//栈顶指针,当前栈存放的有效元素个数指向下一个存放数据的位置
}PStack, *PStack;
//增删改查
//初始化
void InitStack(PStack ps);
//入栈操作(尾插)
bool Push(PStack ps, int val);
//获取栈顶元素的值,但不删除
bool Get_top(PStack ps, int *rtval);// rtval 是我们的输出参数
//获取栈顶元素的值,但删除,出栈操作(尾删)
bool Pop(PStack ps, int *rtval);
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PStack ps);
//判满
bool IsFull(PStack ps);
//获取有效元素个数
int Get_length(PStack ps);
//清空
void Clear(PStack ps);
//销毁
void Destroy(PStack ps);
//扩容
void Inc(PStack ps);
源文件(stack.cpp):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"stack.h"
//初始化
void InitStack(PStack ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL) return;
ps->base = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)* INIT_SIZE);
assert(ps->base != NULL);
ps->top = 0;
ps->stack_Size = INIT_SIZE;
}
//入栈操作(尾插)
bool Push(PStack ps, int val)
{
//断言
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL) return false;
//判满
if (IsFull(ps))
{
//如果满了,扩容
Inc(ps);
}
//插入
//ps->base[ps->top++] = val;
ps->base[ps->top] = val;//数组形式一致
ps->top++;
//返回值
return true;
}
//获取栈顶元素的值,但不删除
//int get_top(pstack ps)
bool Get_top(PStack ps, int *rtval)
{
//断言
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL) return false; //-1 \\0
//\\0只用字符串认识他,别人根本不理它 '#'也不行 ‘#’== 35
if (IsEmpty(ps))
{
return false;
}
*rtval = ps->base[ps->top - 1];
return true;
}
//获取栈顶元素的值,但删除,出栈操作(尾删)
//int Pop(PStack ps)
bool Pop(PStack ps, int *rtval)
{
//断言 ps不能为NULL且栈不能是空栈
assert(ps != NULL && !IsEmpty(ps));
if (ps == NULL || IsEmpty(ps))
return false;
获取值
//*rtval = ps->base[ps->top-1];
有效个数-1
//ps->top--;
返回值
*rtval = ps->base[--ps->top];
return true;
}
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top == 0;
}
//判满
bool IsFull(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top == ps->stack_Size;
}
//获取栈顶元素的值,删除,出栈操作(尾删)
int Get_length(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top;
}
//清空
void Clear(PStack ps)
{
ps->top = 0;
}
//销毁
void Destroy(PStack ps)
{
//断言
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL)
return;
//释放malloc申请的动态内存
free(ps->base);
//将指针赋值为NULL,防止出现野指针
ps->base = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->stack_Size = 0;
}
//扩容
void Inc(PStack ps)
//如果按2倍去扩容 1.5
{
//断言
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL)
return;
//给栈空间最大容量重新赋值
ps->stack_Size *= 2;
//从堆内申请更大的空间给我们
ps->base = (int *)realloc(ps->base, sizeof(int)* ps->stack_Size);
}
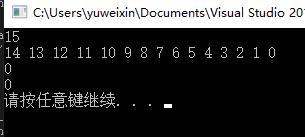
测试函数:
int main()
{
Stack head;
InitStack(&head);
for (int i = 0; i<15; i++)
{
Push(&head, i);
}
int rtval = 0;
printf("%d\\n", Get_length(&head));
while (!IsEmpty(&head))
{
Get_top(&head, &rtval);
printf("%d ", rtval);
Pop(&head, &rtval);
}
printf("\\n");
printf("%d\\n", Get_length(&head));
Clear(&head);
printf("%d\\n", Get_length(&head));
jieg
Destroy(&head);
Destroy(&head);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
以上是关于数据结构--栈(Stack)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章